Abstract
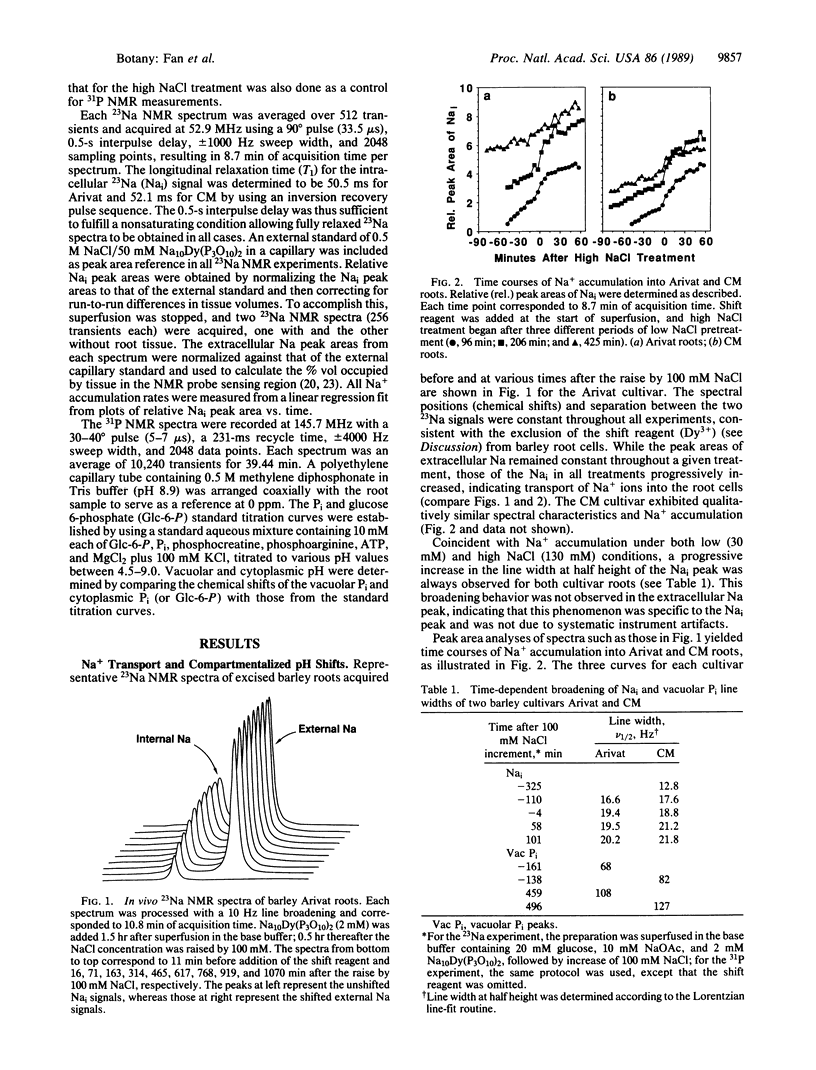
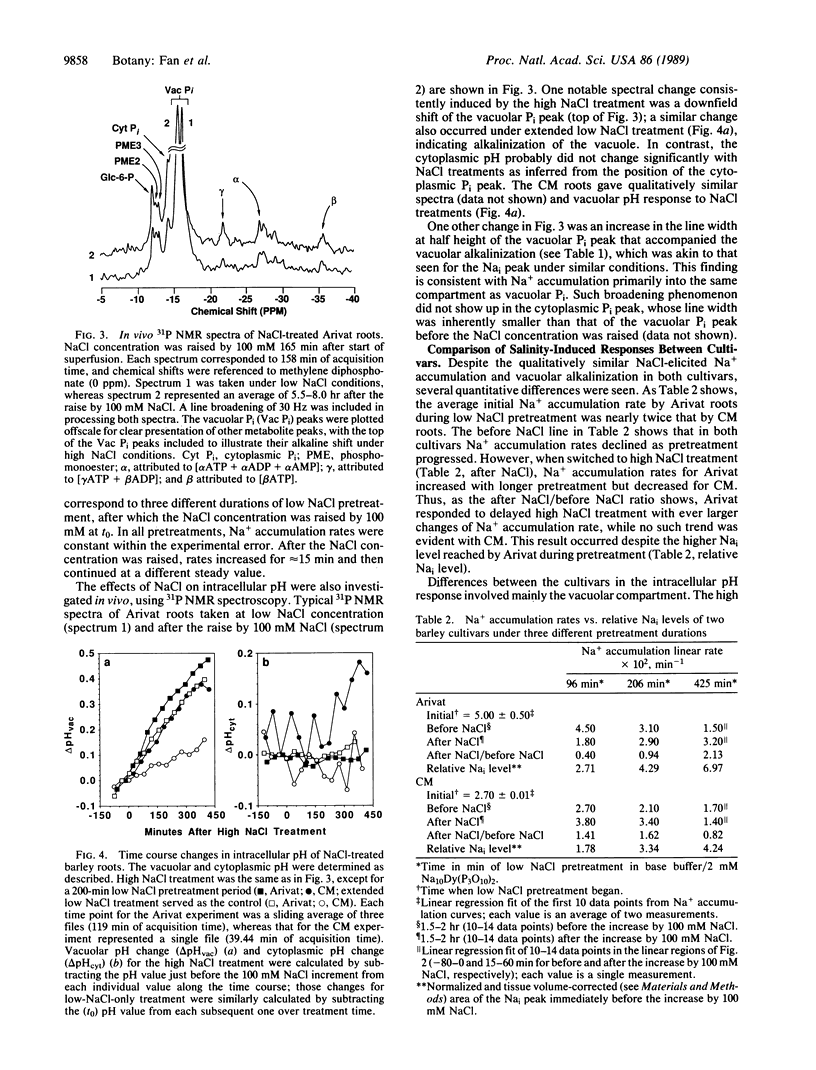
A Na+ uptake-associated vacuolar alkalinization was observed in roots of two barley cultivars (Arivat and the more salt-tolerant California Mariout) by using 23Na and 31P in vivo NMR spectroscopy. A NaCl uptake-associated broadening was also noted for both vacuolar Pi and intracellular Na NMR peaks, consistent with Na+ uptake into the same compartment as the vacuolar Pi. A close coupling of Na+ with H+ transport (presumably the Na+/H+ antiport) in vivo was evidenced by qualitative and quantitative correlations between Na+ accumulation and vacuolar alkalinization for both cultivars. Prolongation of the low NaCl pretreatment (30 mM) increased the activity of the putative antiport in Arivat but reduced it in California Mariout. This putative antiport also showed a dependence on NaCl concentration for California Mariout but not for Arivat. No cytoplasmic acidification accompanied the antiporter activity for either cultivar. The response of adenosine phosphates indicated that ATP utilization exceeded the capacity for ATP synthesis in Arivat, but the two processes seemed balanced in California Mariout. These comparisons provide clues to the role of the tonoplast Na+/H+ antiport and compensatory cytoplasmic adjustments including pH, osmolytes, and energy phosphates in governing the different salt tolerance of the two cultivars.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bental M., Degani H., Avron M. Na-NMR Studies of the Intracellular Sodium Ion Concentration in the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):813–817. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Na/H Antiport in Isolated Tonoplast Vesicles from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):163–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M. Variable Effects of Nitrate on ATP-Dependent Proton Transport by Barley Root Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):526–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Norlyn J. D., Rush D. W., Kingsbury R. W., Kelley D. B., Cunningham G. A., Wrona A. F. Saline culture of crops: a genetic approach. Science. 1980 Oct 24;210(4468):399–404. doi: 10.1126/science.210.4468.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan T. W., Higashi R. M., Lane A. N. An in vivo 1H and 31P NMR investigation of the effect of nitrate on hypoxic metabolism in maize roots. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 1;266(2):592–606. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan T. W., Higashi R. M., Lane A. N. Monitoring of hypoxic metabolism in superfused plant tissues by in vivo 1H NMR. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Dec;251(2):674–687. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90377-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. NaCl Induces a Na/H Antiport in Tonoplast Vesicles from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):231–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. Rapid induction of na/h exchange activity in barley root tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimowicz W. V., Tu S. I., Pfeffer P. E. Energy Facilitated Na Uptake in Excised Corn Roots via P and Na NMR. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):925–928. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guern J., Mathieu Y., Kurkdjian A., Manigault P., Manigault J., Gillet B., Beloeil J. C., Lallemand J. Y. Regulation of Vacuolar pH of Plant Cells: II. A P NMR Study of the Modifications of Vacuolar pH in Isolated Vacuoles Induced by Proton Pumping and Cation/H Exchanges. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):27–36. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. C., Pfeffer P. E., Gerasimowicz W. V. Use of P NMR to Assess Effects of DNP on ATP Levels in Vivo in Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1130–1133. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuhara M., Kuchitsu K., Takeshige K., Tazawa M. Salt Stress-Induced Cytoplasmic Acidification and Vacuolar Alkalization in Nitellopsis obtusa Cells : In VivoP-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):1102–1107. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S., Taiz L. Proton transport in isolated vacuoles from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):104–109. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinoia E., Schramm M. J., Kaiser G., Kaiser W. M., Heber U. Transport of anions in isolated barley vacuoles : I. Permeability to anions and evidence for a cl-uptake system. Plant Physiol. 1986 Apr;80(4):895–901. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matoh T., Ishikawa T., Takahashi E. Collapse of ATP-Induced pH Gradient by Sodium Ions in Microsomal Membrane Vesicles Prepared from Atriplex gmelini Leaves: Possibility of Na/H Antiport. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):180–183. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan P., Girard J. P., Ciapa B. Mechanisms regulating intracellular pH in sea urchin eggs. Dev Biol. 1983 Nov;100(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer P. E., Tu S. I., Gerasimowicz W. V., Cavanaugh J. R. In VivoP NMR Studies of Corn Root Tissue and Its Uptake of Toxic Metals. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):77–84. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Callis J., Wemmer D., Walbot V., Jardetzky O. Mechanisms of cytoplasmic pH regulation in hypoxic maize root tips and its role in survival under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3379–3383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillerud L. O., Heyser J. W. Use of Na-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance To Follow Sodium Uptake and Efflux in NaCl-Adapted and Nonadapted Millet (Panicum miliaceum) Suspensions. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):269–272. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


