Abstract
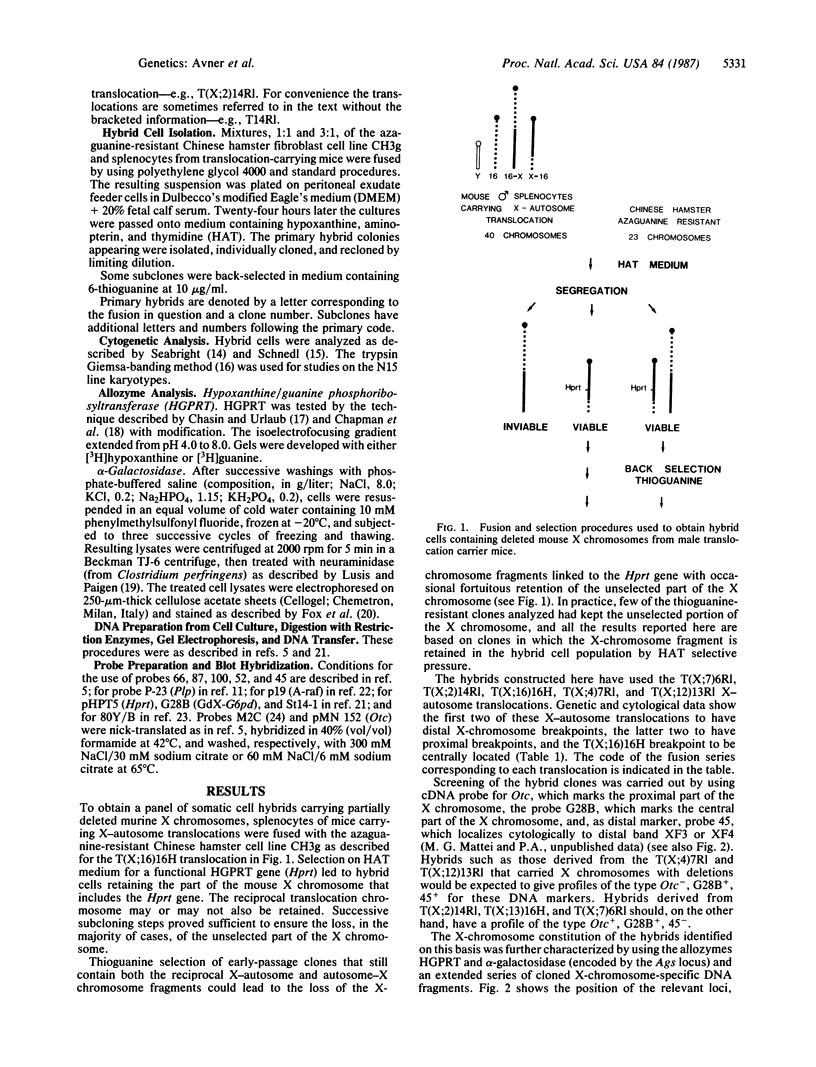
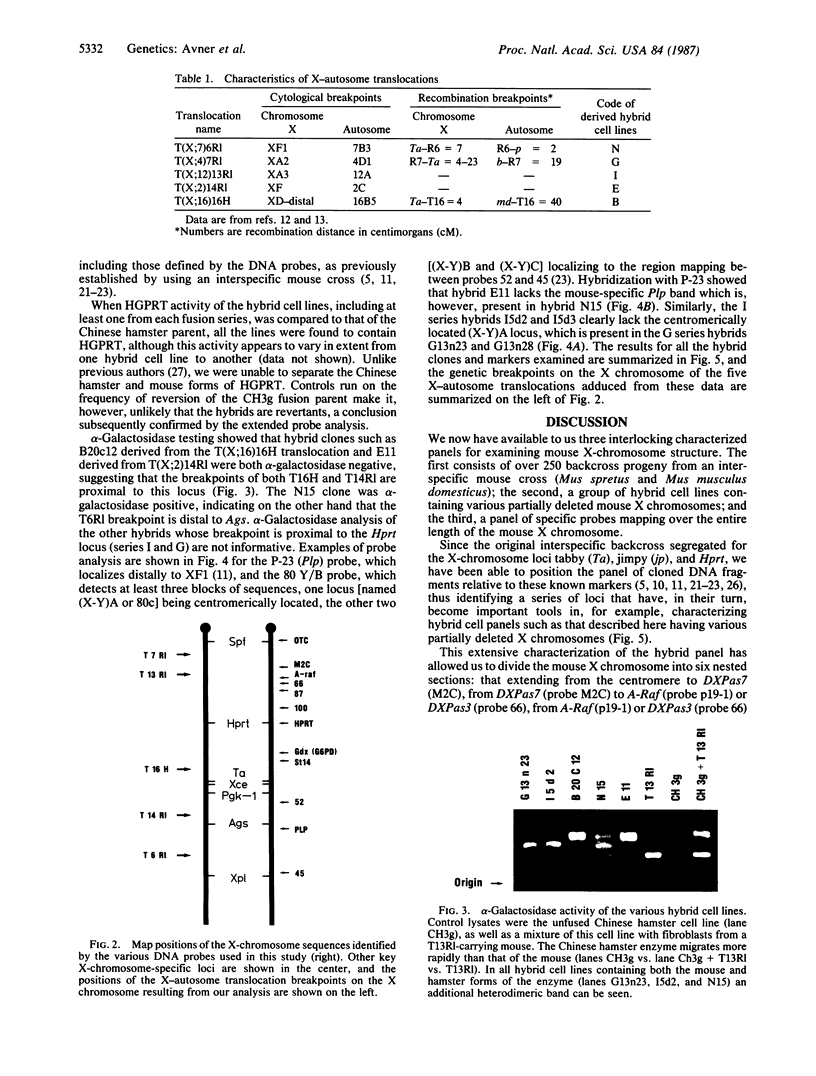
A panel of five hybrid cell lines containing mouse X chromosomes with various deletions has been obtained by fusing splenocytes from male mice carrying one of a series of reciprocal X-autosome translocations with the azaguanine-resistant Chinese hamster cell line CH3g. These hybrids have been extensively characterized by using the allozymes hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (encoded by the Hprt locus) and alpha-galactosidase (Ags) and a series of 11 X-chromosome-specific DNA probes whose localization had been previously established by linkage studies. Such studies have established the genetic breakpoints of the T(X;12)13Rl and T(X;2)14Rl X-autosome translocations on the X chromosome and provided additional information as to the X-chromosome genetic breakpoints of the T(X;16)16H, T(X;4)7Rl, and T(X;7)6Rl translocations. The data establish clearly that both the T(X;4)7Rl and T(X;12)13Rl X-chromosome breakpoints are proximal to Hprt, the breakpoint of the former being more centromeric, lying as it does in the 9-centimorgan interval between the ornithine transcarbamoylase (Otc) and DXPas7 (M2C) loci. Similarly, it is now clear that the T(X;16)16H X-autosome translocation breakpoint lies distal to the DXPas8 (St14-1) locus, narrowing the X-chromosome breakpoint down to a region flanked proximally by this marker and representing, as expected from previous data, the distal quarter of the Hprt-Ta subchromosomal span. These five hybrid cell lines provide, with the previously characterized EBS4 hybrid cell line, a nested series of seven mapping intervals distributed along the length of the mouse X chromosome. Their characterization not only allows further correlation of the genetic and cytological X-chromosome maps but also should permit the rapid identification of DNA probes specific for particular regions of the mouse X chromosome.
Full text
PDF


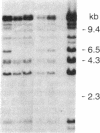
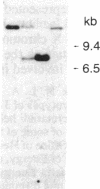
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L. C., Arnaud D., Cambrou J., Guenet J. L., Avner P. R. Mapping of the mouse X chromosome using random genomic probes and an interspecific mouse cross. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3695–3700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Amar L., Arnaud D., Hanauer A., Cambrou J. Detailed ordering of markers localizing to the Xq26-Xqter region of the human X chromosome by the use of an interspecific Mus spretus mouse cross. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1629–1633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Bućan M., Arnaud D., Lehrach H., Rapp U. A-raf oncogene localizes on mouse X chromosome to region some 10-17 centimorgans proximal to hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):267–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01535208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron B., Metezeau P., Kelly F., Bernheim A., Berger R., Guenet J. L., Goldberg M. E. Flow cytometry isolation and improved visualization of sorted mouse chromosomes. Purification of chromosomes X and ISO-1 from cell lines with Robertsonian translocations. Exp Cell Res. 1984 May;152(1):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bućan M., Yang-Feng T., Colberg-Poley A. M., Wolgemuth D. J., Guenet J. L., Francke U., Lehrach H. Genetic and cytogenetic localisation of the homeo box containing genes on mouse chromosome 6 and human chromosome 7. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2899–2905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M., Kratzer P. G., Quarantillo B. A. Electrophoretic variation for X chromosome-linked hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT) in wild-derived mice. Genetics. 1983 Apr;103(4):785–795. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A., Urlaub G. Mutant alleles for hypoxanthine phosphoriboxyltransferase: codominant expression, complementation, and segregation in hybrid Chinese hamster cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Sep;2(5):453–467. doi: 10.1007/BF01542725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautigny A., Mattei M. G., Morello D., Alliel P. M., Pham-Dinh D., Amar L., Arnaud D., Simon D., Mattei J. F., Guenet J. L. The structural gene coding for myelin-associated proteolipid protein is mutated in jimpy mice. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):867–869. doi: 10.1038/321867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Kunkel L. M., Lojewski A., Orkin S. H., Eisenhard M., Sahar E., Travis B., Latt S. A. Isolation of mouse x-chromosome specific DNA from an x-enriched lambda phage library derived from flow sorted chromosomes. Cytometry. 1982 Mar;2(5):282–286. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. M., Cavanna J. S., Brown S. D. Microdissection and microcloning of the mouse X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5846–5849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. F., DuToit D. L., Warnich L., Retief A. E. Regional localization of alpha-galactosidase (GLA) to Xpter----q22, hexosaminidase B (HEXB) to 5q13----qter, and arylsulfatase B (ARSB) to 5pter----q13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(1):45–49. doi: 10.1159/000132028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Taggart R. T. Comparative gene mapping: order of loci on the X chromosome is different in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3595–3599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey N. K., Sakaguchi A. Y., Lalley P. A., Quinto C., MacDonald R. J., Craik C., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J., Naylor S. L. Chromosomal assignments of genes for trypsin, chymotrypsin B, and elastase in mouse. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jul;10(4):377–383. doi: 10.1007/BF01535633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Francke U., Minna J. D. Homologous genes for enolase, phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, phosphoglucomutase, and adenylate kinase are syntenic on mouse chromosome 4 and human chromosome 1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2382–2386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Paigen K. Properties of mouse alpha-galactosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Arveiler B., Camerino G., Hanauer A., Heilig R., Koenig M., Oberlé I. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome: linkage analysis of the q26-q28 region that includes the fragile X locus and isolation of expressed sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):195–203. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S., Stock A. D., Lusby A. A combination of sister chromatid differential staining and giemsa banding. Experientia. 1975 Aug 15;31(8):916–918. doi: 10.1007/BF02358850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Barton P., Minty A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. Investigation of genetic linkage between myosin and actin genes using an interspecific mouse back-cross. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):181–183. doi: 10.1038/314181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhme D., Fox H., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Edström J. E., Mains P., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Molecular clones of the mouse t complex derived from microdissected metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnedl W. Analysis of the human karyotype using a reassociation technique. Chromosoma. 1971;34(4):448–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00326316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]