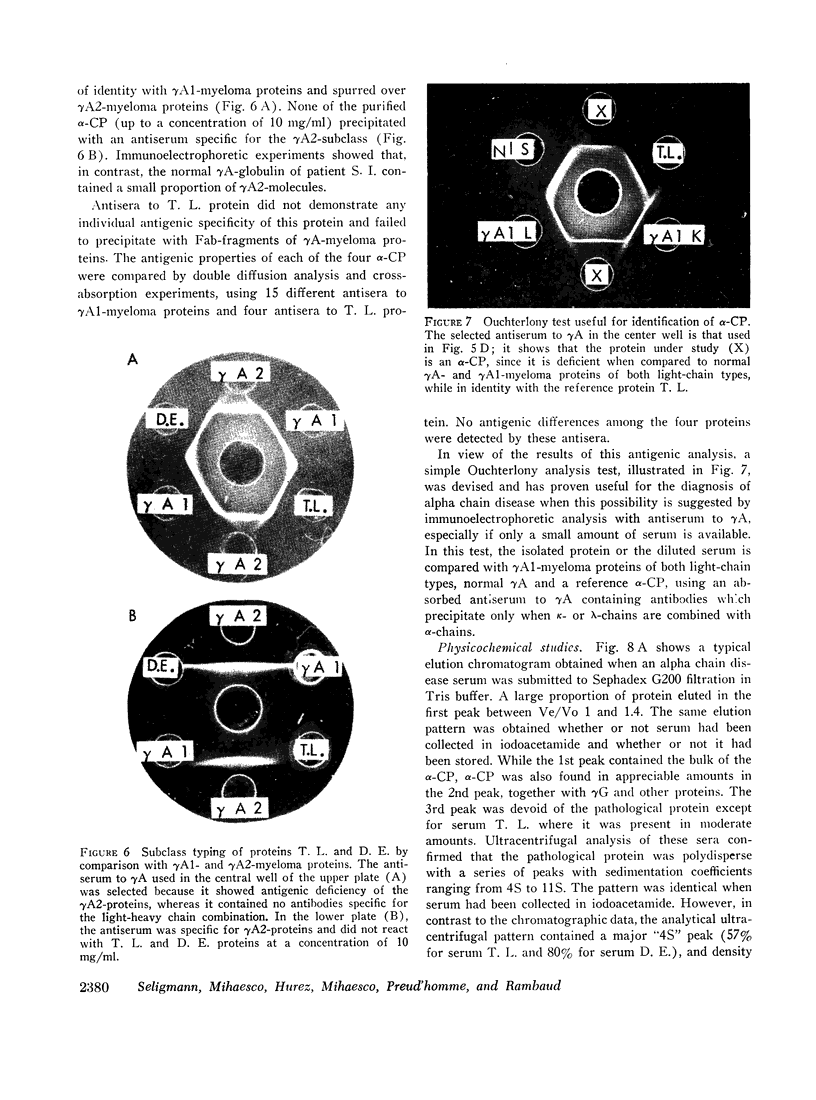
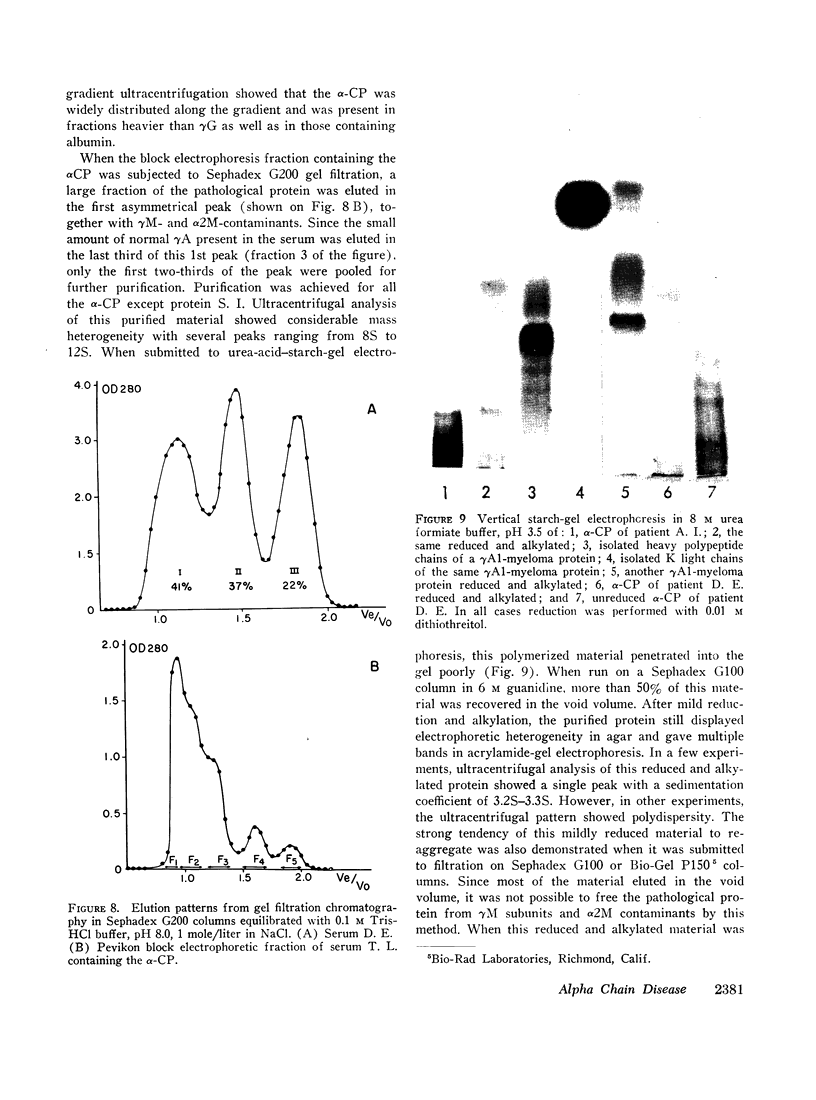
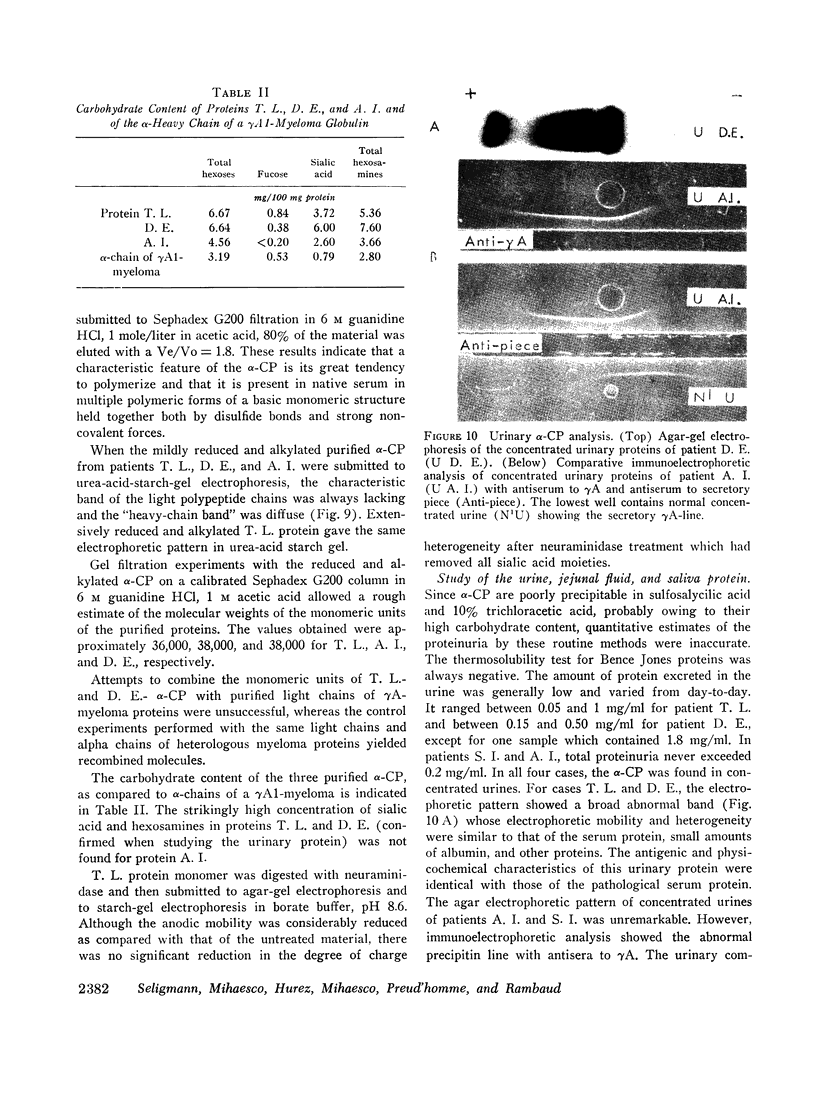
Abstract
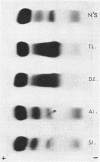
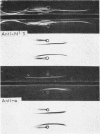
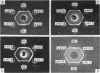
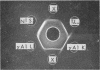
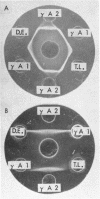
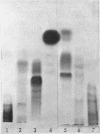
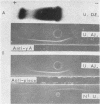
Studies of a number of properties of the pathological γA-proteins in the first four cases of the recently recognized alpha-chain disease demonstrate that, as in γ-heavy-chain disease, the abnormal protein is devoid of light chains and represents a portion of the α-heavy chain related to the Fc-fragment. In two patients, serum electrophoresis showed a broad abnormal band, whereas in the two others the pathological protein was not noticeable on the electrophoretic pattern. The diagnosis of α-chain disease can be established without purification of the protein by immuno-electrophoresis and gel diffusion experiments using selected antisera to γA and a reference α-chain disease protein. All four proteins belonged to the α1-subclass, displayed electrophoretic heterogeneity, and showed a strong tendency to polymerize. The polymers occurred in vivo and were held together both by disulfide bonds and by strong noncovalent forces. Two of the three purified proteins had a very high carbohydrate content. The abnormal protein was always found in concentrated urines in variable but generally low amounts. It was not detected in parotid saliva but was present in significant amounts in jejunal fluid of all four patients. The α-chain disease protein was shown to be associated with the secretory piece in external secretions of two patients.
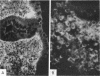
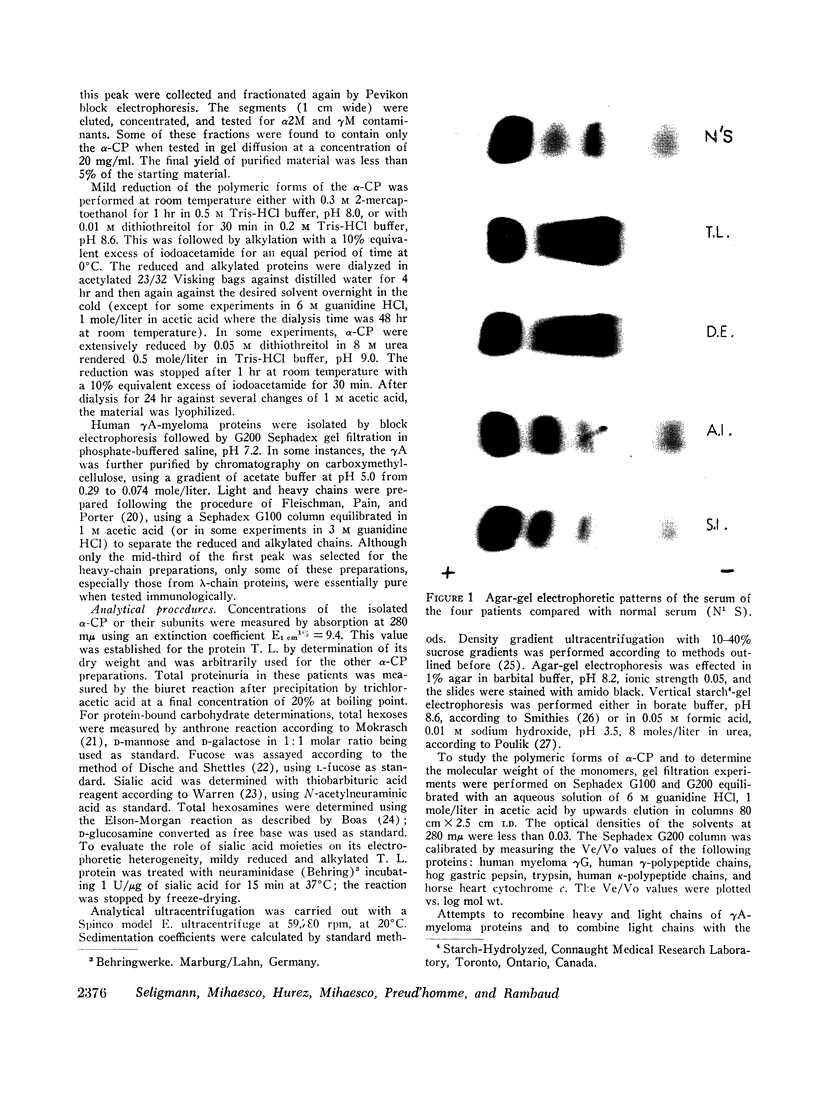
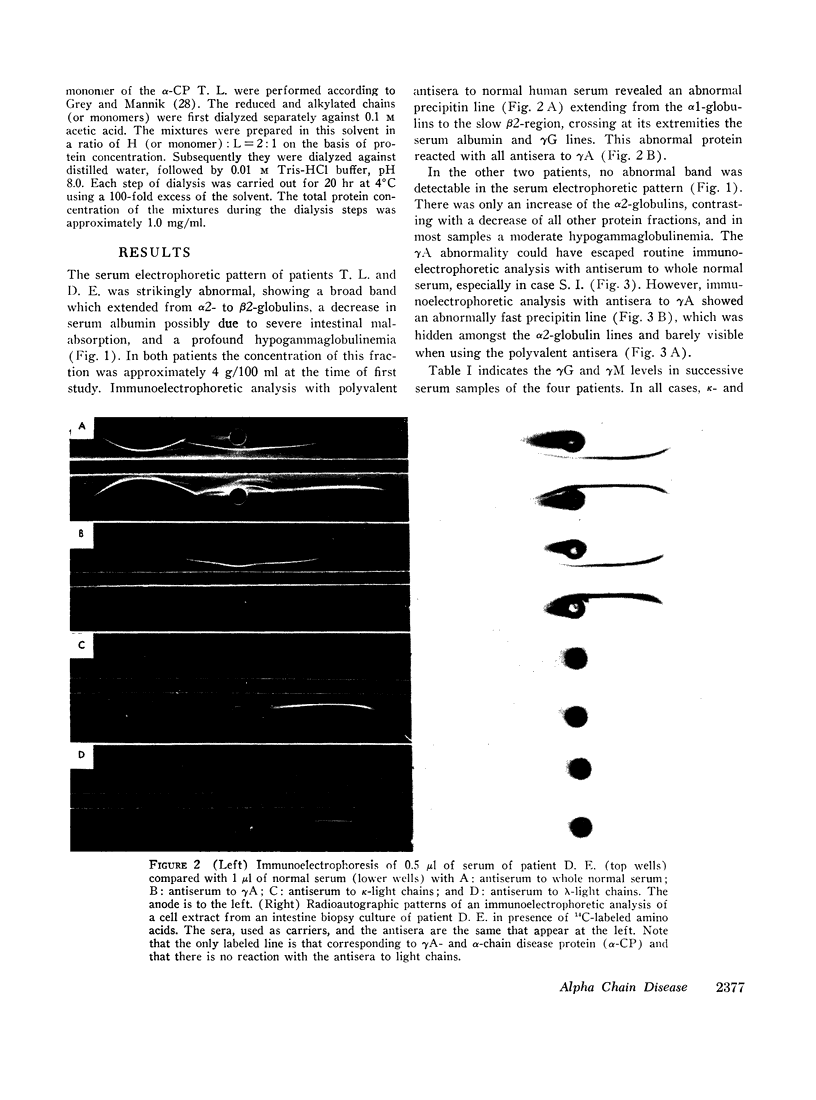
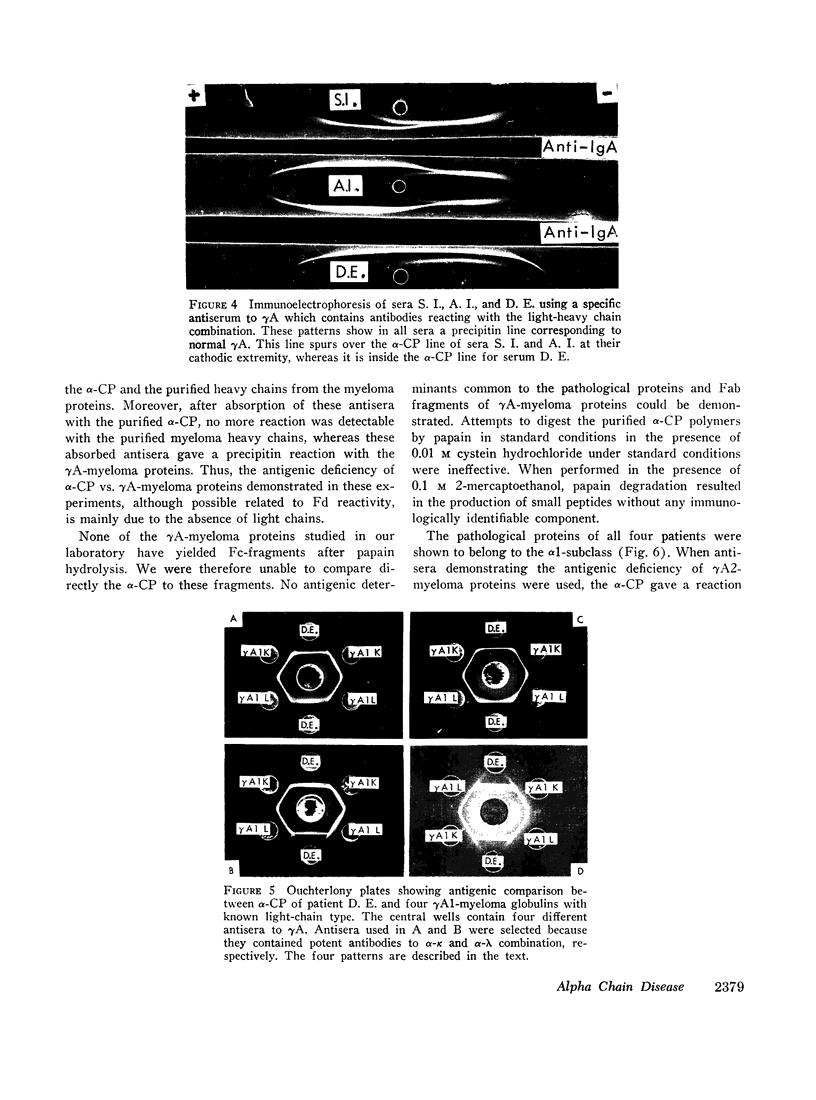
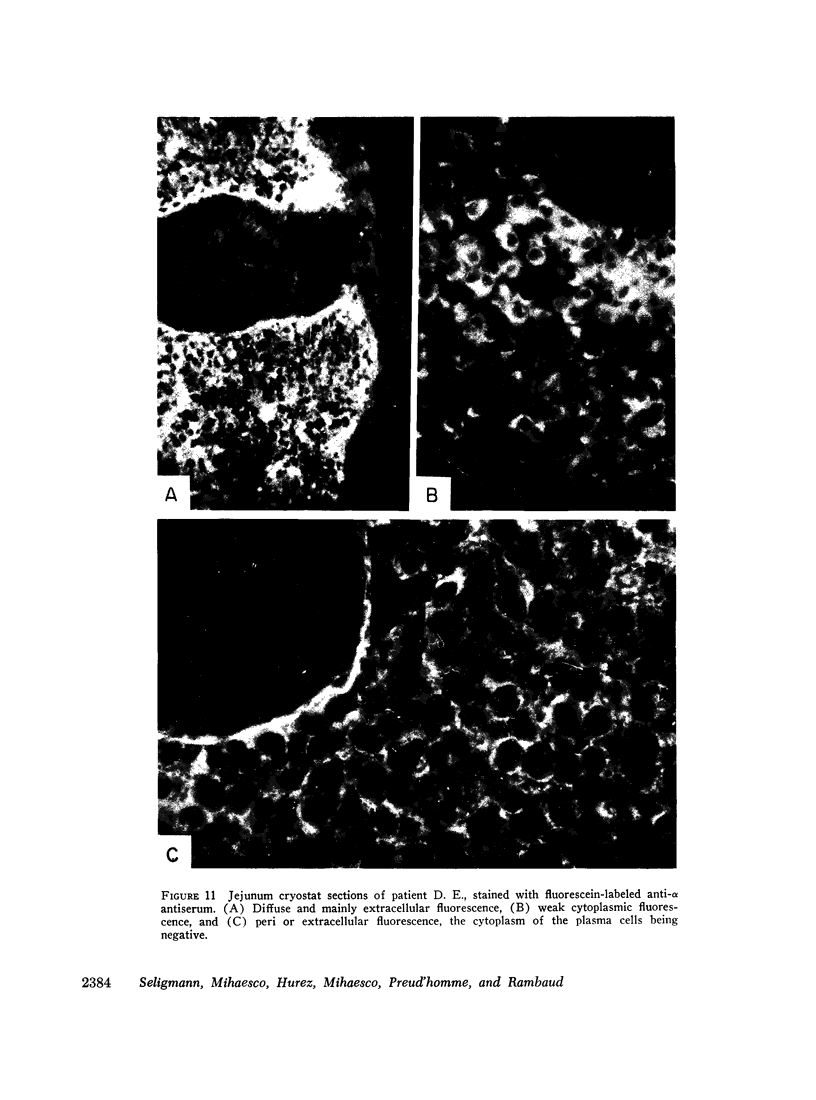
The clinicopathological features were strikingly similar in the four patients. All patients were affected with a neoplastic and mostly plasmacytic proliferation involving primarily the whole length of the small intestine and the mesenteric nodes and all exhibited a severe malabsorption syndrome. While Israeli authors have emphasized the frequency of this type of abdominal lymphoma in young Arabs and non-Ashkenazi Jews, two of our patients were Kabyles, one a Syrian Arab, and one an Eurasian. Cellular studies showed that the pathological protein was synthesized by the proliferating cells in the lymphoid tissue of the digestive tract and in the mesenteric nodes, and that there was no detectable light-chain synthesis at the intracellular level.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOAS N. F. Method for the determination of hexosamines in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):553–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Congy N., Mihaesco C. Méthode pratique d'électrophorèse préparative en bloc de pevikon. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1967 Jun-Jul;12(6):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Heremans J. F. Etude immunohistochimique des plasmocytes de la muqueuse intestinale humaine normale. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1966 May;11(5):484–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman S., Davis S. D. Immunoglobulin content of intestinal mucosal plasma-cells in ataxia telangiectasia. Lancet. 1968 Apr 27;1(7548):884–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D., Buell D. N., Fahey J. L. Biosynthetic and structural studies of a heavy chain disease protein. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):785–793. doi: 10.1172/JCI106036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman L. L., Bloch K. J. Heavy-chain disease. Report of a seventh case. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 30;278(22):1195–1201. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805302782203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAN J. B., PAIN R. H., PORTER R. R. Reduction of gamma-globulins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., LOWENSTEIN J., BIGELOW B., MELTZER M. HEAVY CHAIN DISEASE- A NEW DISORDER OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULINS : REPORT OF THE FIRST CASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:332–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C. STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF HUMAN 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN (G IMMUNOGLOBULIN). FURTHER OBSERVATIONS OF A NATURALLY OCCURRING PROTEIN RELATED TO THE CRYSTALLIZABLE (FAST) FRAGMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:691–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein W. B., Poker N. Multiple myeloma involving the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jul;51(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Abel C. A., Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G. A subclass of human gamma-A-globulins (gamma-A2) which lacks the disulfied bonds linking heavy and light chains. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1223–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Mannik M. Specificity of recombination of H and L chains from human gamma-G-myeloma proteins. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):619–632. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Klein F. An immunofluorescence procedure for the detection of intracellular immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):457–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurez D. Séparation des immunoglobulines par ultracentrifugation en gradient de densité. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1967 Nov;12(9):915–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinich H., Rojas E., Webb J. A., Kelsey J. R., Jr Lymphoma presenting as malabsorption. Gastroenterology. 1968 Mar;54(3):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Prendergast R. A. Subgroups of gamma-A immune globulins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):910–913. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton J. P., Rivat C., Rivat L., Guillemot L., Ropartz C. Une immunoglobulinopathie méconnue: la maladie des chaines lourdes. Presse Med. 1967 Oct 28;75(45):2251–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOKRASCH L. C. Analysis of hexose phosphates and sugar mixtures with the anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F., TAKATSUKI K. CLINICAL AND IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF FOUR CASES OF HEAVY (H-GAMMA-2) CHAIN DISEASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:351–373. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterland C. K., Chaplin H., Jr Atypical antigenic properties of a gamma-A myeloma protein. J Immunol. 1966 May;96(5):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. The use of urea-starch-gel electrophoresis in studies of reductive cleavage of an alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Nov 4;44:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W. N- and C-terminal sequences of a heavy chain disease protein and its genetic implications. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1386–1387. doi: 10.1038/2151386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast R. A., Grey H. M., Kunkel H. G. Recombination of heavy and light chains of human gamma-a-myeloma proteins: formation of hybrid molecules and configurational specificity. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):185–197. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMOT B., SHAHIN N., BUBIS J. J. MALABSORPTION SYNDROME IN LYMPHOMA OF SMALL INTESTINE. A STUDY OF 13 CASES. Isr J Med Sci. 1965 Mar;1:221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaud J. C., Bognel C., Prost A., Bernier J. J., Le Quintrec Y., Lambling A., Danon F., Hurez D., Seligmann M. Clinico-pathological study of a patient with "Mediterranean" type of abdominal lymphoma and a new type of IgA abnormality ("alpha chain disease"). Digestion. 1968;1(6):321–336. doi: 10.1159/000196874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. An improved procedure for starch-gel electrophoresis: further variations in the serum proteins of normal individuals. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):585–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0710585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Cohn M. Immunoglobulin biosynthesis. 3. Blocks in defective synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):273–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seijffers M. J., Levy M., Hermann G. Intractable watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, and malabsorption in a patient with Mediterranean type of abdominal lymphoma. Gastroenterology. 1968 Jul;55(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M. A genetic predisposition to Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;445:140–146. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb02353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Danon F., Hurez D., Mihaesco E., Preud'homme J. L. Alpha-chain disease: a new immunoglobulin abnormality. Science. 1968 Dec 20;162(3860):1396–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3860.1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Mihaesco C. L'importance de la conformation moléculaire dans la structure antigénique. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1967 Nov;12(9):851–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Mihaesco C., Meshaka G. Antigenic determinants common to human immunoglobulins G and M: importance of conformational antigens. Science. 1966 Nov 11;154(3750):790–791. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3750.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Subclasses of human immunoglobulin a based on differences in the alpha polypeptide chains. Science. 1966 Aug 5;153(3736):647–649. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3736.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]