Abstract
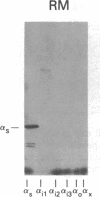
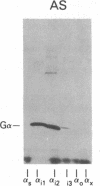
A panel of antibodies to synthetic decapeptides corresponding to the C termini of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein (G protein) alpha subunits has been generated in rabbits. The specificity of each antibody was assessed by ELISA for peptide binding and by immunoblotting for binding to defined, recombinant G alpha subunits expressed in Escherichia coli. Immunoblotting of human platelet membranes with these antibodies identified a variety of endogenous G proteins including Gs (stimulatory), Gi2 (inhibitory), Gi3, and Gx(z) (unknown function). Pretreatment of platelet membranes with C-terminal antibodies reactive with Gi2, but not with antibodies to Gi3 or Gx(z), blocked alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. This identifies Gi2 as the dominant mediator of cyclase inhibition in this pathway. This approach may provide a general means of identifying relevant functional interactions of G proteins with receptors and effectors in situ.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Kroll S., Rajaram R., Unson C., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. M. An antibody directed against the carboxyl-terminal decapeptide of the alpha subunit of the retinal GTP-binding protein, transducin. Effects on transducin function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9345–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Regan J. W., Nakata H., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Gierschik P., Somers R. L., Spiegel A. M., Birnbaumer L., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional reconstitution of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3901–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Gierschik P., Somers R., Spiegel A. M., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Specificity of the functional interactions of the beta-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1493–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Gierschik P., Codina J., Somers R. L., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mechanism of guanine nucleotide regulatory protein-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Studies with isolated subunits of transducin in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9514–9520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Yoshimoto K. K., Eversole-Cire P., Simon M. I. Identification of a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit that lacks an apparent ADP-ribosylation site for pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3066–3070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Falloon J., Milligan G., Pines M., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. Immunochemical evidence for a novel pertussis toxin substrate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8058–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Backlund P. S., Jr, Rossiter K., Carter A., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. Purification of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins from brain: identification of a novel form of Go. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7085–7090. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Rossiter K., Carter A., Simonds W., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Spiegel A. M. Identification of the GTP-binding protein encoded by Gi3 complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6476–6479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Katada T., Ui M., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Kaziro Y. Identification of three pertussis toxin substrates (41, 40 and 39 kDa proteins) in mammalian brain. Comparison of predicted amino acid sequences from G-protein alpha-subunit genes and cDNAs with partial amino acid sequences from purified proteins. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80647-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Saur W., Schultz G. Inhibition of platelet adenylate cyclase by epinephrine requires GTP. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 1;85(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Golf: an olfactory neuron specific-G protein involved in odorant signal transduction. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):790–795. doi: 10.1126/science.2499043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Kozawa O., Kaibuchi K., Katada T., Ui M., Takai Y. Direct evidence for involvement of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in chemotactic peptide-stimulated formation of inositol bisphosphate and trisphosphate in differentiated human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Reconstitution with Gi or Go of the plasma membranes ADP-ribosylated by pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11558–11562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Kaziro Y. Sequence analysis of cDNA and genomic DNA for a putative pertussis toxin-insensitive guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5384–5388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattera R., Yatani A., Kirsch G. E., Graf R., Okabe K., Olate J., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Recombinant alpha i-3 subunit of G protein activates Gk-gated K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):465–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Kelly E. C., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M., Milligan G. Antibodies which recognize the C-terminus of the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gi) demonstrate that opioid peptides and foetal-calf serum stimulate the high-affinity GTPase activity of two separate pertussis-toxin substrates. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):653–659. doi: 10.1042/bj2490653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S., Pang I. H., Gilman A. G., Sternweis P. C. Chromatographic resolution and immunologic identification of the alpha 40 and alpha 41 subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2020–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Katada T., Tohkin M., Itoh H., Kaziro Y., Ui M., Nozawa Y. GTP-binding proteins in human platelet membranes serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 12;237(1-2):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga K., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kanagawa K., Hiranaga M., Matsuo Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of bovine adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G-protein deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall T., Harris B. A. Identification of the lesion in the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of the uncoupled S49 lymphoma. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 30;224(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M. Use of glutaraldehyde as a coupling agent for proteins and peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):159–165. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Woodard C. J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Receptor and effector interactions of Gs. Functional studies with antibodies to the alpha s carboxyl-terminal decapeptide. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80622-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M., Aurbach G. D. Binding of 5'-guanylyl-imidodiphosphate to turkey erythrocyte membranes and effects on beta-adrenergic-activated adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7630–7636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Masters S. B., Beiderman B., Heideman W., Bourne H. R. Identification of receptor contact site involved in receptor-G protein coupling. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):758–760. doi: 10.1038/330758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. J., Katial A., Craft C., Shinohara T. Sequence analysis of bovine retinal S-antigen. Relationships with alpha-transducin and G-proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]