Abstract
We demonstrate that blockade of the lymphocyte voltage-gated K+ channel by charybdotoxin (CTX) inhibits lymphocyte mitogenesis. Charybdotoxin blocks conductance with a Ki of 0.3 nM and inhibits mitogen- and antigen-stimulated proliferation with a Ki of 0.5 nM. As opposed to the other blockers of the lymphocyte K+ channel, the inhibition of mitogenesis by CTX can be overcome selectively by exogenous recombinant interleukin 2 (IL-2); endogenous levels of IL-2 in the culture supernatants of stimulated cells are decreased by the presence of CTX. Our results suggest that the voltage-gated K+ channel is either directly or indirectly involved in IL-2 synthesis and/or secretion.
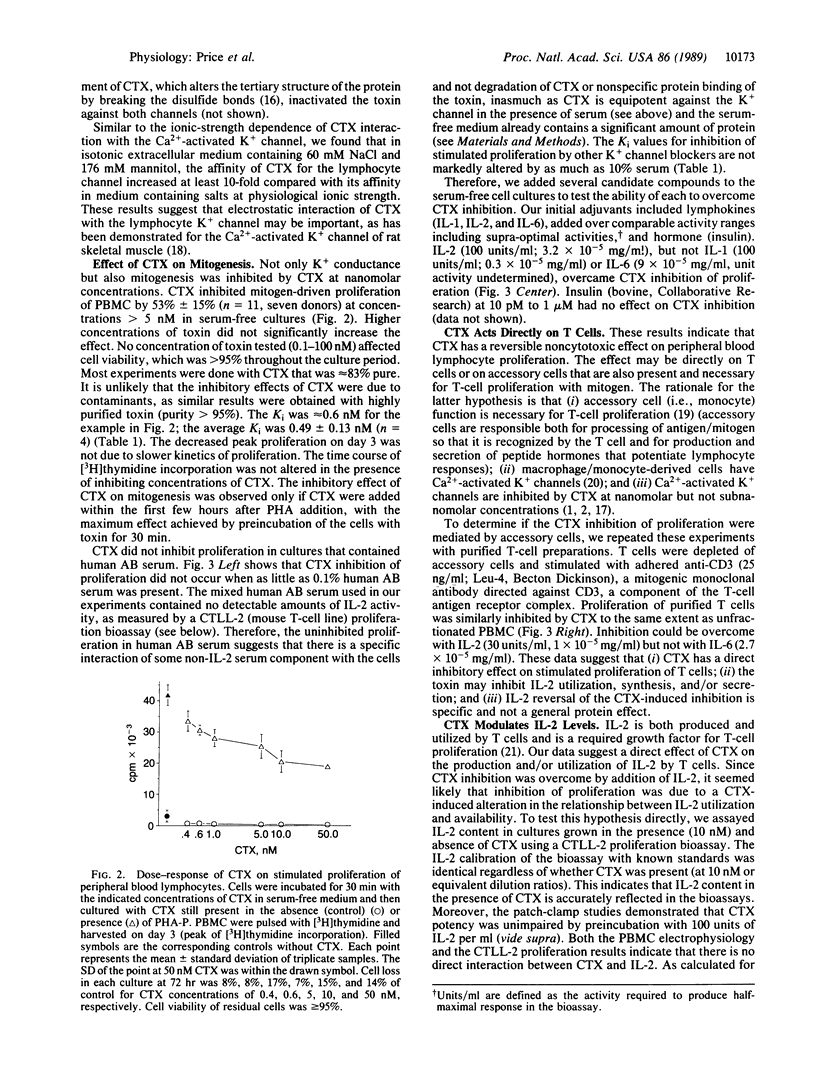
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Cahalan M. D., McLaughlin C., Gupta S. Voltage-gated potassium channels are required for human T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):369–385. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Mitogen induction of ion channels in murine T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Mar;89(3):405–420. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.3.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C. J., Holian A., Holian S. K., Daniele R. P., Wilson D. F. Transmembrane electrical and pH gradients across human erythrocytes and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Apr;99(1):79–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C., Krause D., Lee S. C. Voltage-gated potassium conductance in human T lymphocytes stimulated with phorbol ester. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:405–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Ionic channels in leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Mar;39(3):241–254. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P., Alcover A., Kuno M., Moingeon P., Weyand C. M., Goronzy J., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of T-lymphocytes via either T3-Ti or T11 surface structures opens a voltage-insensitive plasma membrane calcium-permeable channel: requirement for interleukin-2 gene function. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1068–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S. Role of membrane potential in the regulation of lectin-induced calcium uptake. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Dec;121(3):533–539. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Navia M. A., Reuben J. P., Katz G. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification, sequence, and model structure of charybdotoxin, a potent selective inhibitor of calcium-activated potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Leonard W. J. The human interleukin-2 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:69–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Erxleben C. Charybdotoxin selectively blocks small Ca-activated K channels in Aplysia neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):27–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Harris J. E. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the antigen-induced blastogenic response of human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Price M., Prystowsky M. B., Deutsch C. Volume response of quiescent and interleukin 2-stimulated T-lymphocytes to hypotonicity. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):C286–C296. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.2.C286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Sabath D. E., Deutsch C., Prystowsky M. B. Increased voltage-gated potassium conductance during interleukin 2-stimulated proliferation of a mouse helper T lymphocyte clone. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1200–1208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Mechanism of charybdotoxin block of the high-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):335–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Deutsch C. K channels in T lymphocytes: a patch clamp study using monoclonal antibody adhesion. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):468–471. doi: 10.1038/307468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. B., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S., Gelfand E. W. Increase in cytosolic free calcium concentration is an intracellular messenger for the production of interleukin 2 but not for expression of the interleukin 2 receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1640–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modiano J. F., Kelepouris E., Kern J. A., Nowell P. C. Requirement for extracellular calcium or magnesium in mitogen-induced activation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jun;135(3):451–458. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Terhorst C., Cantley L. C., Rosoff P. M. Stimulation of the T3-T cell receptor complex induces a membrane-potential-sensitive calcium influx. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Montecucco C., Hesketh T. R., Tsien R. Y. Lymphocyte membrane potential assessed with fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;595(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands S. B., Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. Charybdotoxin blocks voltage-gated K+ channels in human and murine T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jun;93(6):1061–1074. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.6.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Phillips M., Miller C. Purification of charybdotoxin, a specific inhibitor of the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14607–14613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Heaney L. A., Wallace A. A., Baskin E. P., Stein R. B., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


