Abstract
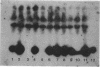
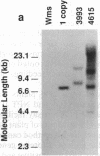
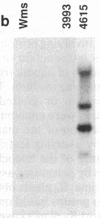
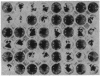
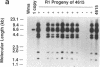
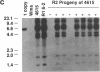
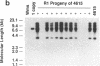
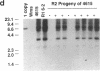
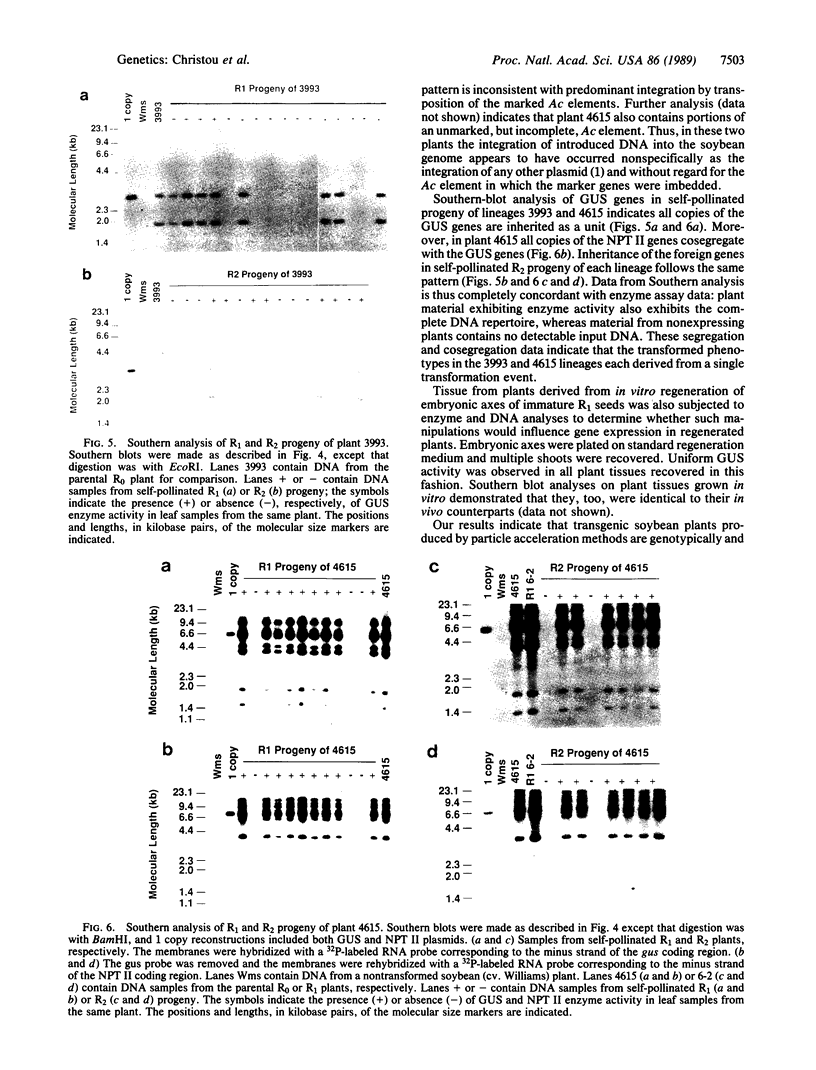
DNA-coated gold particles were introduced into meristems of immature soybean seeds using electric discharge particle acceleration to produce transgenic fertile soybean plants. The lineages of integrated foreign DNA in two independently transformed plants were followed in the first (R1) and second (R2) generation of self-pollinated progeny. One plant (4615) was transformed with the Escherichia coli genes for β-glucuronidase and neomycin phosphotransferase II; the other (3993) was transformed only with the gene for β-glucuronidase. Segregation ratios for the introduced gene(s) were approximately 3:1 for plant 4615 and 1:1 for plant 3993 in the R1 generation. DNA analysis showed 100% concordance between presence of the foreign gene sequences and enzyme activity. Moreover, all copies of the foreign genes are inherited as a unit in each plant. Plant 3993 segregated in a 1:1 ratio in the R2 generation. R1 plants derived from plant 4615, which expressed both genes, gave either 100% or 3:1 expression of both genes in the R2 generation, demonstrating recovery of both homozygous and heterozygous R1 plants. Our results show that foreign DNA introduced into soybean plants using electric discharge particle acceleration can be inherited in a Mendelian manner. Results also demonstrate cotransformation of tandem markers and show that both markers are inherited as closely linked genes in subsequent generations. These results indicate that whole plants can be derived from single transformed cells by a de novo organogenic pathway.
Keywords: Glycine max, particle acceleration, genetics, transformation
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. D., Smith J. B. Nuclear dna amounts in angiosperms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 May 27;274(933):227–274. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1976.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christou P., McCabe D. E., Swain W. F. Stable Transformation of Soybean Callus by DNA-Coated Gold Particles. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jul;87(3):671–674. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christou P., Murphy J. E., Swain W. F. Stable transformation of soybean by electroporation and root formation from transformed callus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3962–3966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze R., Stochaj U., Laufs J., Starlinger P. Transcription of transposable element Activator (Ac) of Zea mays L. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1555–1563. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02400.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss B., Sprengel R., Will H., Schaller H. A new sensitive method for qualitative and quantitative assay of neomycin phosphotransferase in crude cell extracts. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]