Abstract
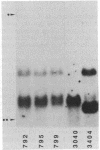
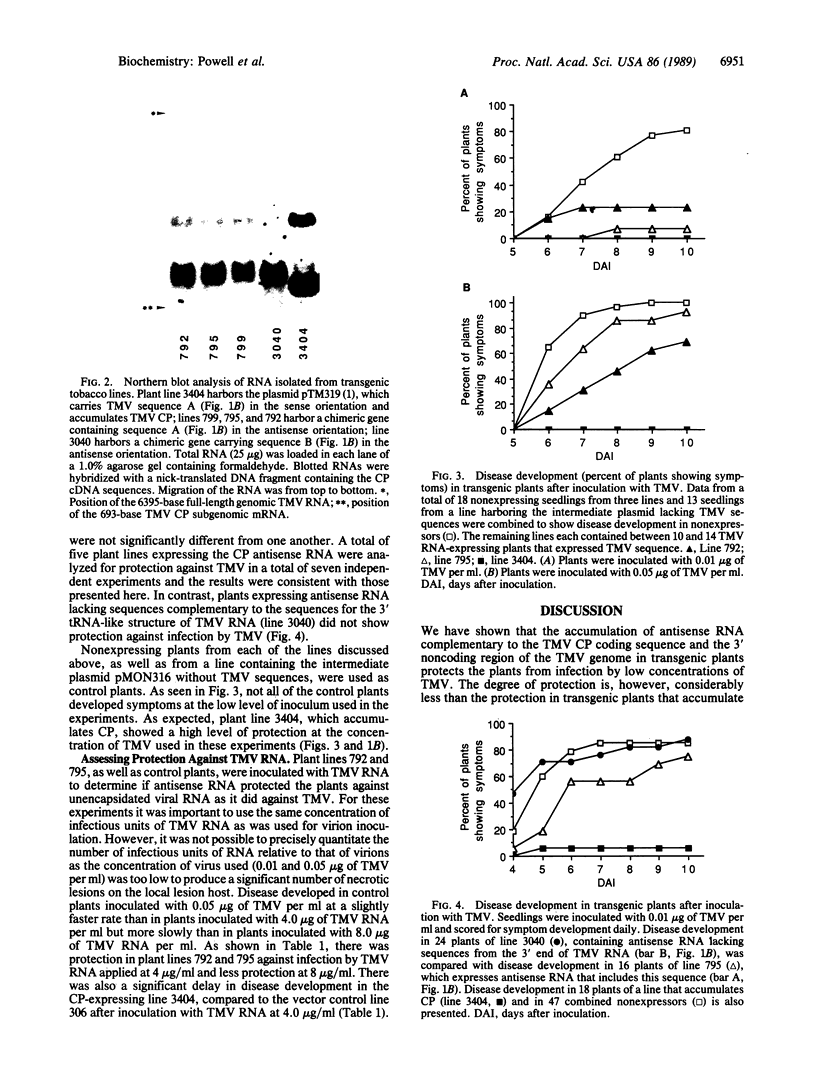
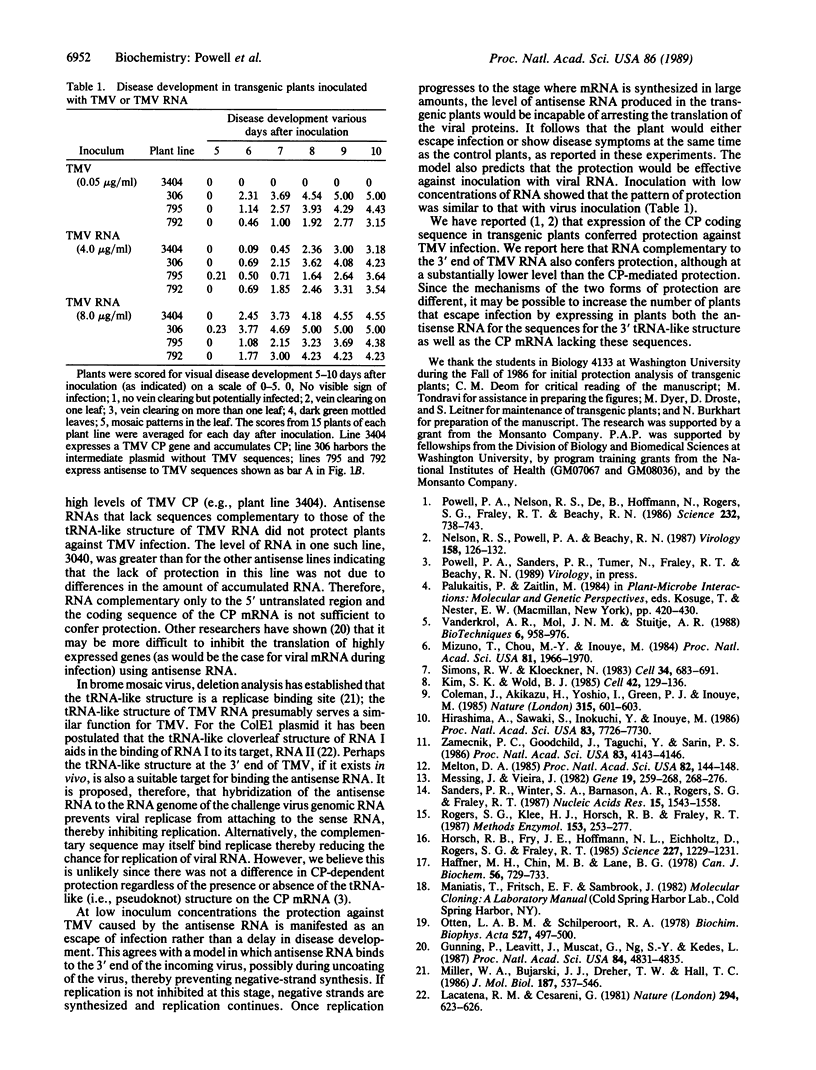
Transgenic tobacco plants that express RNA sequences complementary to the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) coat protein (CP) coding sequence with or without the tRNA-like structure at the 3' end of the TMV RNA were produced. Progeny of self-pollinated plants were challenged with TMV to determine their resistance to infection. Plants that expressed RNA sequences complementary to the CP coding region and the 3' untranslated region, including the tRNA-like sequences, were protected from infection by TMV at low levels of inoculum. However, plants that expressed RNA complementary to the CP coding sequence alone were not protected from infection. These results indicate that sequences complementary to the terminal 117 nucleotides of TMV, which include a putative replicase binding site, are responsible for the protection. However, the level of protection in these plants was considerably less than in transgenic plants that expressed the TMV CP gene and accumulated CP. Since the mechanisms of protection in the two systems are different, it may be possible to increase protection by introducing both sequences into transgenic plants.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1229–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4691.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abel P. P., Nelson R. S., De B., Hoffmann N., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T., Beachy R. N. Delay of disease development in transgenic plants that express the tobacco mosaic virus coat protein gene. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):738–743. doi: 10.1126/science.3457472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Hirashima A., Inokuchi Y., Green P. J., Inouye M. A novel immune system against bacteriophage infection using complementary RNA (micRNA). Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):601–603. doi: 10.1038/315601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner M. H., Chin M. B., Lane B. G. Wheat embryo ribonucleates. XII. Formal characterization of terminal and penultimate nucleoside residues at the 5'-ends of "capped" RNA from imbibing wheat embryos. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jul;56(7):729–733. doi: 10.1139/o78-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima A., Sawaki S., Inokuchi Y., Inouye M. Engineering of the mRNA-interfering complementary RNA immune system against viral infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7726–7730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacatena R. M., Cesareni G. Base pairing of RNA I with its complementary sequence in the primer precursor inhibits ColE1 replication. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):623–626. doi: 10.1038/294623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Injected anti-sense RNAs specifically block messenger RNA translation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. A., Bujarski J. J., Dreher T. W., Hall T. C. Minus-strand initiation by brome mosaic virus replicase within the 3' tRNA-like structure of native and modified RNA templates. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten L. A., Schilperoort R. A. A rapid micro scale method for the detection of lysopine and nopaline dehydrogenase activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 8;527(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. R., Winter J. A., Barnason A. R., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T. Comparison of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S and nopaline synthase promoters in transgenic plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1543–1558. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Goodchild J., Taguchi Y., Sarin P. S. Inhibition of replication and expression of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III in cultured cells by exogenous synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4143–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Krol A. R., Mol J. N., Stuitje A. R. Modulation of eukaryotic gene expression by complementary RNA or DNA sequences. Biotechniques. 1988 Nov-Dec;6(10):958–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]