Abstract
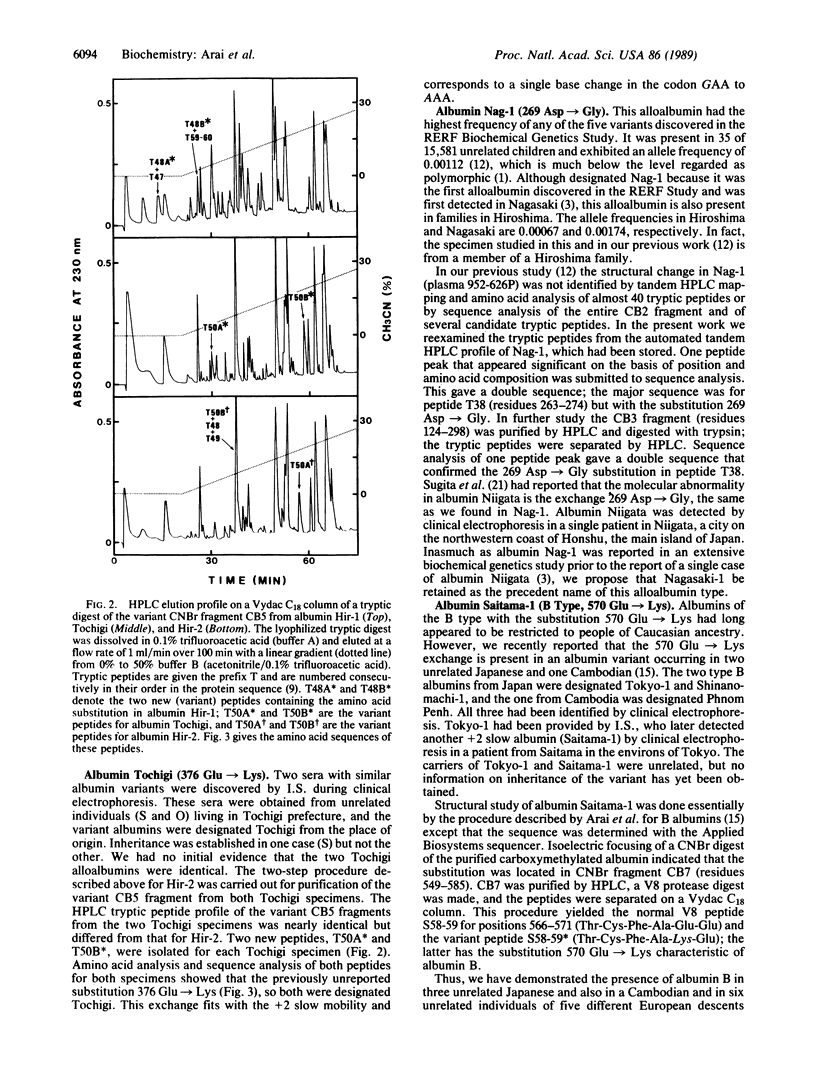
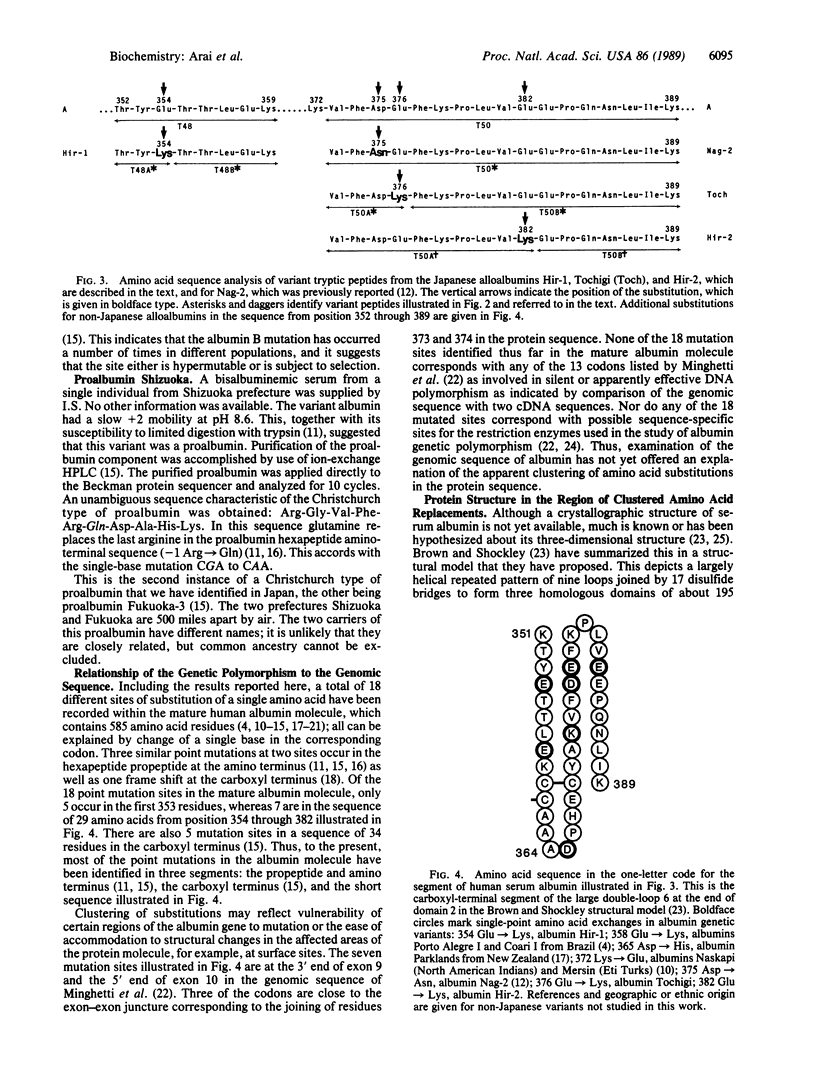
We have completed the structural study of five rare types of inherited albumin variants (alloalbumins) discovered in the Biochemical Genetics Study of 15,581 unrelated children in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. We have also identified the structural change in five other alloalbumin specimens detected during clinical electrophoresis of sera from Japanese living near Tokyo. Each of the five albumin variants from Nagasaki and Hiroshima has a single amino acid substitution. All of these substitutions differ, and none has been reported in non-Japanese populations. No instances of proalbumin variants or of albumin B (the most frequent alloalbumins in Caucasians) were detected in the children in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. However, one instance of a variant proalbumin and two examples of albumin B occurred in Japanese from the vicinity of Tokyo. In addition a previously unreported point substitution was found in albumin Tochigi, which is present in two unrelated persons from Tochigi prefecture. Four of the point mutations in the Japanese alloalbumins are in close proximity in a short segment of the polypeptide chain (residues 354-382) in which three additional point substitutions have been reported in diverse populations. These results, combined with earlier data, suggest that point substitutions are grouped in certain segments of the albumin molecule.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Huss K., Madison J., Putnam F. W., Salzano F. M., Franco M. H., Santos S. E., Freitas M. J. Amino acid substitutions in albumin variants found in Brazil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Ishioka N., Huss K., Madison J., Putnam F. W. Identical structural changes in inherited albumin variants from different populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan S. O., Carrell R. W. A circulating variant of human proalbumin. Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):908–909. doi: 10.1038/274908a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan S. O. The molecular abnormality of albumin Parklands: 365 Asp----His. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 23;830(3):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell R. E., Ueda N., Satoh C., Tanis R. J., Neel J. V., Hamilton H. B., Inamizu T., Baba K. The frequency in Japanese of genetic variants of 22 proteins. I. Albumin, ceruloplasmin, haptoglobin, and transferrin. Ann Hum Genet. 1977 May;40(4):407–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. M., Marneux M., Rochu D. Human albumin genetic variants: an attempt at a classification of European allotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;40(3):278–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga F. H., Glober G. A. Serum albumin polymorphism: bisalbuminemia in Hawaii-Japanese. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Dec;60(6):867–869. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.6.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliano M., Minchiotti L., Iadarola P., Zapponi M. C., Ferri G., Castellani A. A. Structural characterization of a chain termination mutant of human serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4283–4287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huss K., Madison J., Ishioka N., Takahashi N., Arai K., Putnam F. W. The same substitution, glutamic acid----lysine at position 501, occurs in three alloalbumins of Asiatic origin: albumins Vancouver, Birmingham, and Adana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6692–6696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huss K., Putnam F. W., Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Weaver G. A., Peters T., Jr Albumin Cooperstown: a serum albumin variant with the same (313 Lys----Asn) mutation found in albumins in Italy and New Zealand. Clin Chem. 1988 Jan;34(1):183–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Ogushi F., Ogawa K., Katunuma N. Structure and properties of albumin Tokushima and its proteolytic processing by cathepsin B in vitro. J Biochem. 1986 Aug;100(2):375–379. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchiotti L., Galliano M., Iadarola P., Stoppini M., Ferri G., Castellani A. A. Structural characterization of two genetic variants of human serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 18;916(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minghetti P. P., Ruffner D. E., Kuang W. J., Dennison O. E., Hawkins J. W., Beattie W. G., Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6747–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Mills K. A., Demopulos C. M., Hornung S., Motulsky A. G. Linkage disequilibrium and evolutionary relationships of DNA variants (restriction enzyme fragment length polymorphisms) at the serum albumin locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3486–3490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V., Satoh C., Goriki K., Asakawa J., Fujita M., Takahashi N., Kageoka T., Hazama R. Search for mutations altering protein charge and/or function in children of atomic bomb survivors: final report. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):663–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Lehmann H. Molecular pathology of human haemoglobin. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):902–909. doi: 10.1038/219902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita O., Endo N., Yamada T., Yakata M., Odani S. The molecular abnormality of albumin Niigata: 269 Asp----Gly. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 May 15;164(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Blumberg B. S., Putnam F. W. Amino acid substitutions in genetic variants of human serum albumin and in sequences inferred from molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4413–4417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Ishioka N., Blumberg B. S., Putnam F. W. Application of an automated tandem high-performance liquid chromatographic system to peptide mapping of genetic variants of human serum albumin. J Chromatogr. 1986 May 30;359:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(86)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Isobe T., Putnam F. W., Fujita M., Satoh C., Neel J. V. Amino acid substitutions in inherited albumin variants from Amerindian and Japanese populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8001–8005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Structural changes and metal binding by proalbumins and other amino-terminal genetic variants of human serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7403–7407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tárnoky A. L. Genetic and drug-induced variation in serum albumin. Adv Clin Chem. 1980;21:101–146. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., McDermid E. M., Neel J. V., Fine J. M., Petrini C., Bonazzi L., Ortali V., Porta F., Tanis R., Harris D. J. Additional data on the population distribution of human serum albumin genes; three new variants. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Oct;37(2):219–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb01829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]