Abstract
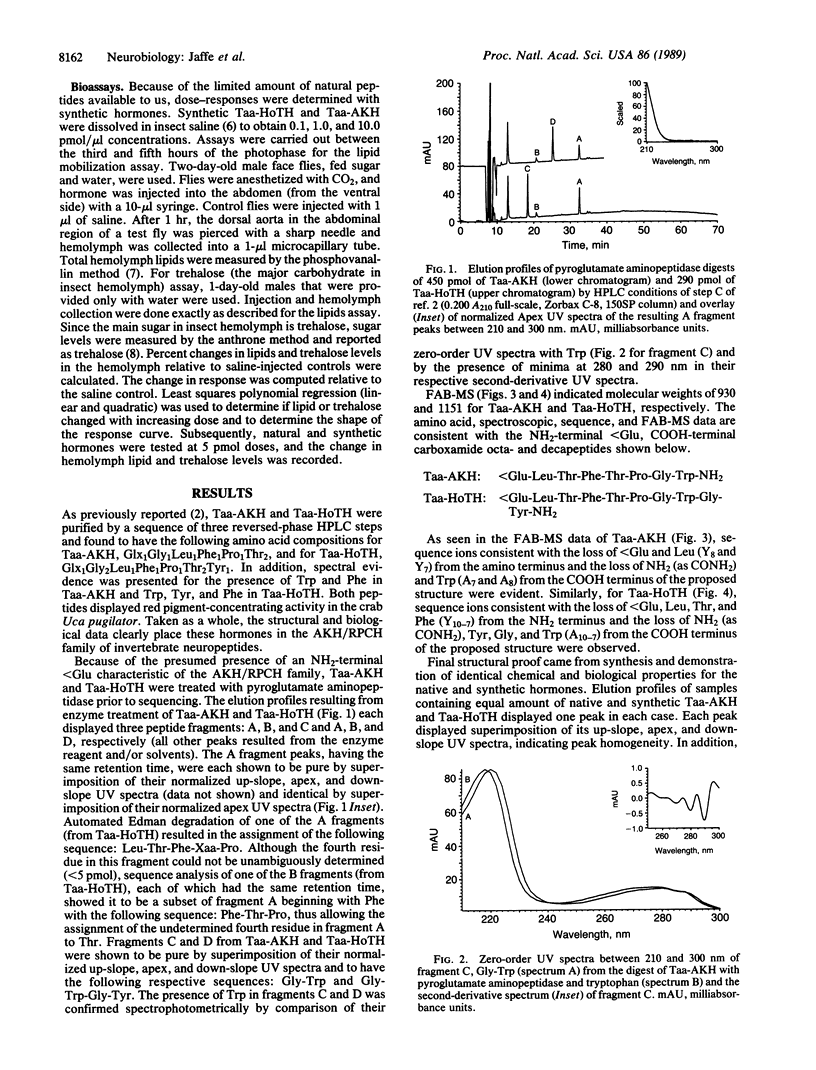
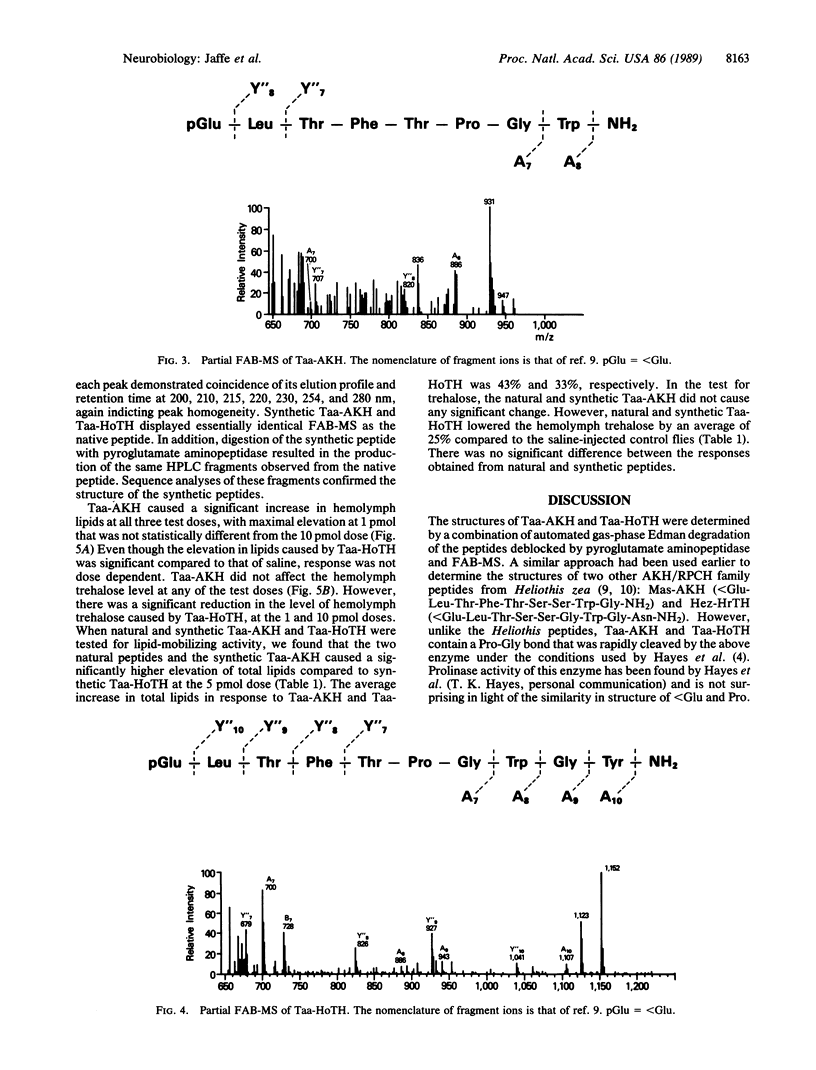
The primary structures of two neuropeptides, Tabanus atratus adipokinetic hormone (Taa-AKH) and Tabanus atratus hypotrehalosemic hormone (Taa-HoTH), from the corpora cardiaca of horse flies (Diptera: Tabanidae) have been determined. Amino acid sequences of Taa-AKH (less than Glu-Leu-Thr-Phe-Thr-Pro-Gly-Trp-NH2) and Taa-HoTH (less than Glu-Leu-Thr-Phe-Thr-Pro-Gly-Trp-Gly-Tyr-NH2) (where less than Glu = pyroglutamic acid) were determined by automated gas-phase Edman degradation of the peptides deblocked by pyroglutamate aminopeptidase and by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. The hormones were synthesized, and the natural and synthetic peptides exhibited identical chromatographic, spectroscopic, and biological properties. When assayed in adult face fly males, Taa-AKH and Taa-HoTH demonstrated hyperlipemic activity, in addition, Taa-HoTH also demonstrated a significant hypotrehalosemic activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buko A. M., Fraser B. A. Peptide studies using a fast atom bombardment high field mass spectrometer and data system. 4. Disulfide-containing peptides. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1985 Oct;12(10):577–585. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200121002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. K., Keeley L. L., Knight D. W. Insect hypertrehalosemic hormone: isolation and primary structure from Blaberus discoidalis cockroaches. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):674–678. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90784-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H., Raina A. K., Fraser B. A., Keim P., Rao K. R., Zhang Y. S., Lancaster J. L., Hayes D. K. Isolation of two neuropeptides in the AKH/RPCH-family from horseflies (Diptera). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):656–663. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80331-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H., Raina A. K., Riley C. T., Fraser B. A., Bird T. G., Tseng C. M., Zhang Y. S., Hayes D. K. Isolation and primary structure of a neuropeptide hormone from Heliothis zea with hypertrehalosemic and adipokinetic activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):344–350. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H., Raina A. K., Riley C. T., Fraser B. A., Holman G. M., Wagner R. M., Ridgway R. L., Hayes D. K. Isolation and primary structure of a peptide from the corpora cardiaca of Heliothis zea with adipokinetic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):622–628. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert K., Morgan P., Mordue W. Primary structures of locust adipokinetic hormones II. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Aug;366(8):723–727. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. V., Mordue W., Batley K. E., Morris H. R. Structure of locust adipokinetic hormone, a neurohormone that regulates lipid utilisation during flight. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):207–211. doi: 10.1038/263207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


