Abstract
The body weight of rats was reduced by exercise or by restriction of food intake over a period of 18 wk. Body composition was studied to determine if exercise protects against the loss of lean tissue that can occur as a result of a negative caloric balance.
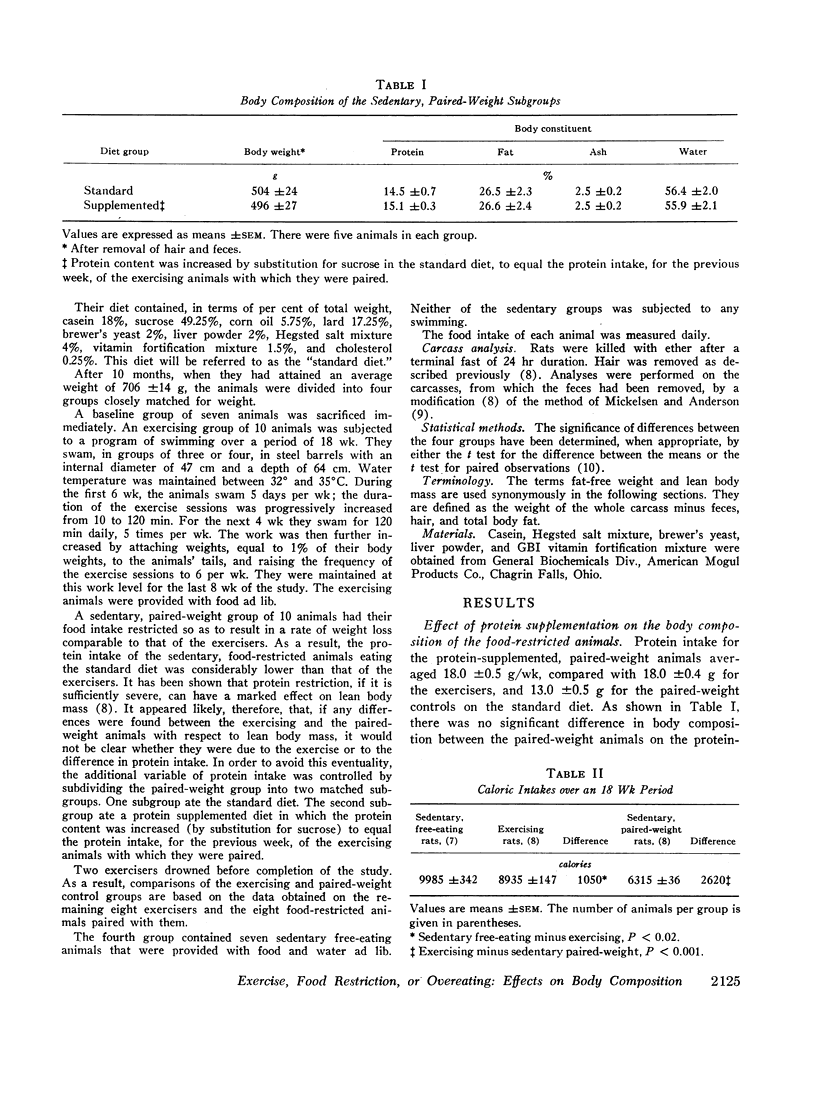
Rats weighing 706 ±14 g were divided into four groups matched for weight. A baseline group was killed at the beginning of the study. An exercising group, fed ad lib., was subjected to a program of swimming. A sedentary, free-eating group was provided with food ad lib. Two sedentary, paired-weight subgroups were calorie restricted so that they lost weight at the same rate as the exercisers. The protein intake of one paired-weight subgroup was matched with that of the exercising group. The other sedentary, paired-weight animals ate the standard diet.
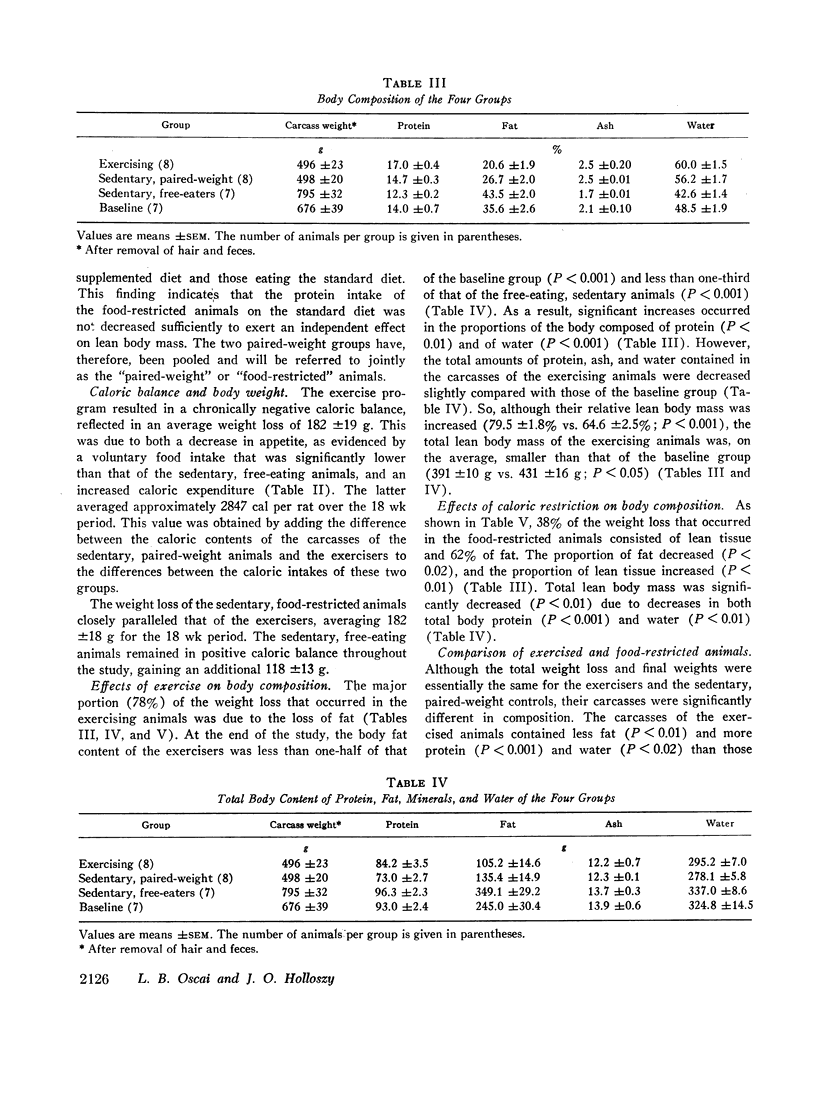
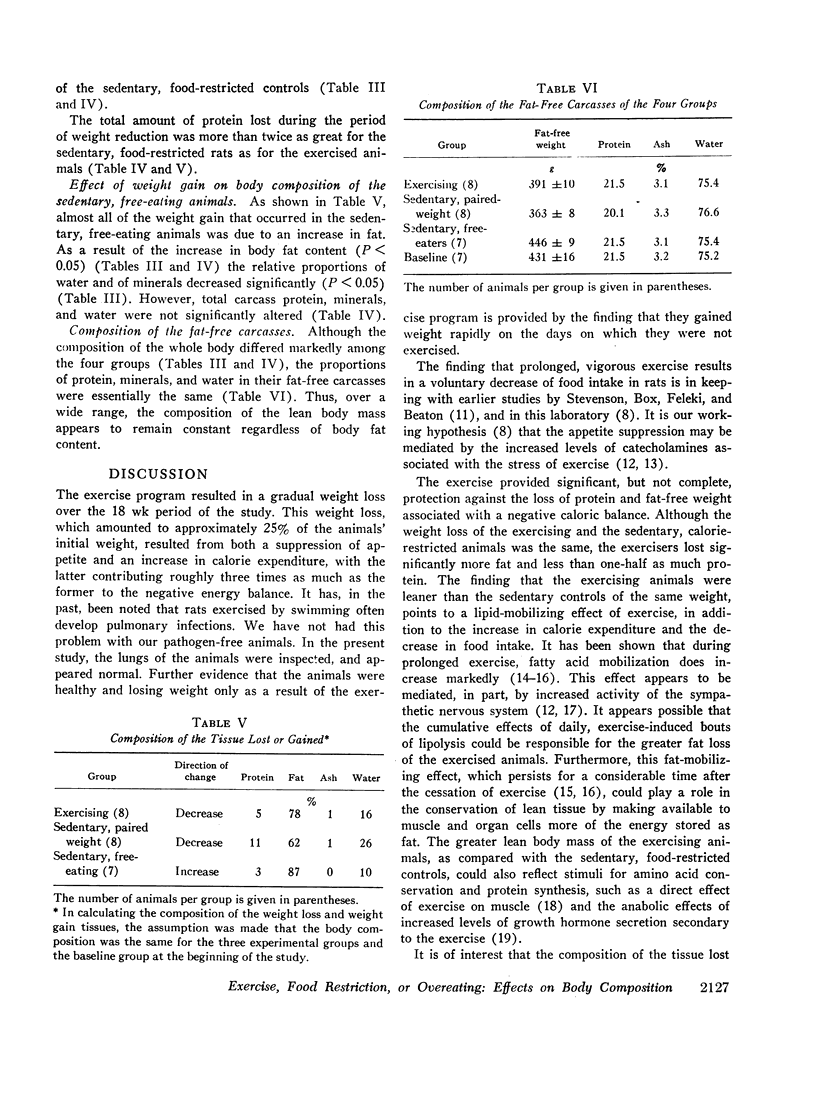
There was no significant difference in body composition between the two sedentary, paired-weight subgroups which were, therefore, pooled for comparison with the other groups. The exercisers lost 182±19 g as a result of both an increase in caloric expenditure and a decrease in appetite. The sedentary, food-restricted animals lost an average of 182±18 g. The sedentary, free-eating animals gained 118±13 g. The carcasses of the exercised animals contained significantly less fat and more lean tissue than those of the sedentary, paired-weight animals, providing evidence for a fat mobilizing and protein conserving effect of exercise. The composition of the body substance lost by the exercising animals was 78% fat, 5% protein, 1% minerals, and 16% water, compared to 62% fat, 11% protein, 1% minerals, and 26% water for the sedentary, food-restricted rats. Fat accounted for 87% and water for 10% of the weight gained by the sedentary, free-eating animals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BASU A., PASSMORE R., STRONG J. A. The effect of exercise on the level of non-esterified fatty acids in the blood. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1960 Jul;45:312–317. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1960.sp001476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROZEK J., GRANDE F., ANDERSON J. T., KEYS A. DENSITOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF BODY COMPOSITION: REVISION OF SOME QUANTITATIVE ASSUMPTIONS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:113–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSKIRK E. R., THOMPSON R. H., LUTWAK L., WHEDON G. D. ENERGY BALANCE OF OBESE PATIENTS DURING WEIGHT REDUCTION: INFLUENCE OF DIET RESTRICTION AND EXERCISE. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:918–940. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb15811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews E. L., 3rd, Fuge K. W., Oscai L. B., Holloszy J. O., Shank R. E. Weight, food intake, and body composition: effects of exercise and of protein deficiency. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):359–363. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENTENMAN C., GOLDWATER W. H., AYRES N. S., BEHNKE A. R., Jr Analysis of adipose tissue in relation to body weight loss in man. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Jul;13(1):129–134. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.13.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLICK S. M., ROTH J., YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. THE REGULATION OF GROWTH HORMONE SECRETION. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1965;21:241–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., NAIMARK A., BORCHGREVINK C. F. Turnover rate and oxidation of free fatty acids of blood plasma in man during exercise: studies during continuous infusion of palmitate-1-C14. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1054–1063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosch M., Lesch M., Baron J., Kaufman S. Enhanced protein synthesis in a cell-free system from hypertrophied skeletal muscle. Science. 1967 Aug 25;157(3791):935–937. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3791.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES E. M., MONTOYE H. J., JOHNSON P. B., MARTIN J. M., VANHUSS W. D., CEDERQUIST D. EFFECTS OF EXERCISE AND FOOD RESTRICTION ON SERUM CHOLESTEROL AND LIVER LIPIDS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Aug;207:460–466. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.2.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYS A., ANDERSON J. T., BROZEK J. Weight gain from simple overeating. I. Character of the tissue gained. Metabolism. 1955 Sep;4(5):427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYS A., BROZEK J. Body fat in adult man. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jul;33(3):245–325. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LJUNGGREN H., IKKOS D., LUFT R. The composition of tissue lost through reduction of diet in obese patients. Br J Nutr. 1959;13:485–487. doi: 10.1079/bjn19590062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICKELSEN O., ANDERSON A. A. A method for preparing intact animals for carcass analyses. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Feb;53(2):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIR G. G., CHAMBERLAIN D. A., PEDOE D. T. EFFECTS OF BETA-SYMPATHETIC BLOCKADE ON NON-ESTERIFIED-FATTY-ACID AND CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM AT REST AND DURING EXERCISE. Lancet. 1964 Oct 31;2(7366):930–932. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90862-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARIZKOVA J. IMPACT OF AGE, DIET, AND EXERCISE ON MAN'S BODY COMPOSITION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:661–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb15788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODAHL K., MILLER H. I., ISSEKUTZ B., Jr PLASMA FREE FATTY ACIDS IN EXERCISE. J Appl Physiol. 1964 May;19:489–492. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSEK M., PINA S. Conditioning of adrenalin anorexia. Nature. 1962 Mar 31;193:1296–1297. doi: 10.1038/1931296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRONG J. A., PASSMORE R., RITCHIE F. J. Clinical observations on obese patients during a strict reducing regimen. Br J Nutr. 1958;12(1):105–112. doi: 10.1079/bjn19580014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schemmel R., Mickelsen O., Tolgay Z. Dietary obesity in rats: influence of diet, weight, age, and sex on body composition. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):373–379. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson J. A., Box B. M., Feleki V., Beaton J. R. Bouts of exercise and food intake in the rat. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):118–122. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. M., DiGiacomo M. M. Protein utilization and changes in body composition during weight reduction. Metabolism. 1965 Oct;14(10):1084–1094. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(65)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


