Abstract
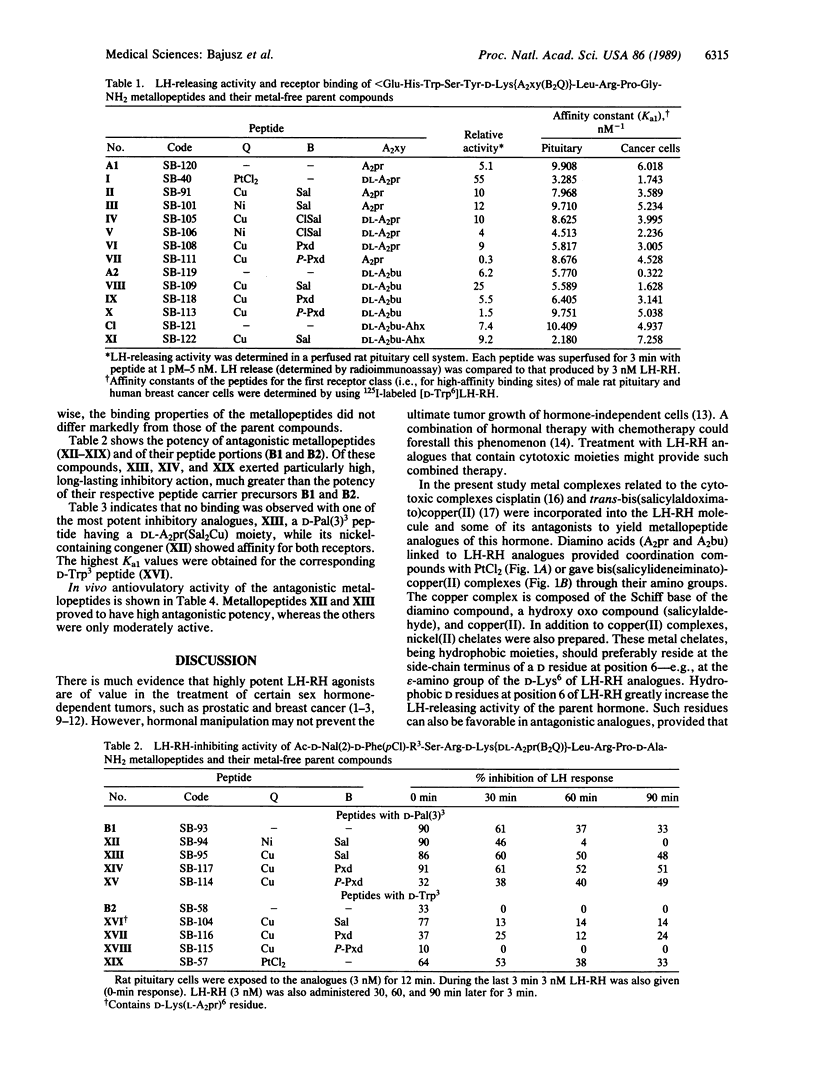
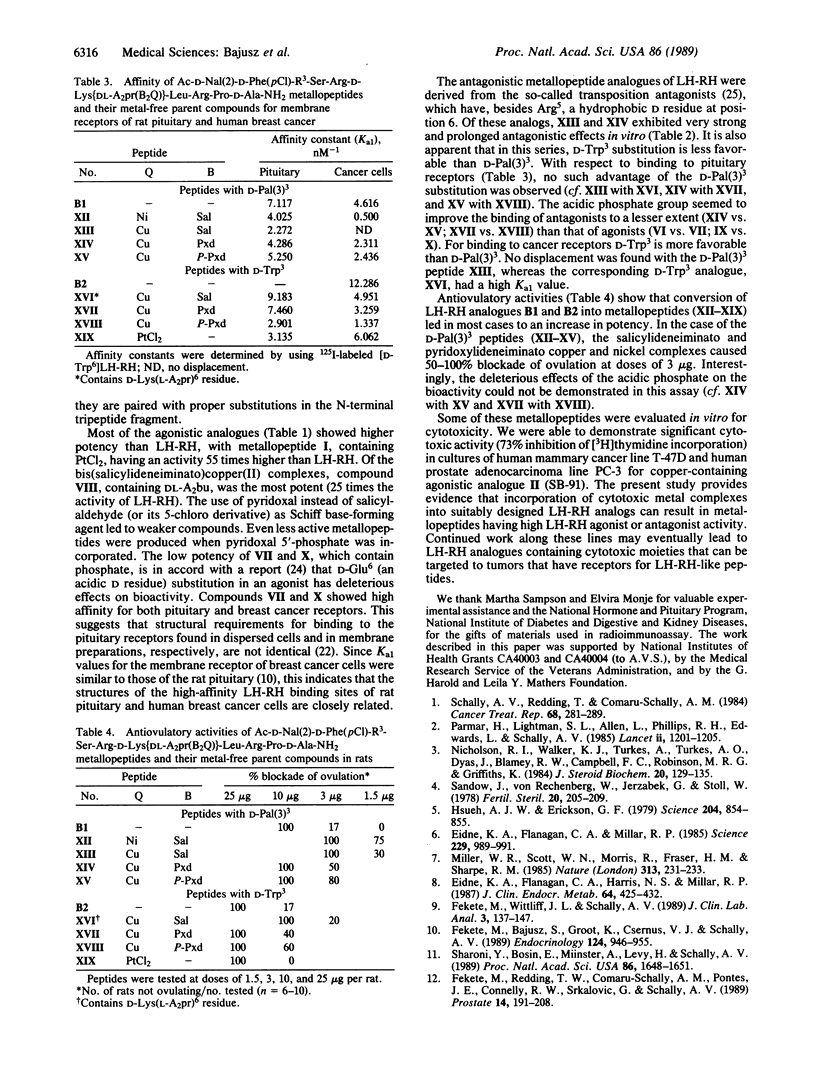
Metal complexes related to the cytotoxic complexes cisplatin [cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)] and transbis(salicylaldoximato)copper(II) were incorporated into suitably modified luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) analogues containing D-lysine at position 6. Some of the metallopeptides thus obtained proved to be highly active LH-RH agonists or antagonists. For instance, SB-40, a PtCl2-containing metallopeptide in which platinum is coordinated to an N epsilon-(DL-2,3-diaminopropionyl)-D-lysine residue [D-Lys(DL-A2pr] at position 6, showed 50 times higher LH-releasing potency than the native hormone. SB-95, [Ac-D-Nal(2)1,D-Phe(pCl)2, D-Pal(3)2, Arg5,D-Lys[DL-A2pr(Sal2Cu)]6,D-Ala10]LH-RH, where Nal(2) is 3-(2-naphthyl)alanine, Pal(3) is 3-(3-pyridyl)alanine, and copper(II) is coordinated to the salicylideneimino moieties resulting from condensation of salicylaldehyde with D-Lys(DL-A2pr)6, caused 100% inhibition of ovulation at a dose of 3 micrograms in rats. Most metallopeptide analogues of LH-RH showed high affinities for the membrane receptors of rat pituitary and human breast cancer cells. Some of these metallopeptides had cytotoxic activity against human breast cancer and prostate cancer cell lines in vitro (this will be the subject of a separate paper on cytotoxicity evaluation). Such cytostatic metallopeptides could be envisioned as targeted chemotherapeutic agents in cancers that contain receptors for LH-RH-like peptides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajusz S., Csernus V. J., Janaky T., Bokser L., Fekete M., Schally A. V. New antagonists of LHRH. II. Inhibition and potentiation of LHRH by closely related analogues. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1988 Dec;32(6):425–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1988.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajusz S., Janaky T., Csernus V. J., Bokser L., Fekete M., Srkalovic G., Redding T. W., Schally A. V. Highly potent analogues of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone containing D-phenylalanine nitrogen mustard in position 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6318–6322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidne K. A., Flanagan C. A., Harris N. S., Millar R. P. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-binding sites in human breast cancer cell lines and inhibitory effects of GnRH antagonists. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Mar;64(3):425–432. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-3-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidne K. A., Flanagan C. A., Millar R. P. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone binding sites in human breast carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.2992093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elo H. O., Lumme P. O. Antitumor activity of trans-bis(salicylaldoximato)copper(II): a novel antiproliferative metal complex. Cancer Treat Rep. 1985 Sep;69(9):1021–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete M., Bajusz S., Groot K., Csernus V. J., Schally A. V. Comparison of different agonists and antagonists of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone for receptor-binding ability to rat pituitary and human breast cancer membranes. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):946–955. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete M., Redding T. W., Comaru-Schally A. M., Pontes J. E., Connelly R. W., Srkalovic G., Schally A. V. Receptors for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone, somatostatin, prolactin, and epidermal growth factor in rat and human prostate cancers and in benign prostate hyperplasia. Prostate. 1989;14(3):191–208. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete M., Wittliff J. L., Schally A. V. Characteristics and distribution of receptors for [D-TRP6]-luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone, somatostatin, epidermal growth factor, and sex steroids in 500 biopsy samples of human breast cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. 1989;3(3):137–147. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh A. J., Erickson G. F. Extrapituitary action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone: direct inhibition ovarian steroidogenesis. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):854–855. doi: 10.1126/science.375393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. T., Coffey D. S. Adaptation versus selection as the mechanism responsible for the relapse of prostatic cancer to androgen ablation therapy as studied in the Dunning R-3327-H adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1981 Dec;41(12 Pt 1):5070–5075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. T. The timing of androgen ablation therapy and/or chemotherapy in the treatment of prostatic cancer. Prostate. 1984;5(1):1–17. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990050102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karten M. J., Rivier J. E. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog design. Structure-function studies toward the development of agonists and antagonists: rationale and perspective. Endocr Rev. 1986 Feb;7(1):44–66. doi: 10.1210/edrv-7-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. R., Scott W. N., Morris R., Fraser H. M., Sharpe R. M. Growth of human breast cancer cells inhibited by a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):231–233. doi: 10.1038/313231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. I., Walker K. J., Turkes A., Turkes A. O., Dyas J., Blamey R. W., Campbell F. C., Robinson M. R., Griffiths K. Therapeutic significance and the mechanism of action of the LH-RH agonist ICI 118630 in breast and prostate cancer. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Jan;20(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90199-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmar H., Phillips R. H., Lightman S. L., Edwards L., Allen L., Schally A. V. Randomised controlled study of orchidectomy vs long-acting D-Trp-6-LHRH microcapsules in advanced prostatic carcinoma. Lancet. 1985 Nov 30;2(8466):1201–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90739-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J. E., Porter J., Rivier C. L., Perrin M., Corrigan A., Hook W. A., Siraganian R. P., Vale W. W. New effective gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonists with minimal potency for histamine release in vitro. J Med Chem. 1986 Oct;29(10):1846–1851. doi: 10.1021/jm00160a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg B., VanCamp L., Trosko J. E., Mansour V. H. Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):385–386. doi: 10.1038/222385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow J., Von Rechenberg W., Jerzabek G., Stoll W. Pituitary gonadotropin inhibition by a highly active analog of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Fertil Steril. 1978 Aug;30(2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)43461-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Redding T. W., Comaru-Schally A. M. Potential use of analogs of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormones in the treatment of hormone-sensitive neoplasms. Cancer Treat Rep. 1984 Jan;68(1):281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharoni Y., Bosin E., Miinster A., Levy J., Schally A. V. Inhibition of growth of human mammary tumor cells by potent antagonists of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1648–1651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Rivier C., Brown M., Leppaluoto J., Ling N., Monahan M., Rivier J. Pharmacology of hypothalamic regulatory peptides. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976;5 (Suppl):261S–273S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb03834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigh S., Schally A. V. Interaction between hypothalamic peptides in a superfused pituitary cell system. Peptides. 1984;5 (Suppl 1):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90282-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


