Abstract
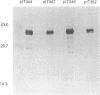
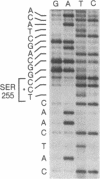
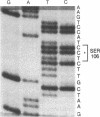
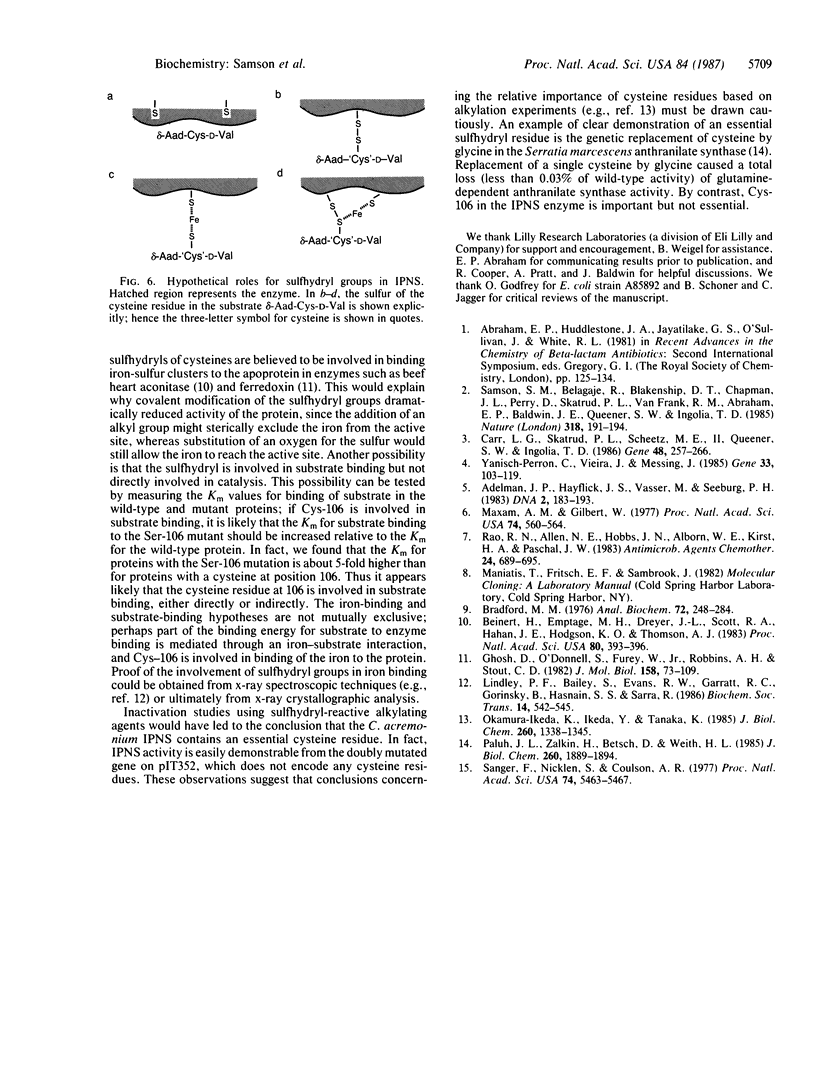
The predicted amino acid sequences of isopenicillin N synthetase from both Cephalosporium acremonium and Penicillium chrysogenum have two cysteine residues in analogous positions (Cys-106 and Cys-255 in the C. acremonium numbering). To examine the role of these cysteine residues in the activity of the C. acremonium enzyme, we used site-directed in vitro mutagenesis to change these cysteine residues to serine residues. Mutation of Cys-255 reduces specific activity approximately equal to 50%, whereas mutation of Cys-106 or mutation of both Cys-106 and Cys-255 reduces specific activity about 97%. This suggests that the cysteines are important but not essential for IPNS activity. Alkylation of IPNS also almost completely inactivated the enzyme, but residual activity could have been due to incomplete alkylation. Atomic substitution via genetic manipulation in this case is a more accurate means of assessing the role of sulfhydryl moieties in enzyme activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Hayflick J. S., Vasser M., Seeburg P. H. In vitro deletional mutagenesis for bacterial production of the 20,000-dalton form of human pituitary growth hormone. DNA. 1983;2(3):183–193. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinert H., Emptage M. H., Dreyer J. L., Scott R. A., Hahn J. E., Hodgson K. O., Thomson A. J. Iron-sulfur stoichiometry and structure of iron-sulfur clusters in three-iron proteins: evidence for [3Fe-4S] clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):393–396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr L. G., Skatrud P. L., Scheetz M. E., 2nd, Queener S. W., Ingolia T. D. Cloning and expression of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Penicillium chrysogenum. Gene. 1986;48(2-3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D., O'Donnell S., Furey W., Jr, Robbins A. H., Stout C. D. Iron-sulfur clusters and protein structure of Azotobacter ferredoxin at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):73–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley P. F., Bailey S., Evans R. W., Garratt R. C., Gorinsky B., Hasnain S. S., Sarra R. Transferrin: a study of the iron-binding sites using extended X-ray absorption fine structure and anomalous dispersion techniques. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Jun;14(3):542–545. doi: 10.1042/bst0140542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura-Ikeda K., Ikeda Y., Tanaka K. An essential cysteine residue located in the vicinity of the FAD-binding site in short-chain, medium-chain, and long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1338–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paluh J. L., Zalkin H., Betsch D., Weith H. L. Study of anthranilate synthase function by replacement of cysteine 84 using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1889–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Allen N. E., Hobbs J. N., Jr, Alborn W. E., Jr, Kirst H. A., Paschal J. W. Genetic and enzymatic basis of hygromycin B resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):689–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
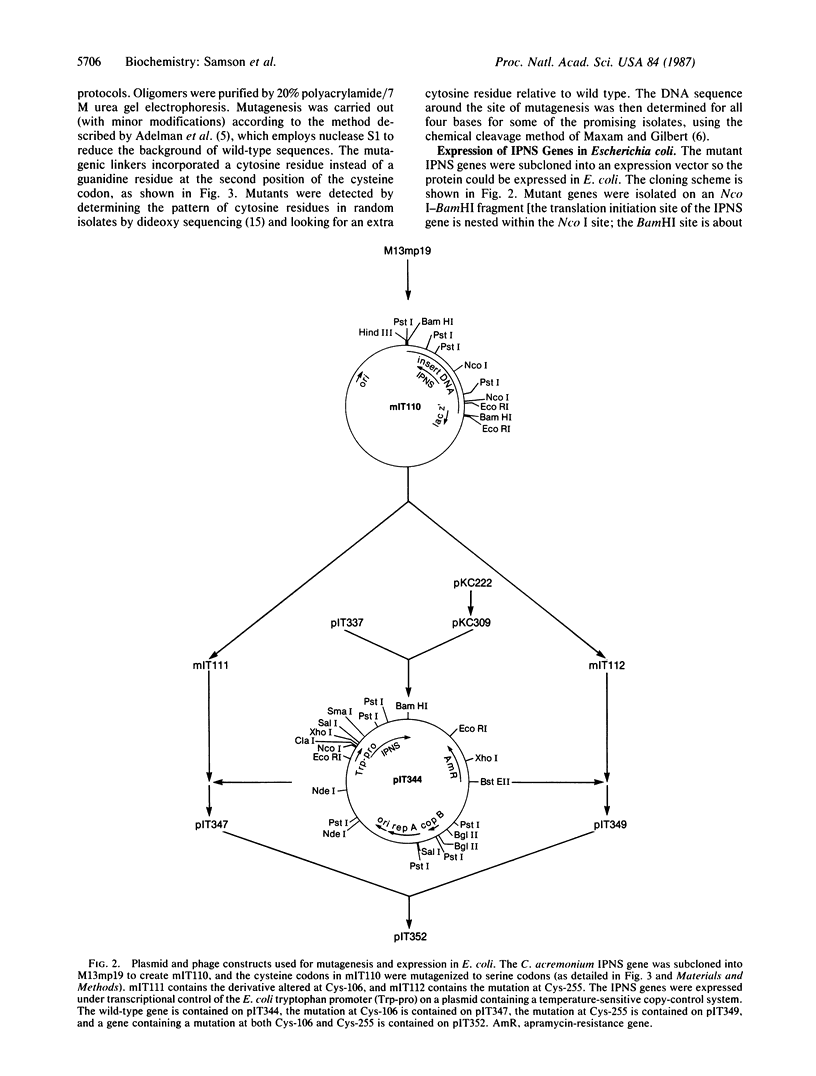
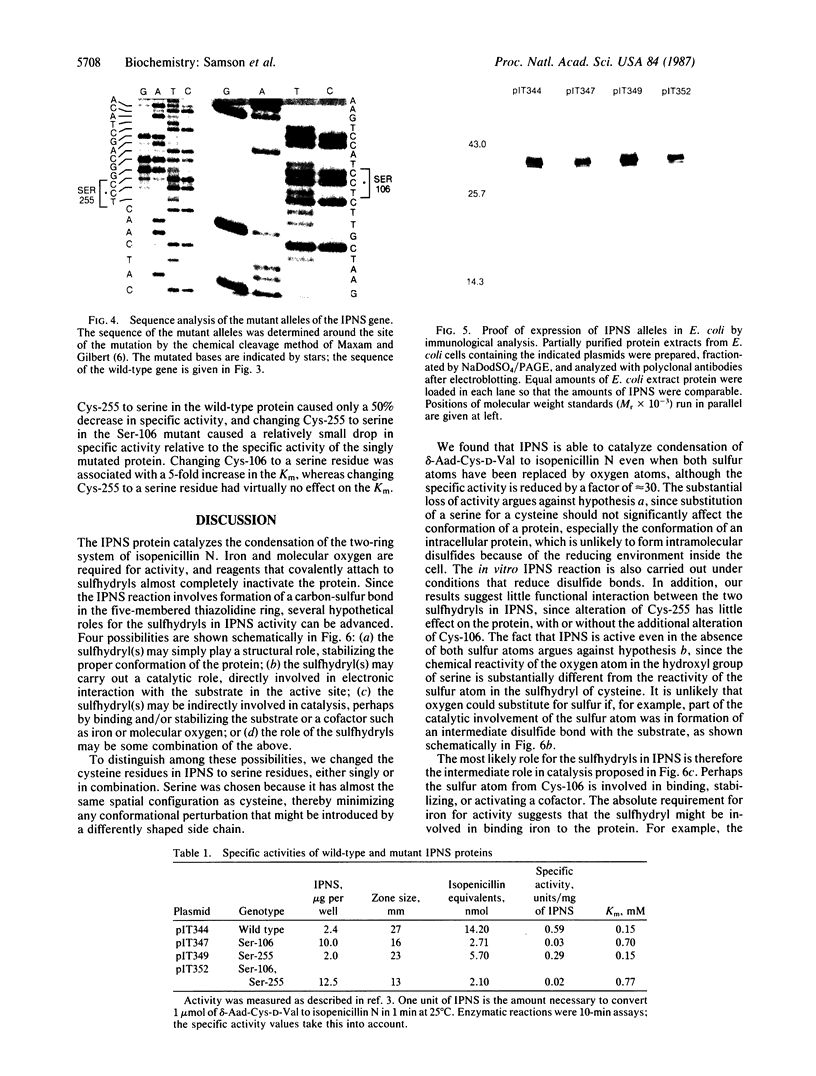
- Samson S. M., Belagaje R., Blankenship D. T., Chapman J. L., Perry D., Skatrud P. L., VanFrank R. M., Abraham E. P., Baldwin J. E., Queener S. W. Isolation, sequence determination and expression in Escherichia coli of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Cephalosporium acremonium. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):191–194. doi: 10.1038/318191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]