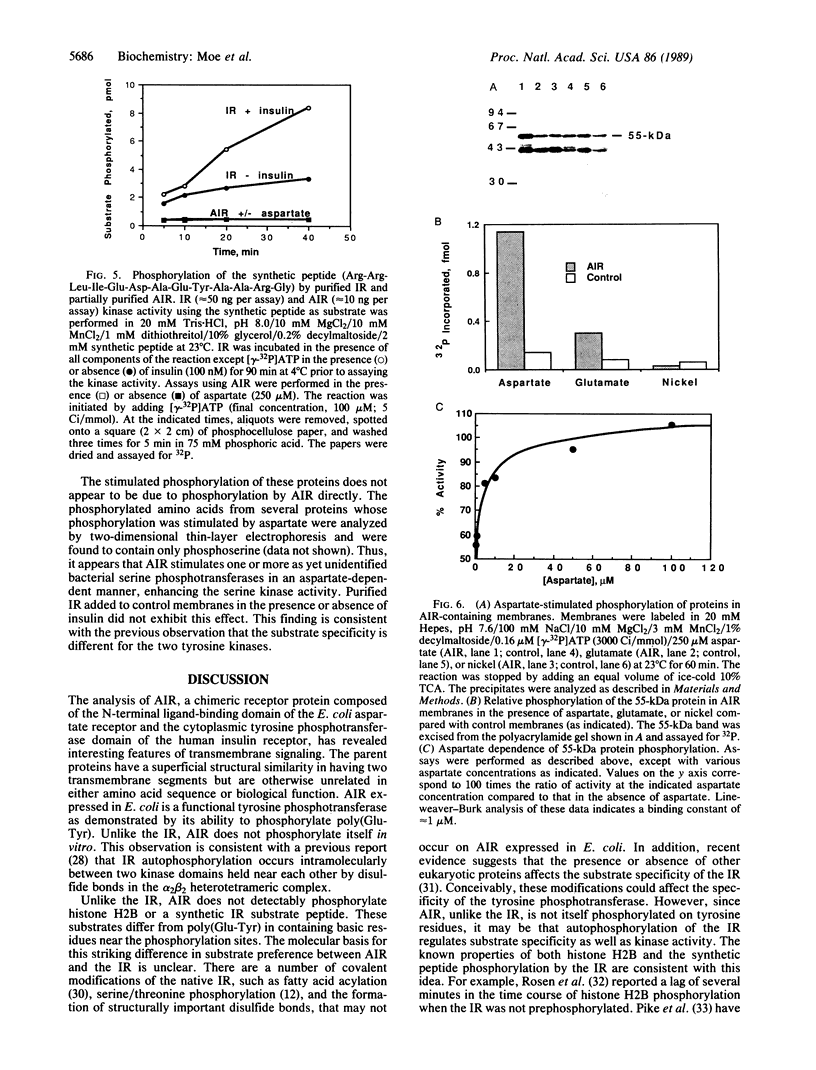
Abstract
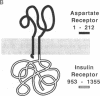
Since many receptors apparently contain only one or two membrane-spanning segments, their transmembrane topology should be similar. This feature suggests that these receptors share common mechanisms of transmembrane signaling. To test the degree of conservation of signaling properties, a chimeric receptor containing the ligand-binding extracellular domain of the Escherichia coli aspartate chemoreceptor and the cytosolic portion of the human insulin receptor was constructed. This chimeric receptor is active as a tyrosine kinase, and aspartate stimulates its activity. Some interesting differences are noted in the target proteins phosphorylated by the chimera compared to the wild-type insulin receptor. These results indicate that features of the signaling mechanisms used by these diverse receptors are conserved, but that interesting changes in the protein properties are caused by differences in the neighboring domains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogonez E., Koshland D. E., Jr Solubilization of a vectorial transmembrane receptor in functional form: aspartate receptor of chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4891–4895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollinger J., Park C., Harayama S., Hazelbauer G. L. Structure of the Trg protein: Homologies with and differences from other sensory transducers of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Kendall K., Simon M. I. Structure of the serine chemoreceptor in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):623–626. doi: 10.1038/301623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Morgan D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr, Clauser E., Moe G. R., Bollag G., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Linking functional domains of the human insulin receptor with the bacterial aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8137–8141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Nucleotidylation, not phosphorylation, is the major source of the phosphotyrosine detected in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):272–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.272-279.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzano H., Kowalski A., Fehlmann M., Van Obberghen E. Two different protein kinase activities are associated with the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):575–582. doi: 10.1042/bj2160575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Collier E., Watkinson A. Myristyl and palmityl acylation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):954–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Szapary D., Bellot F., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Schmidt A. Ligand-induced stimulation of epidermal growth factor receptor mutants with altered transmembrane regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9567–9571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Kutsukake K., Iino T. Definition of additional flagellar genes in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1980 Feb;94(2):277–290. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison B. D., Pessin J. E. Insulin stimulation of the insulin receptor kinase can occur in the complete absence of beta subunit autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2861–2868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Munson R. Separation of the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Eakes A. T., Krebs E. G. Characterization of affinity-purified insulin receptor/kinase. Effects of dithiothreitol on receptor/kinase function. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3782–3789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. R., Bennett G. N. Construction and analysis of in vivo activity of E. coli promoter hybrids and promoter mutants that alter the -35 to -10 spacing. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A. F., Koshland D. E., Jr Separation of signal transduction and adaptation functions of the aspartate receptor in bacterial sensing. Science. 1983 Jun 3;220(4601):1016–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.6302843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Kranz D. M., Takagaki Y., Hayday A. C., Eisen H. N., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structure of a heterodimeric T-cell receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):757–762. doi: 10.1038/309757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Chamberlin M. J. Amplification and isolation of Escherichia coli nusA protein and studies of its effects on in vitro RNA chain elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Morrison B. D., Wilden P. A., Pessin J. E. Insulin-dependent intermolecular subunit communication between isolated alpha beta heterodimeric insulin receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16730–16738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Bogonez E., Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Sites of methyl esterification on the aspartate receptor involved in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9608–9611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Avruch J. Relationship of site-specific beta subunit tyrosine autophosphorylation to insulin activation of the insulin receptor (tyrosine) protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4593–4601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Kuppuswamy D., Visvanathan A., Pike L. J. Substrate specificity and kinetic mechanism of human placental insulin receptor/kinase. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1428–1433. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Khalaf N., Czech M. P. Insulin stimulates a novel Mn2+-dependent cytosolic serine kinase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16677–16685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]