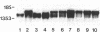Abstract
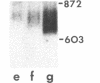
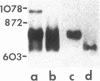
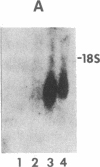
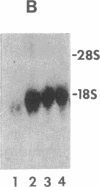
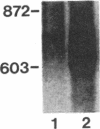
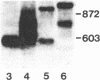
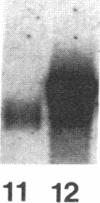
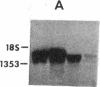
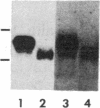
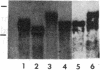
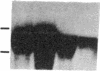
Spermatogenic cells have been previously shown to be a major site of testicular proenkephalin gene expression. Using RNA gel-blot analysis of purified mouse and hamster germ cells and of testes from prepuberal and germ cell-deficient mutant mice, we now have demonstrated that, in addition to its previously described expression by somatic (Leydig) cells, the gene for a second opioid peptide precursor, pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), is also expressed by spermatogenic cells. Of particular significance is the finding that the RNAs for proenkephalin and POMC are differentially regulated during spermatogenesis. Two forms of POMC RNA were detected in mouse testis, a larger component 675- to 750-nucleotides (nt) in size common to somatic and spermatogenic cells and a smaller 625-nt RNA found only in pachytene spermatocytes. Two distinct, cell-specific proenkephalin RNAs were also shown to be present in mouse testis: a 1700-nt transcript previously shown to be expressed by spermatogenic cells and a 1450-nt form associated with somatic cells. These data suggest that proenkephalin- and POMC-derived peptides are produced by both somatic cells and germ cells in the testis and in germ cells these two families of opioid peptides may function at different stages of spermatogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergh A. Paracrine regulation of Leydig cells by the seminiferous tubules. Int J Androl. 1983 Feb;6(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1983.tb00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Dionne F. T., Roberts J. L. Regulation of the pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA levels in rat pituitary by dopaminergic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Mather J. P., Morris P. L., Bardin C. W. Expression of pro-opiomelanocortin-like gene in the testis and epididymis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5672–5675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng M. C., Clements J. A., Smith A. I., Lolait S. J., Funder J. W. N-acetyl endorphin in rat spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):832–835. doi: 10.1172/JCI111779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb C., Nolan C. Genetic control of steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in inbred mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;438:519–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb38322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Kleene K. C., Hecht N. B. Haploid expression of a mouse testis alpha-tubulin gene. Science. 1984 Apr 6;224(4644):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.6701535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Cox B., Quinn B., Civelli O., Herbert E. Expression of the prodynorphin gene in male and female mammalian reproductive tissues. Endocrinology. 1987 Feb;120(2):707–713. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-2-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri A., Tsai-Morris C. H., Luna S., Fraioli F., Dufau M. L. Opiate receptors are present in the rat testis. Identification and localization in Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2544–2546. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Klagsbrun M., Bellvé A. R. Mitogenic polypeptide of the mammalian seminiferous epithelium: biochemical characterization and partial purification. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1435–1443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerendai I., Shaha C., Gunsalus G. L., Bardin C. W. The effects of opioid receptor antagonists suggest that testicular opiates regulate Sertoli and Leydig cell function in the neonatal rat. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):2039–2044. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-2039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizang-Ginsberg E., Wolgemuth D. J. Expression of the proopiomelanocortin gene is developmentally regulated and affected by germ cells in the male mouse reproductive system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizang-Ginsberg E., Wolgemuth D. J. Localization of mRNAs in mouse testes by in situ hybridization: distribution of alpha-tubulin and developmental stage specificity of pro-opiomelanocortin transcripts. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90484-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht N. B., Bower P. A., Waters S. H., Yelick P. C., Distel R. J. Evidence for haploid expression of mouse testicular genes. Exp Cell Res. 1986 May;164(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90465-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howells R. D., Kilpatrick D. L., Bhatt R., Monahan J. J., Poonian M., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of rat preproenkephalin cDNA: sensitive probe for studying transcriptional changes in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7651–7655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Howells R. D., Noe M., Bailey L. C., Udenfriend S. Expression of preproenkephalin-like mRNA and its peptide products in mammalian testis and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7467–7469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Millette C. F. Expression of proenkephalin messenger RNA by mouse spermatogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5015–5018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Rosenthal J. L. The proenkephalin gene is widely expressed within the male and female reproductive systems of the rat and hamster. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):370–374. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Translational regulation and deadenylation of a protamine mRNA during spermiogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1984 Sep;105(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather J. P., Gunsalus G. L., Musto N. A., Cheng C. Y., Parvinen M., Wright W., Pérez-Infante V., Margioris A., Liotta A., Becker R. The hormonal and cellular control of Sertoli cell secretion. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1A):41–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Longtin J., Brock W. A., Grimes S. R., Jr, Mace M. L. Purification of rat spermatogenic cells and preliminary biochemical analysis of these cells. Biol Reprod. 1981 Dec;25(5):1065–1077. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Schachter B. S., Herman A. B., Durgerian S., Krieger D. T. Characterization and localization of proopiomelanocortin messenger RNA in the adult rat testis. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):632–634. doi: 10.1126/science.6740329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Wolgemuth D. J. Haploid expression of a unique c-abl transcript in the mouse male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1791–1794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzén E. M. Chemical messengers between Sertoli cells and neighbouring cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1B):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Tansey T. R., Ruderman J. V. Sequence-specific adenylations and deadenylations accompany changes in the translation of maternal messenger RNA after fertilization of Spisula oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):309–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. R., Toth L. E., Patel M. D., D'Eustachio P., Nguyen-Huu M. C. A mouse homeo box gene is expressed in spermatocytes and embryos. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):663–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3726554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe R. M. Intratesticular factors controlling testicular function. Biol Reprod. 1984 Feb;30(1):29–49. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod30.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Fritz I. B. Testicular peritubular cells secrete a protein under androgen control that modulates Sertoli cell functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):114–118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L., Gold B., Hecht N. B. Gene expression during mammalian spermatogenesis. I. Evidence for stage-specific synthesis of polypeptides in vivo. Biol Reprod. 1983 Mar;28(2):483–496. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod28.2.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vournakis J. N., Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C. Electrophoretic patterns of deadenylylated chorion and globin mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters S. H., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Mouse testes contain two size classes of actin mRNA that are differentially expressed during spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1649–1654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Engelmyer E., Duggal R. N., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Mutter G. L., Ponzetto C., Viviano C., Zakeri Z. F. Isolation of a mouse cDNA coding for a developmentally regulated, testis-specific transcript containing homeo box homology. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1229–1235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]