Abstract
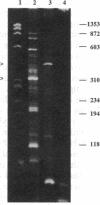
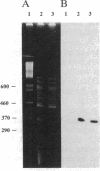
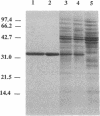
The thymidylate synthase (TS) gene from Pneumocystis carinii has been isolated from complementary and genomic DNA libraries and expressed in Escherichia coli. The coding sequence of TS is 891 nucleotides, encoding a 297-amino acid protein of Mr 34,269. The deduced amino acid sequence is similar to TS from other organisms and is most closely related to the enzyme from Saccharomyces cerevisiae with 65% identity. TS is found on a 330-kilobase-pair chromosome in P. carinii. While TS and dihydrofolate reductase reside on a single polypeptide chain in all protozoa studied to date, TS is not linked to dihydrofolate reductase in P. carinii. The TS gene shows the presence of four small intervening sequences, some of which interrupt the coding sequence in highly ordered structural regions of the protein. Heterologous expression of P. carinii TS in E. coli was accomplished by cloning the coding sequence into plasmid vectors under control of the lac and tac promoters. These constructs direct the synthesis of catalytically active enzyme to the extent of 2% of total soluble protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M., Ellenberger T. E., Cordingley J. S. Primary structure of the gene encoding the bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase of Leishmania major. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Thorner J. Thymidylate synthetase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification and enzymic properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12456–12462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Li W. B., Horii T., Inselburg J. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8360–8364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maley G. F., Maley F., Belfort M. Intervening sequence in the thymidylate synthase gene of bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3049–3053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T. L., Li D. W., Jenh C. H., Johnson L. F. Structure of the gene for mouse thymidylate synthase. Locations of introns and multiple transcriptional start sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16000–16005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A., Masur H., Santi D. V., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):519–522. doi: 10.1038/334519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R., Washtien W. L., Caput D., Santi D. V. Bifunctional thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase from Leishmania tropica: sequence homology with the corresponding monofunctional proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5387–5391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy L. W., Finer-Moore J. S., Montfort W. R., Jones M. O., Santi D. V., Stroud R. M. Atomic structure of thymidylate synthase: target for rational drug design. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):448–455. doi: 10.1126/science.3099389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Bodemer W., Cameron K. R., Niller H. H., Fleckenstein B., Randall R. E. The A+T-rich genome of Herpesvirus saimiri contains a highly conserved gene for thymidylate synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3604–3608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Swan J. C., Moss J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Identification of antigens and antibodies specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Hiemenz J. W., Macher A. M., Stover D., Murray H. W., Shelhamer J., Lane H. C., Urmacher C., Honig C., Longo D. L. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a comparison between patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and patients with other immunodeficiencies. Ann Intern Med. 1984 May;100(5):663–671. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-5-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maley G. F., Bellisario R. L., Guarino D. U., Maley F. The primary structure of Lactobacillus casei thymidylate synthetase. III. The use of 2-(2-nitrophenylsulfenyl)-3-methyl-3-bromoindolenine and limited tryptic peptides to establish the complete amino acid sequence of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1301–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertins P., Gallwitz D. Nuclear pre-mRNA splicing in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe strictly requires an intron-contained, conserved sequence element. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1757–1763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. Pneumocystis carinii and Toxoplasma gondii infections in patients with AIDS. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1001–1011. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter K., Davisson V. J., Santi D. V. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the Lactobacillus casei thymidylate synthase gene. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):235–241. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogolotti A. L., Jr, Danenberg P. V., Santi D. V. Kinetics and mechanism of interaction of 10-propargyl-5,8-dideazafolate with thymidylate synthase. J Med Chem. 1986 Apr;29(4):478–482. doi: 10.1021/jm00154a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogolotti A. L., Jr, Weill C., Santi D. V. Thymidylate synthetase catalyzed exchange of tritiumfrom [5-3H]-2'-deoxyuridylate for protons of water. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2794–2798. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., McHenry C. S., Perriard E. R. A filter assay for thymidylate synthetase using 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridylate as an active site titrant. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):467–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., McHenry C. S., Sommer H. Mechanism of interaction of thymidylate synthetase with 5-fluorodeoxyuridylate. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):471–481. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. C., Richards C. A., Ferone R., Benedict D., Ray P. Cloning, purification, and properties of Candida albicans thymidylate synthase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1372–1378. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1372-1378.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Kaneda S., Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Gotoh O., Seno T. Nucleotide sequence of a functional cDNA for human thymidylate synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2035–2043. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. R., Lagosky P. A., Storms R. K., Haynes R. H. Molecular characterization of the cell cycle-regulated thymidylate synthase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5298–5307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth I., Lazar G., Goodman H. M. Purification and immunochemical characterization of a dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase enzyme complex from wild-carrot cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1853–1858. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]