Abstract
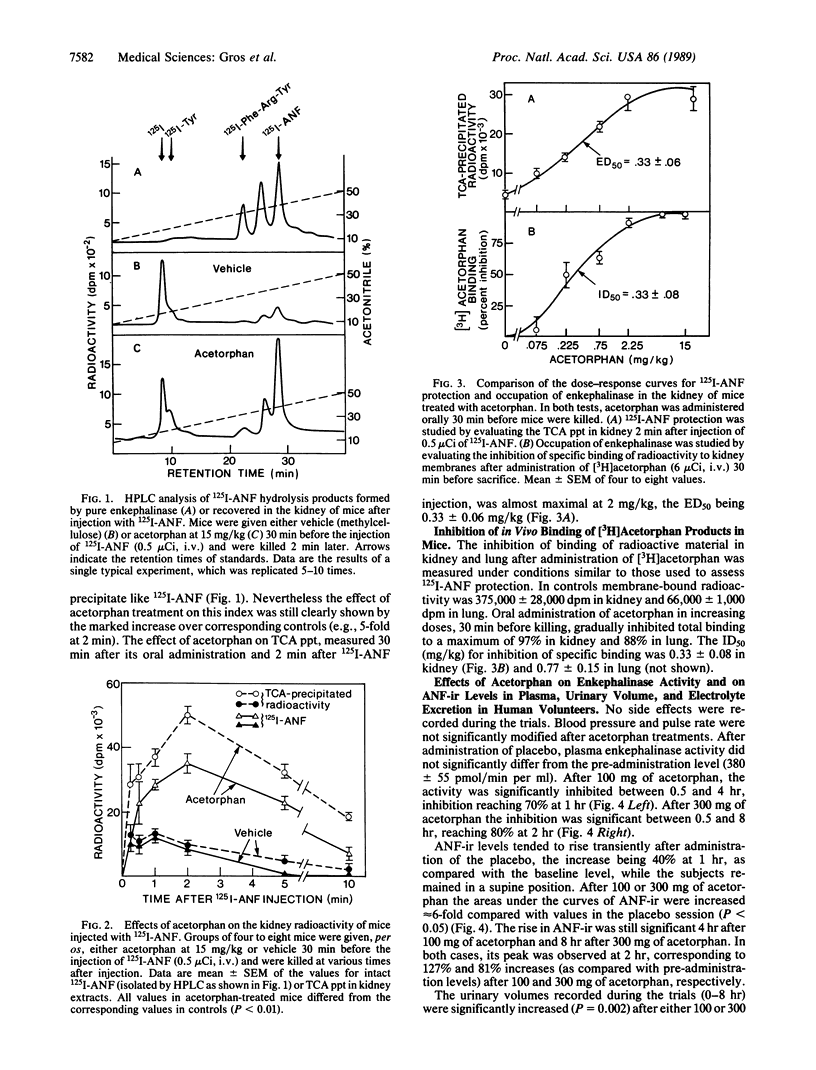
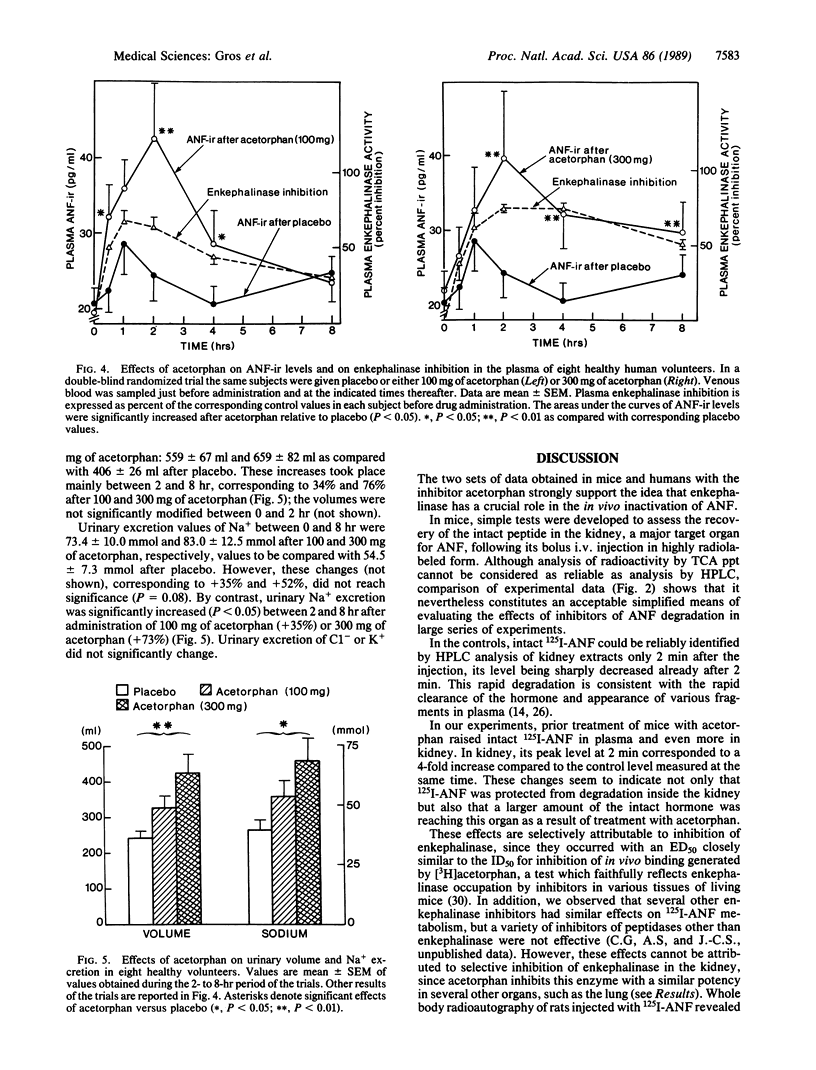
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) might be beneficial in several cardiovascular disorders, but its poor oral absorption and rapid inactivation in vivo have so far prevented its use in therapeutics. We have assessed the role of enkephalinase (membrane metallo-endopeptidase, EC 3.4.24.11) in the in vivo inactivation of ANF in mice and healthy human volunteers by evaluating the effects of acetorphan, a potent inhibitor. In mice, the degradation of 125I-labeled ANF was markedly delayed, as shown by the levels of the intact peptide in the plasma and the kidney, a major target organ. The effect of acetorphan was due to the inhibition of enkephalinase activity, since it occurred at an ED50 very close to this drug's ID50 for the inhibition of the specific binding of radioactive material to the kidney or lung peptidase that was measured after administration of [3H]acetorphan. The effects of acetorphan were also studied in eight healthy human volunteers by using a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled design. Oral administration of acetorphan elicited a lasting elevation of plasma ANF-like immunoreactivity, with a time course parallel to that of the inhibition of plasma enkephalinase activity. These effects were accompanied by significant increases in urinary volume and sodium excretion, two well-established renal responses to ANF peptides. These results indicate that enkephalinase plays a critical role in ANF degradation in vivo and that its inhibition enhances the levels of circulating endogenous ANF, which, in turn, results in diuresis and natriuresis. Enkephalinase inhibition may constitute another therapeutic approach to the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, such as congestive heart failure or essential hypertension, on which ANF is postulated to have a beneficial effect.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertrand P., Doble A. Degradation of atrial natriuretic peptides by an enzyme in rat kidney resembling neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 15;37(20):3817–3821. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Genest J. The heart and the atrial natriuretic factor. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):107–127. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody R. J., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Kubo S. H., Covit A. B., Ryman K. S., Shaknovich A., Pondolfino K., Clark M., Camargo M. J. Atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and heart failure patients. Plasma levels and renal, hormonal, and hemodynamic responses to peptide infusion. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1362–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI112723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condra C. L., Leidy E. A., Bunting P., Colton C. D., Nutt R. F., Rosenblatt M., Jacobs J. W. Clearance and early hydrolysis of atrial natriuretic factor in vivo. Structural analysis of cleavage sites and design of an analogue that inhibits hormone cleavage. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1348–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI113462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusson J. R., Du Souich P., Hamet P., Schiffrin E. L., Kuchel O., Tremblay J., Cantin M., Genest J., Larochelle P. Effects and pharmacokinetics of bolus injections of atrial natriuretic factor in normal volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;11(6):635–642. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198806000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Baume S., Brion F., Dam Trung Tuong M., Schwartz J. C. Evaluation of enkephalinase inhibition in the living mouse, using [3H]acetorphan as a probe. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Nov;247(2):653–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Hamet P., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of chronic infusion of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor (ANF 8-33) in conscious two-kidney, one-clip hypertensive rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Jan;178(1):155–159. doi: 10.3181/00379727-178-rc12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., Gros C., Schwartz J. C., Danvy D., Plaquevent J. C., Duhamel L., Duhamel P., Vlaiculescu A., Costentin J., Lecomte J. M. Enantiomers of thiorphan and acetorphan: correlation between enkephalinase inhibition, protection of endogenous enkephalins and behavioral effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Nov;243(2):666–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsube N., Schwartz D., Needleman P. Atriopeptin turnover: quantitative relationship between in vivo changes in plasma levels and atrial content. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Nov;239(2):474–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehn J. A., Norman J. A., Jones B. N., LeSueur L., Sakane Y., Ghai R. D. Degradation of atrial natriuretic factor by kidney cortex membranes. Isolation and characterization of the primary proteolytic product. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11623–11627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H. Atrial natriuretic hormone, the renin-aldosterone axis, and blood pressure-electrolyte homeostasis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 21;313(21):1330–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511213132106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte J. M., Costentin J., Vlaiculescu A., Chaillet P., Marcais-Collado H., Llorens-Cortes C., Leboyer M., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological properties of acetorphan, a parenterally active "enkephalinase" inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):937–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Lang R. E., Aronoff G. R., Ruskoaho H., Toth M., Ganten D., Sterzel R. B., Unger T. Atriopeptin III kinetics and pharmacodynamics in normal and anephric rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):416–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. R., Braas K. M., Snyder S. H. Atrial natriuretic factor receptors in rat kidney, adrenal gland, and brain: autoradiographic localization and fluid balance dependent changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3557–3561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Schofield P. R. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of human enkephalinase (neutral endopeptidase). FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. K., Thibault G., Schiffrin E. L., Garcia R., Chartier L., Gutkowska J., Genest J., Cantin M. Disappearance of atrial natriuretic factor from circulation in the rat. Peptides. 1986 Mar-Apr;7(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier M. A., Vandlen R. L., Albers-Schönberg G., Nutt R. F., Brady S., Lyle T., Winquist R., Faison E. P., Heinel L. A., Blaine E. H. Specific membrane receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in renal and vascular tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5946–5950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins G. M., Spear K. L., Siegel N. R., Zurcher-Neely H. A. Inactivation of atrial natriuretic factor by the renal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 10;901(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G., Espiner E. A., Ikram H., Yandle T. G., Joyce S. L., Cullens M. M. Effects of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):812–817. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Pollard H., Galceran M., Delauche M., Schwartz J. C., Verroust P. Distribution of enkephalinase (membrane metalloendopeptidase, E.C. 3.4.24.11) in rat organs. Detection using a monoclonal antibody. Lab Invest. 1988 Feb;58(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugg E. L., Aiton J. F., Cramb G. Degradation of [125I]-atrial natriuretic peptide by a soluble metallopeptidase isolated from rat ventricular myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):294–300. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra J. M., Correa F. M., Plunkett L. M., Israel A., Kurihara M., Shigematsu K. Binding of angiotensin and atrial natriuretic peptide in brain of hypertensive rats. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):758–760. doi: 10.1038/320758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov I. Y., Dukhanina E. A., Molokoedov A. S., Danilov S. M., Ovchinnikov M. V., Bespalova Z. D., Titov M. I. Atriopeptin 2 is hydrolysed by cardiac but not pulmonary isozyme of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Sakane Y., Jeng A. Y., Koehn J. A., Ansell J. A., Wennogle L. P., Ghai R. D. Identification of protease 3.4.24.11 as the major atrial natriuretic factor degrading enzyme in the rat kidney. Peptides. 1988 Jan-Feb;9(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini M. G., Panconesi A., Del Bianco P. L., Sicuteri F. Enkephalinase and angiotensin converting enzyme activities in human venous and arterial plasma. Neuropeptides. 1986 Aug-Sep;8(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(86)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. The hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide by pig kidney microvillar membranes is initiated by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2430183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Almeida F. A., Nussenzveig D. R., Sawyer D., Maack T. Binding and functional effects of atrial natriuretic factor in isolated rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F917–F928. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Xie C. W., Xie X. Z., Gao X. M., Chang J. K. Dynorphin A-(1-10) amide stimulates the release of atrial natriuretic polypeptide (ANP) from rat atrium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 29;136(3):449–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Xie C. W., Xu C. B., Jiang B. Q., Xu Y. Y., Zhang J. Y., Meng Z. H., Wu H. J., Liu L. S., Chang D. Therapeutic actions of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide in 16 clinical cases. Life Sci. 1987 May 25;40(21):2077–2086. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ura N., Carretero O. A., Erdös E. G. Role of renal endopeptidase 24.11 in kinin metabolism in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int. 1987 Oct;32(4):507–513. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


