Abstract
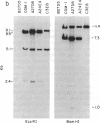
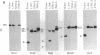
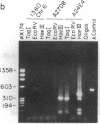
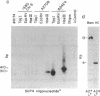
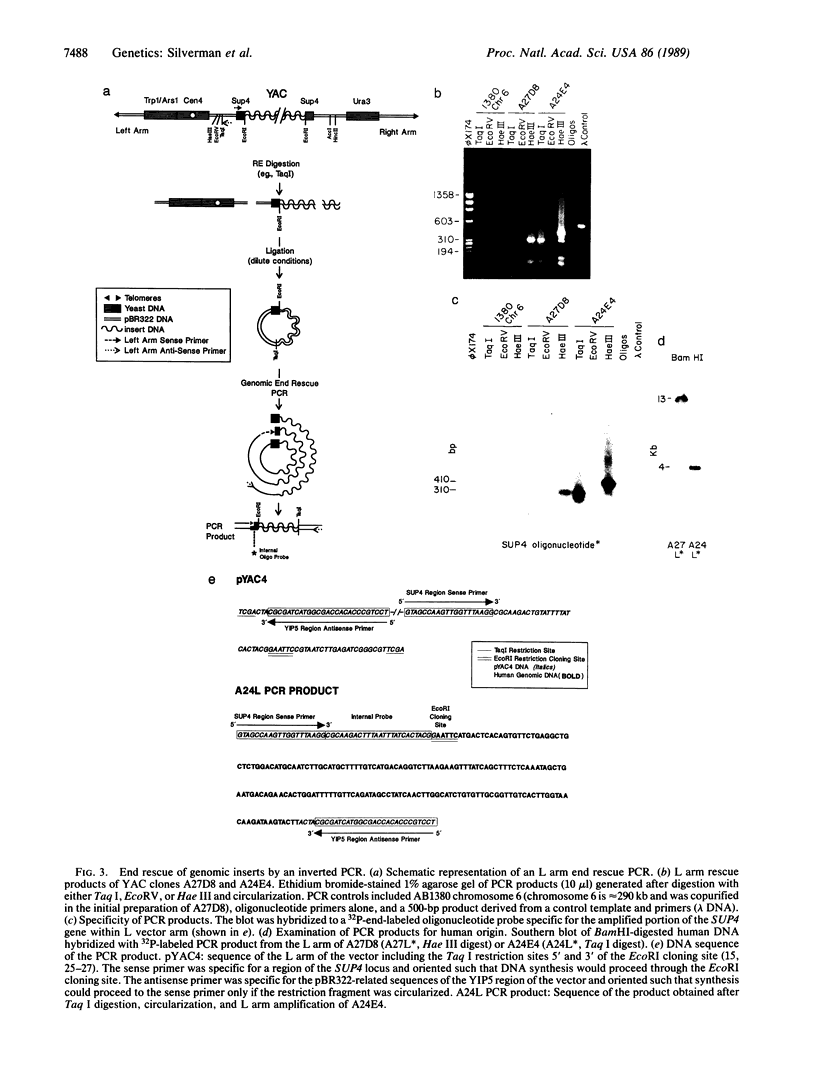
Well-characterized large genomic clones obtained from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) libraries provide the framework to localize genes and approach genetic disease. We developed universally applicable approaches to establish authenticity, localize and orient internal genes, map restriction sites, and rescue the distal ends of large human genomic DNA inserts. We selected human chromosome segment 18q21.3 as a model system. Molecular cloning of this segment was initiated by characterizing three plasminogen activator inhibitor type 2 (PAI-2) clones [290, 180, and 60 kilobases (kb)] isolated from a YAC library. Comparison of YAC and bacteriophage lambda genomic DNA clones confirmed the fidelity of the PAI-2 locus. Detailed rare cutting restriction maps were generated by ramped contour-clamped homogeneous electric field electrophoresis. The PAI-2 locus was located and oriented within the YACs, which span a distance 70 kb 5' to 220 kb 3' of PAI-2. Moreover, both left and right ends of the YAC genomic DNA inserts were rescued by amplifying circularized cloning sites with an inverted form of the polymerase chain reaction. These unique terminal genomic DNA fragments were used to rescreen the YAC library and isolate overlapping clones that extend the map. These approaches will enable neighboring loci to be definitively linked and establish the feasibility of using YAC technology to clone and map chromosomal segments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakhshi A., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Wright J. J., McBride O. W., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Wright J. J., Graninger W., Seto M., Owens J., Cossman J., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Korsmeyer S. J. Mechanism of the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation: structural analysis of both derivative 14 and 18 reciprocal partners. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein B. H., Silverman G. A., Little R. D., Burke D. T., Korsmeyer S. J., Schlessinger D., Olson M. V. Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1348–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.2544027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasalow F. I., Blethen S. L., Knight S. M., Taysi K. 18q deletion syndrome in a child with steroid-17,20-lyase deficiency. Steroids. 1986 Jun;47(6):421–429. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(86)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobkin C., Ferrando C., Brown W. PFGE of human DNA: 5-azacytidine improves restriction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3183–3183. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Olson M. V., Hall B. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mutant eukaryotic gene: the yeast tyrosine-inserting ochre suppressor SUP4-o. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebacq-Verheyden A. M., Bertness V., Kirsch I., Hollis G. F., McBride O. W., Battey J. Human gastrin-releasing peptide gene maps to chromosome band 18q21. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Jan;13(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02422302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlhens F., Delattre O., Bernard A., Olschwang S., Dutrillaux B., Thomas G. RFLP identified by the anonymous DNA segment OL VII E10 at 18q21.3 (HGM no. D18S8). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1348–1348. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Gerber A. S., Hartl D. L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):621–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Identification of the constant chromosome regions involved in human hematologic malignant disease. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):749–751. doi: 10.1126/science.7079737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto M., Jaeger U., Hockett R. D., Graninger W., Bennett S., Goldman P., Korsmeyer S. J. Alternative promoters and exons, somatic mutation and deregulation of the Bcl-2-Ig fusion gene in lymphoma. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):123–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Lawrance S. K., Gillespie G. A., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M., Collins F. S. Strategies for mapping and cloning macroregions of mammalian genomes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:461–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertelecki W., Gerald P. S. Clinical and chromosomal studies of the 18q- syndrome. J Pediatr. 1971 Jan;78(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80262-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. G., Towner J. W., Forsman I., Siris E. Syndromes associated with deletion of the long arm of chromosome 18[del(18q)]. Am J Med Genet. 1979;3(2):155–174. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Ahern S. M., Le Beau M. M., Lebo R. V., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human plasminogen activator inhibitor-2. The nearest mammalian homologue of chicken ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5495–5502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Wun T. C., Sadler J. E. cDNA cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a plasminogen activator inhibitor from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3718–3725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M. C., Sasaki M., Mise K., Semba K., Nishizawa M., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Regional mapping of the human proto-oncogene c-yes-1 to chromosome 18 at band q21.3. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Jul;76(7):559–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]