Abstract
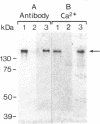
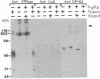
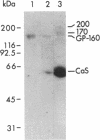
Antibody screening was used to isolate a cDNA encoding the 160-kDa glycoprotein of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. The cDNA is identical to that encoding the 53-kDa glycoprotein except that it contains an in-frame insertion of 1308 nucleotides near its 5' end, apparently resulting from alternative splicing. The protein encoded by the cDNA would contain a 19-residue NH2-terminal signal sequence and a 453-residue COOH-terminal sequence identical to the 53-kDa glycoprotein. It would also contain a 436-amino acid insert between these sequences. This insert would be highly acidic, suggesting that it might bind Ca2+. The purified 160-kDa glycoprotein and the glycoprotein expressed in COS-1 cells transfected with cDNA encoding the 160-kDa glycoprotein were shown to bind 45Ca2+ in a gel overlay assay. The protein was shown to be located in the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and to be associated through Ca2+ with the membrane. We propose that this lumenal Ca2+ binding glycoprotein of the sarcoplasmic reticulum be designated "sarcalumenin."
Full text
PDF


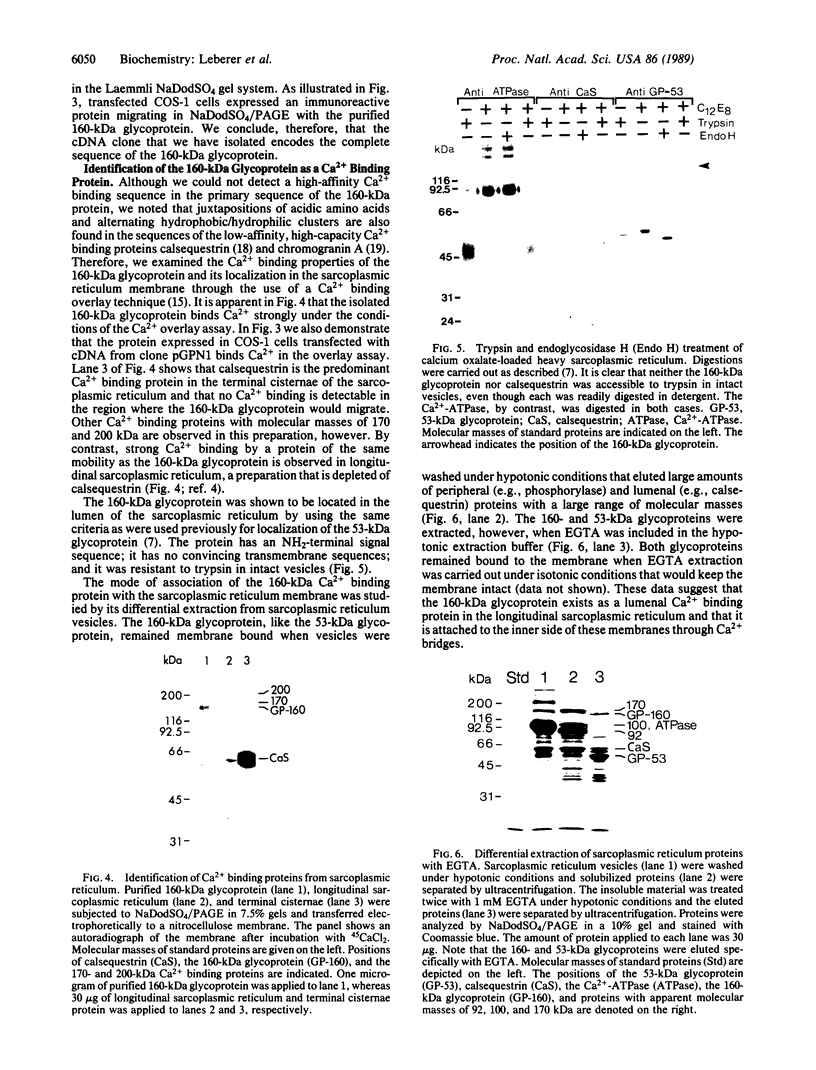

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H., Jorgensen A. O., Mintzer M. C. Purification and characterization of calsequestrin from canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and identification of the 53,000 dalton glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1197–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H., Jorgensen A. O. Staining of the Ca2+-binding proteins, calsequestrin, calmodulin, troponin C, and S-100, with the cationic carbocyanine dye "Stains-all". J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11267–11273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Purification and characterization of the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4626–4632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Carafoli E. The regulation of Ca2+ transport by fast skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Role of calmodulin and of the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):984–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C. Anionic regions in nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1479–1482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Ohnishi M., Carpenter M. R., Khanna V. K., Reithmeier R. A., MacLennan D. H. Amino acid sequence of rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle calsequestrin deduced from cDNA and peptide sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1167–1171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Kalnins V., MacLennan D. H. Localization of sarcoplasmic reticulum proteins in rat skeletal muscle by immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):372–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Charuk J. H., Clarke D. M., Green N. M., Zubrzycka-Gaarn E., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3484–3493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonards K. S., Kutchai H. Coupling of Ca2+ transport to ATP hydrolysis by the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum: potential role of the 53-kilodalton glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4876–4884. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Wong P. T. Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., MacLennan D. H. Mutation of aspartic acid-351, lysine-352, and lysine-515 alters the Ca2+ transport activity of the Ca2+-ATPase expressed in COS-1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3314–3318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Isolation and characterization of two types of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 21;389(1):51–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Seiler S., Chu A., Fleischer S. Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):875–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Volpe P. Calcium binding proteins of junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum: detection by 45Ca ligand overlay. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Mar;261(2):324–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]