Abstract
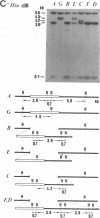
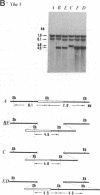
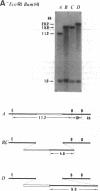
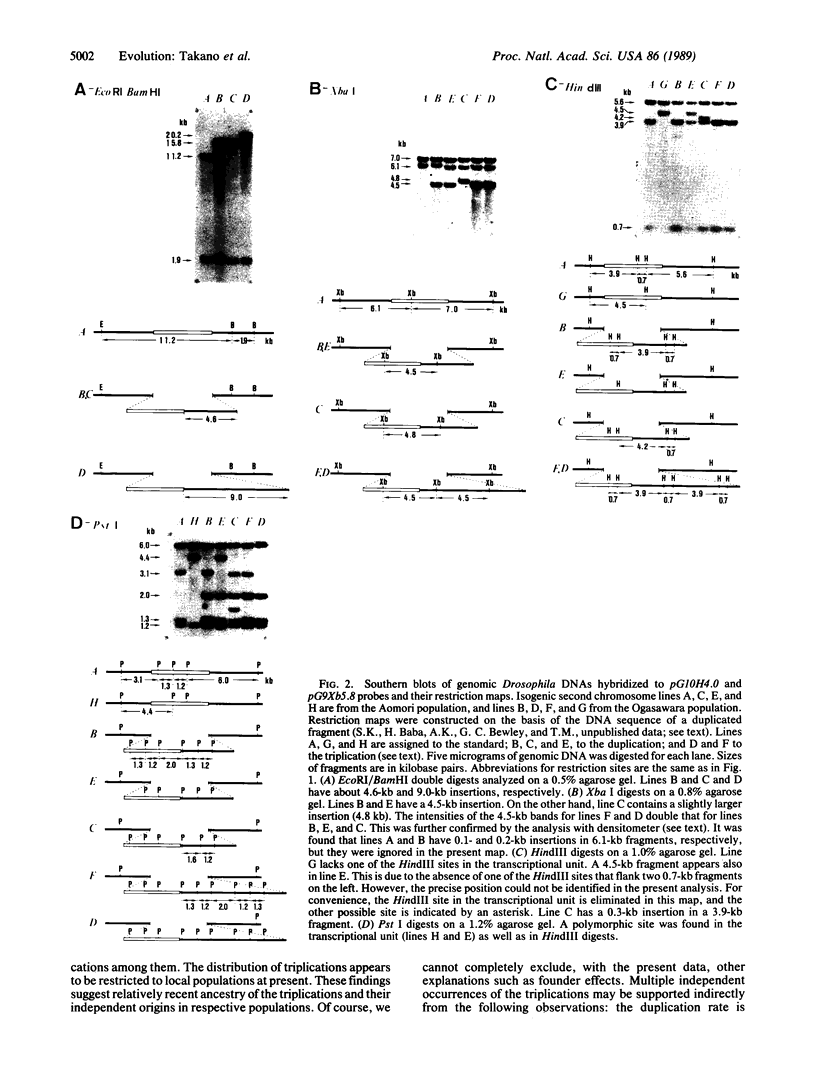
A 26-kilobase-pair region encompassing the sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (sn-glycerol-3-phosphate:NAD+ 2-oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.8) locus in Drosophila melanogaster from two natural populations in Japan was surveyed by restriction mapping. Both tandem duplications and triplications in this region were found in both populations. Detailed analysis of 86 chromosome 2 lines revealed restriction site and allozyme polymorphisms in the transcriptional unit: two restriction sites and the allozymes [fast (F) or slow (S)] were polymorphic among both duplication-bearing chromosomes and those carrying the standard sequence. This finding suggests recurrent recombination and/or gene conversion in this 5-kilobase-pair region. The differences observed for restriction site and allozyme haplotypes among the triplicated sequence both within and between populations, together with the distribution in natural populations, suggest a relatively recent ancestry of the triplication events and an independent origin in respective populations. Such events may represent the process of the formation of multigene families [compare Ohta, T. (1987) Genetics 115, 207-213]. Finally, the evolution of this type of polymorphism is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W., Spierer P., Hogness D. S. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia W., Savakis C., Karp R., Pelham H., Ashburner M. Mutation of the Adh gene of Drosophila melanogaster containing an internal tandem duplication. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Bewley G. C., Shaffer J. B. Drosophila sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase isozymes are generated by alternate pathways of RNA processing resulting in different carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10858–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Shaffer J. B., Bewley G. C., MacIntyre R. J., Wright D. A. Isolation of a genomic clone for Drosophila sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase using synthetic oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11751–11755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. S., Shen M. W., Judd B. H. Asymmetrical pairings of transposons in and proximal to the white locus of Drosophila account for four classes of regularly occurring exchange products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):174–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart W. M., Chovnick A. Spontaneous unequal exchange in the rosy region of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1979 Jul;92(3):849–859. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Levy J. N., Doane W. W. Molecular cloning of alpha-amylase genes from Drosophila melanogaster. I. Clone isolation by use of a mouse probe. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):299–312. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Sheen J. Y., Gehring W. J., Green M. M. Unequal crossing-over associated with asymmetrical synapsis between nomadic elements in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5017–5021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):624–626. doi: 10.1038/217624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Kitagawa H., Fukushima D., Takagaki Y., Miyata T., Nakanishi S. Structural organization of the human kininogen gene and a model for its evolution. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8610–8617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M., Aguadé M. Genetic uniformity in two populations of Drosophila melanogaster as revealed by filter hybridization of four-nucleotide-recognizing restriction enzyme digests. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3562–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. N., Gemmill R. M., Doane W. W. Molecular cloning of alpha-amylase genes from Drosophila melanogaster. II. Clone organization and verification. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):313–324. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Blattner F. R. Lambda Charon vectors (Ch32, 33, 34 and 35) adapted for DNA cloning in recombination-deficient hosts. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni G., Wise J., Young J. E., Otto E. Metallothionein gene duplications and metal tolerance in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):739–744. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Tajima F. DNA polymorphism detectable by restriction endonucleases. Genetics. 1981 Jan;97(1):145–163. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T. On the evolution of multigene families. Theor Popul Biol. 1983 Apr;23(2):216–240. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T. Simulating evolution by gene duplication. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):207–213. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto E., Young J. E., Maroni G. Structure and expression of a tandem duplication of the Drosophila metallothionein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6025–6029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer S. W., Aquadro C. F. Nucleotide sequence of the Adh gene region of Drosophila pseudoobscura: evolutionary change and evidence for an ancient gene duplication. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):61–73. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Finnerty V. G. The use of genetic complementation in the study of eukaryotic macromolecular evolution: rate of spontaneous gene duplication at two loci of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(2):159–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02099910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A H. The Effects of Unequal Crossing over at the Bar Locus in Drosophila. Genetics. 1925 Mar;10(2):117–147. doi: 10.1093/genetics/10.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Kusakabe S., Mukai T. The genetic structure of natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. XX. Comparison of genotype-environment interaction in viability between a northern and a southern population. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):245–254. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]