Abstract
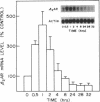
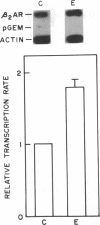
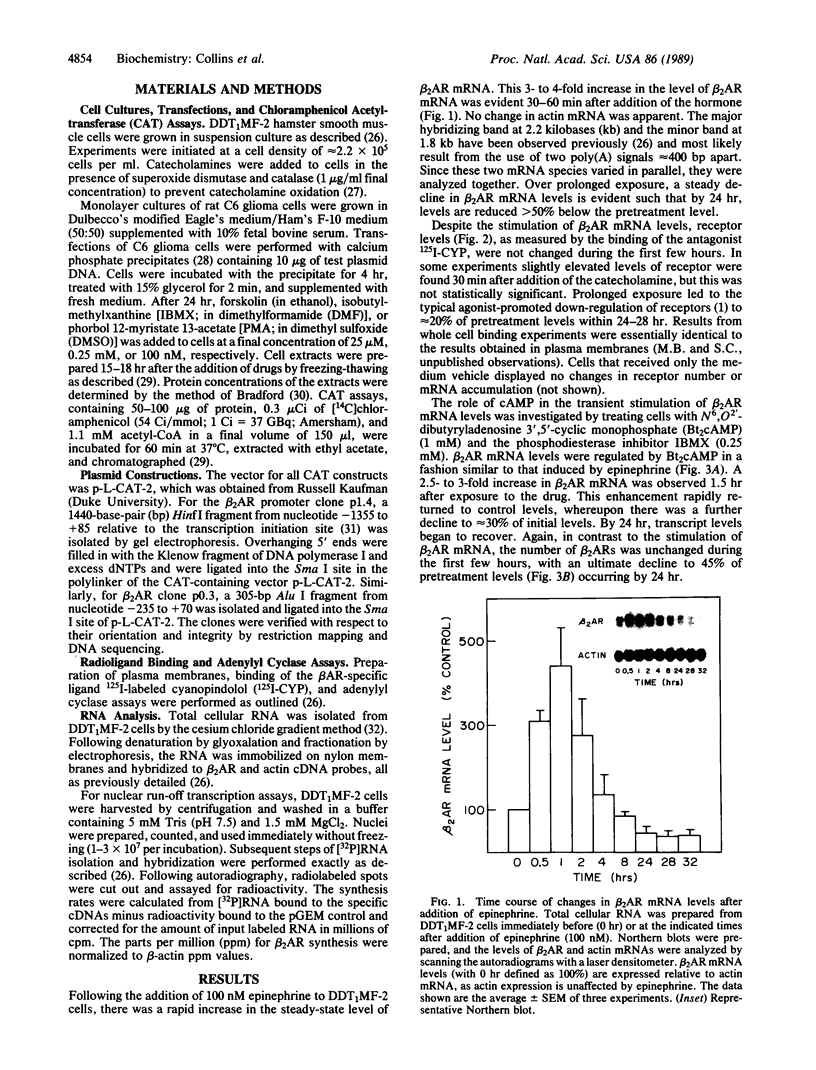
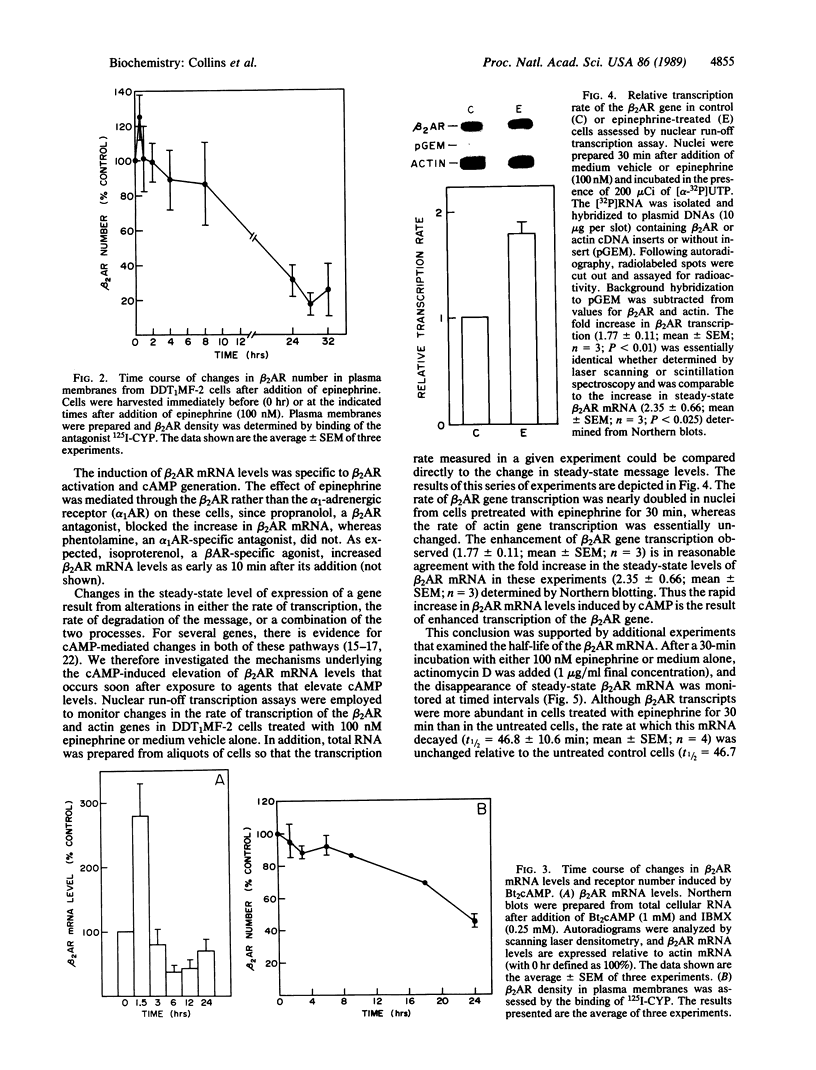
In addition to conveying cellular responses to an effector molecule, receptors are often themselves regulated by their effectors. We have demonstrated that epinephrine modulates both the rate of transcription of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor (beta 2AR) gene and the steady-state level of beta 2AR mRNA in DDT1MF-2 cells. Short-term (30 min) exposure to epinephrine (100 nM) stimulates the rate of beta 2AR gene transcription, resulting in a 3- to 4-fold increase in steady-state beta 2AR mRNA levels. These effects are mimicked by 1 mM N6,O2'-dibutyryladenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (Bt2cAMP) or foskolin but not by phorbol esters. The half-life of the beta 2AR mRNA after addition of actinomycin D (46.7 +/- 10.2 min; mean +/- SEM; n = 5) remained unchanged after 30 min of epinephrine treatment (46.8 +/- 10.6 min; mean +/- SEM; n = 4), indicating that a change in transcription rate is the predominant factor responsible for the increase of beta 2AR mRNA. Whereas brief exposure to epinephrine or Bt2cAMP does not significantly affect the total number of cellular beta 2ARs (assessed by ligand binding), continued exposure results in a gradual decline in beta 2AR number to approximately 20% (epinephrine) or approximately 45% (Bt2cAMP) of the levels in control cells by 24 hr. Similar decreases in agonist-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity are observed. This loss of receptors with prolonged agonist exposure is accompanied by a 50% reduction in beta 2AR mRNA. Transfection of the beta 2AR promoter region cloned onto a reporter gene (bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase) allowed demonstration of a 2- to 4-fold induction of transcription by agents that elevate cAMP levels, such as forskolin or phosphodiesterase inhibitors. These results establish the presence of elements within the proximal promoter region of the beta 2AR gene responsible for the transcriptional enhancing activity of cAMP and demonstrate that beta 2AR gene expression is regulated by a type of feedback mechanism involving the second messenger cAMP.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., Bouvier M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adenylyl cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:405–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Pike L. J., Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Yoshimasa T., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation of the mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Regulation of the rate of receptor phosphorylation and dephosphorylation by agonist occupancy and effects on coupling of the receptor to the stimulatory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7094–7101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokar J. A., Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Kaetzel D. M., Hanson R. W., Nilson J. H. Characterization of the cAMP responsive elements from the genes for the alpha-subunit of glycoprotein hormones and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Conserved features of nuclear protein binding between tissues and species. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19740–19747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Hausdorff W. P., De Blasi A., O'Dowd B. F., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Removal of phosphorylation sites from the beta 2-adrenergic receptor delays onset of agonist-promoted desensitization. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):370–373. doi: 10.1038/333370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ishii S., Richert N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor regulates the expression of its own receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8374–8378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors in hamster smooth muscle cells are transcriptionally regulated by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9067–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Y., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A., Okret S. Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor expression: evidence for transcriptional and posttranslational mechanisms. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1256–1264. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. S., Verhave M., Kasper S., Tsukada T., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. The CGTCA sequence motif is essential for biological activity of the vasoactive intestinal peptide gene cAMP-regulated enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors: agonist-induced reduction in receptor mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by "permissive" hormones: glucocorticoids increase steady-state levels of receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8415–8419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP stabilizes the mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) against degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7747–7752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Jaffe R. C., Gleason S. L., Habener J. F. Transcriptional regulation of chorionic gonadotropin alpha- and beta-subunit gene expression by 8-bromo-adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2560–2567. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Kelley D. C., Miles M. F., Milkowski D. M. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Isoproterenol and N6,O2-dibutyryl cyclic amp increase the rate of transcription and change the stability of lactate dehydrogenase a subunit messenger RNA in rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5312–5318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Dixon R. A., Keller P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Delineation of the intronless nature of the genes for the human and hamster beta 2-adrenergic receptor and their putative promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7321–7327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Adrenergic receptors. Models for the study of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):4993–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. From epinephrine to cyclic AMP. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):800–806. doi: 10.1126/science.2841758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Insel P. A. Use of superoxide dismutase and catalase to protect catecholamines from oxidation in tissue culture studies. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):208–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Mangelsdorf D. J., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the avian receptor for vitamin D. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1214–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.3029866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Poellinger L., Dong Y., Gustafsson J. A. Down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by glucocorticoid hormones and recognition by the receptor of a specific binding sequence within a receptor cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5899–5903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Straub R. E., Traktman P., Gershengorn M. C. Decreased TRH receptor mRNA activity precedes homologous downregulation: assay in oocytes. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1406–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.2825350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Yamamoto T., Schneider W. J., Slaughter C. J., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. cDNA cloning of the bovine low density lipoprotein receptor: feedback regulation of a receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7501–7505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Liu A. Y. Increased turnover of the messenger RNA encoding tyrosine aminotransferase can account for the desensitization and de-induction of tyrosine aminotransferase by 8-bromo-cyclic AMP treatment and removal. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3711–3716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. L., Krett N. L., Francis M. D., Gordon D. F., Wood W. M., O'Malley B. W., Horwitz K. B. Multiple human progesterone receptor messenger ribonucleic acids and their autoregulation by progestin agonists and antagonists in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;2(1):62–72. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-1-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]