Abstract
The coumarin ring system in the title compound, C15H18O5 [IUPAC name: 8-(2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one], isolated from Muraya paniculata, is planar (r.m.s. deviation 0.017 Å). In the crystal, the two hydroxy groups are involved in O—H⋯O hydrogen bonding with adjacent molecules, forming a sheet structure.
Related literature
For the asymmetric synthesis and absolute configuration of meranzin hydrate, see: Grundon & McColl (1975 ▶).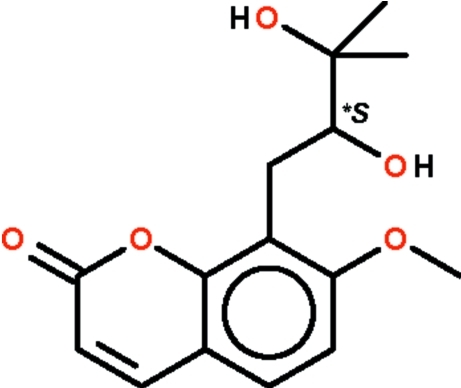
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H18O5
M r = 278.29
Monoclinic,
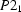
a = 5.8061 (7) Å
b = 10.5146 (13) Å
c = 11.4477 (14) Å
β = 91.547 (2)°
V = 698.61 (15) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.35 × 0.15 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX diffractometer
6694 measured reflections
1699 independent reflections
1338 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.040
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.102
S = 1.00
1699 reflections
192 parameters
3 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005386/bt5194sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005386/bt5194Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O4—H4⋯O2i | 0.84 (1) | 2.01 (1) | 2.842 (3) | 169 (5) |
| O5—H5⋯O2ii | 0.85 (1) | 2.12 (2) | 2.936 (3) | 163 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 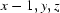 ; (ii)
; (ii) 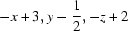 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Directorate General of Higher Education, Ministry of National Education, Indonesia (BPPS-Doctoral Program), the I-MHERE Project of Padjadjaran University, the Science Fund of Malaysia (12-02-03-2063) and the University of Malaya.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Muraya paniculata (Rutaceae, known as kemuning in Indonesia) is a perennial herb having succulent leaves. The plant is used for the treatment of orchitis, bronchitis and urine infections.
Experimental
M. paniculata was collected in from Bandung, Indonesia. The plant was identified by the Department of Biology of Padjadjaran University. The dried leaves of M. paniculata (4 kg) was extracted exhaustively by methanol at room temperature and then concentrated to yield a methanol extract (438 g); 200 g was partitioned between n-hexane and methanol containing 10% water. The aqueous extract was extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate portion was removed and subjected to column chromatography on silica gel 60 by using a step gradient of n-hexane–ethyl acetate–methanol. The fraction eluted by n-hexane/ethyl acetate (1:4) was further separated by column chromatography on silica gel (chloroform:ethyl acetate 1:1) to give meranzin hydrate, 8-[2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutyl]-7-methoxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one (12 mg).
Refinement
Carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.93 to 0.97 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) set to 1.2 to 1.5U(C).
The oxygen-bound H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map, and were refined isotropically with a distance restraint of O—H 0.84 (1) Å.
In the absence of anomalous scatterers, Friedel pairs were merged. The absolute configuration was set to match the one determined by the asymmetric synthesis of meranzin (Grundon & McColl, 1975).
Figures
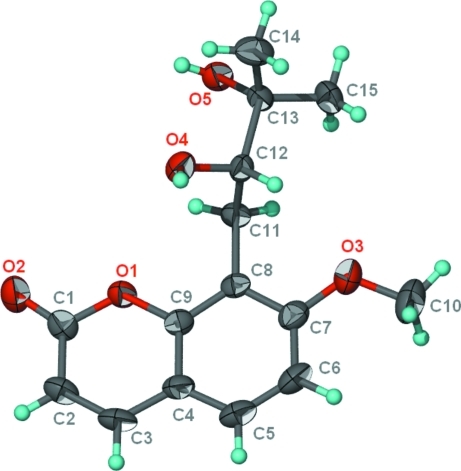
Fig. 1.
Anisotropic displacement ellipsoid plot (Barbour, 2001) of C15H18O5; at the 50% probability level; hydrogen atoms are drawn as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C15H18O5 | F(000) = 296 |
| Mr = 278.29 | Dx = 1.323 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 1731 reflections |
| a = 5.8061 (7) Å | θ = 2.6–22.3° |
| b = 10.5146 (13) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 11.4477 (14) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 91.547 (2)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 698.61 (15) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.15 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX diffractometer | 1338 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.040 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.8° |
| ω scans | h = −7→7 |
| 6694 measured reflections | k = −11→13 |
| 1699 independent reflections | l = −14→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0603P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1699 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 192 parameters | Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3 |
| 3 restraints | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 1.4383 (3) | 0.50000 (16) | 0.83522 (15) | 0.0436 (4) | |
| O2 | 1.7272 (3) | 0.51296 (19) | 0.96204 (18) | 0.0592 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.8098 (4) | 0.4410 (2) | 0.57958 (18) | 0.0677 (6) | |
| O4 | 1.0213 (3) | 0.30444 (18) | 0.91374 (15) | 0.0500 (5) | |
| O5 | 1.1435 (3) | 0.06759 (16) | 0.79342 (17) | 0.0490 (4) | |
| C1 | 1.5866 (4) | 0.5712 (3) | 0.9034 (2) | 0.0461 (6) | |
| C2 | 1.5618 (5) | 0.7069 (3) | 0.8999 (3) | 0.0553 (7) | |
| H2 | 1.6632 | 0.7576 | 0.9436 | 0.066* | |
| C3 | 1.3954 (5) | 0.7612 (3) | 0.8350 (3) | 0.0567 (7) | |
| H3 | 1.3813 | 0.8493 | 0.8345 | 0.068* | |
| C4 | 1.2374 (5) | 0.6858 (2) | 0.7657 (2) | 0.0476 (6) | |
| C5 | 1.0585 (5) | 0.7350 (3) | 0.6972 (3) | 0.0596 (8) | |
| H5A | 1.0373 | 0.8226 | 0.6939 | 0.071* | |
| C6 | 0.9124 (5) | 0.6572 (3) | 0.6344 (3) | 0.0610 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.7931 | 0.6918 | 0.5888 | 0.073* | |
| C7 | 0.9433 (5) | 0.5268 (3) | 0.6391 (2) | 0.0513 (7) | |
| C8 | 1.1185 (4) | 0.4708 (2) | 0.7080 (2) | 0.0415 (5) | |
| C9 | 1.2625 (4) | 0.5534 (2) | 0.7693 (2) | 0.0400 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.6251 (5) | 0.4863 (4) | 0.5056 (3) | 0.0792 (11) | |
| H10A | 0.5429 | 0.4153 | 0.4723 | 0.119* | |
| H10B | 0.6864 | 0.5372 | 0.4442 | 0.119* | |
| H10C | 0.5222 | 0.5367 | 0.5507 | 0.119* | |
| C11 | 1.1382 (4) | 0.3280 (2) | 0.7160 (2) | 0.0419 (5) | |
| H11A | 1.2906 | 0.3052 | 0.7459 | 0.050* | |
| H11B | 1.1181 | 0.2912 | 0.6387 | 0.050* | |
| C12 | 0.9563 (4) | 0.2742 (2) | 0.79647 (19) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.8090 | 0.3159 | 0.7777 | 0.047* | |
| C13 | 0.9231 (4) | 0.1295 (2) | 0.7838 (2) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.7685 (5) | 0.0804 (3) | 0.8780 (3) | 0.0628 (8) | |
| H14A | 0.7520 | −0.0100 | 0.8704 | 0.094* | |
| H14B | 0.6199 | 0.1200 | 0.8700 | 0.094* | |
| H14C | 0.8354 | 0.1002 | 0.9534 | 0.094* | |
| C15 | 0.8225 (5) | 0.0987 (3) | 0.6642 (3) | 0.0628 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.7866 | 0.0096 | 0.6600 | 0.094* | |
| H15B | 0.9324 | 0.1193 | 0.6059 | 0.094* | |
| H15C | 0.6846 | 0.1474 | 0.6505 | 0.094* | |
| H4 | 0.935 (6) | 0.363 (3) | 0.937 (4) | 0.119 (17)* | |
| H5 | 1.183 (6) | 0.068 (4) | 0.8650 (12) | 0.089 (12)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0453 (9) | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0515 (10) | 0.0040 (7) | −0.0063 (7) | −0.0039 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0526 (10) | 0.0556 (12) | 0.0683 (12) | 0.0103 (9) | −0.0159 (9) | −0.0154 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0719 (13) | 0.0715 (15) | 0.0581 (12) | −0.0035 (11) | −0.0275 (10) | 0.0085 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0630 (11) | 0.0466 (11) | 0.0400 (9) | 0.0096 (9) | −0.0081 (8) | −0.0065 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0460 (9) | 0.0389 (10) | 0.0616 (12) | 0.0071 (7) | −0.0058 (8) | −0.0042 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0428 (12) | 0.0441 (15) | 0.0512 (14) | 0.0015 (11) | −0.0013 (11) | −0.0098 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0581 (15) | 0.0403 (15) | 0.0676 (18) | −0.0087 (12) | −0.0002 (14) | −0.0088 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0722 (17) | 0.0299 (13) | 0.0683 (18) | −0.0035 (13) | 0.0078 (15) | −0.0034 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0567 (14) | 0.0356 (14) | 0.0508 (15) | 0.0018 (12) | 0.0047 (12) | 0.0054 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0716 (18) | 0.0427 (16) | 0.0645 (18) | 0.0122 (14) | 0.0013 (15) | 0.0140 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0656 (17) | 0.0572 (19) | 0.0599 (17) | 0.0137 (14) | −0.0073 (14) | 0.0186 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0573 (15) | 0.0544 (17) | 0.0416 (14) | 0.0014 (13) | −0.0065 (12) | 0.0098 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0475 (12) | 0.0371 (12) | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0011 (10) | −0.0002 (10) | 0.0037 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0450 (12) | 0.0345 (13) | 0.0406 (13) | 0.0035 (10) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0042 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0586 (16) | 0.114 (3) | 0.0636 (19) | 0.001 (2) | −0.0203 (15) | 0.016 (2) |
| C11 | 0.0447 (12) | 0.0353 (12) | 0.0455 (13) | −0.0001 (10) | −0.0016 (10) | −0.0042 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0402 (10) | 0.0373 (12) | 0.0384 (12) | 0.0051 (10) | −0.0072 (9) | −0.0023 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0373 (10) | 0.0343 (12) | 0.0499 (13) | −0.0004 (10) | −0.0055 (9) | −0.0011 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0524 (15) | 0.0546 (17) | 0.082 (2) | −0.0116 (13) | 0.0071 (14) | 0.0101 (16) |
| C15 | 0.0668 (17) | 0.0530 (17) | 0.0672 (18) | −0.0063 (14) | −0.0239 (14) | −0.0130 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.369 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.400 (3) |
| O1—C9 | 1.373 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.383 (3) |
| O2—C1 | 1.209 (3) | C8—C11 | 1.509 (3) |
| O3—C7 | 1.361 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| O3—C10 | 1.430 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| O4—C12 | 1.421 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| O4—H4 | 0.840 (10) | C11—C12 | 1.529 (3) |
| O5—C13 | 1.437 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| O5—H5 | 0.846 (10) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.434 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.540 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.332 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—C15 | 1.510 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.434 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.512 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (4) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C9 | 1.401 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.369 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.383 (4) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | ||
| C1—O1—C9 | 122.44 (19) | O3—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C7—O3—C10 | 118.9 (3) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C12—O4—H4 | 109 (3) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C13—O5—H5 | 107 (3) | C8—C11—C12 | 110.6 (2) |
| O2—C1—O1 | 116.4 (2) | C8—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 125.8 (3) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.9 (2) | C8—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.8 (3) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | O4—C12—C11 | 108.45 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.0 (2) | O4—C12—C13 | 109.84 (19) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C11—C12—C13 | 113.30 (19) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 | O4—C12—H12 | 108.4 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 117.6 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 108.4 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 124.4 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 108.4 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 118.0 (2) | O5—C13—C15 | 107.1 (2) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.3 (3) | O5—C13—C14 | 109.6 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.3 | C15—C13—C14 | 110.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.3 | O5—C13—C12 | 109.36 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.6 (3) | C15—C13—C12 | 110.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.2 | C14—C13—C12 | 110.2 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.2 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C6 | 124.5 (2) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C8 | 113.5 (2) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 122.0 (3) | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 116.2 (2) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C11 | 123.4 (2) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C11 | 120.4 (2) | C13—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C8 | 116.90 (19) | C13—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C4 | 119.8 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C4 | 123.3 (2) | C13—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O3—C10—H10A | 109.5 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O3—C10—H10B | 109.5 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | ||
| C9—O1—C1—O2 | 176.4 (2) | C1—O1—C9—C4 | 3.2 (3) |
| C9—O1—C1—C2 | −3.2 (4) | C7—C8—C9—O1 | −178.6 (2) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −177.7 (3) | C11—C8—C9—O1 | 3.6 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 1.9 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.8 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (5) | C11—C8—C9—C4 | −177.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 179.2 (3) | C5—C4—C9—O1 | 179.5 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | 0.5 (4) | C3—C4—C9—O1 | −1.8 (4) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.6 (4) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | 0.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −179.2 (3) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | 178.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.0 (5) | C9—C8—C11—C12 | 101.1 (3) |
| C10—O3—C7—C6 | 0.6 (4) | C7—C8—C11—C12 | −76.7 (3) |
| C10—O3—C7—C8 | −179.7 (2) | C8—C11—C12—O4 | −73.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—O3 | −179.4 (3) | C8—C11—C12—C13 | 164.76 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.0 (5) | O4—C12—C13—O5 | −70.5 (2) |
| O3—C7—C8—C9 | 179.0 (2) | C11—C12—C13—O5 | 51.0 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −1.3 (4) | O4—C12—C13—C15 | 172.2 (2) |
| O3—C7—C8—C11 | −3.1 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C15 | −66.4 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C11 | 176.6 (3) | O4—C12—C13—C14 | 50.0 (2) |
| C1—O1—C9—C8 | −177.4 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 171.5 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O4—H4···O2i | 0.84 (1) | 2.01 (1) | 2.842 (3) | 169 (5) |
| O5—H5···O2ii | 0.85 (1) | 2.12 (2) | 2.936 (3) | 163 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+3, y−1/2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5194).
References
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem.1, 189–191.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Grundon, M. F. & McColl, I. S. (1975). Phytochemistry, 14, 143–150.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). publCIF In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005386/bt5194sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810005386/bt5194Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report