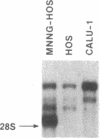
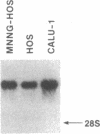
Abstract
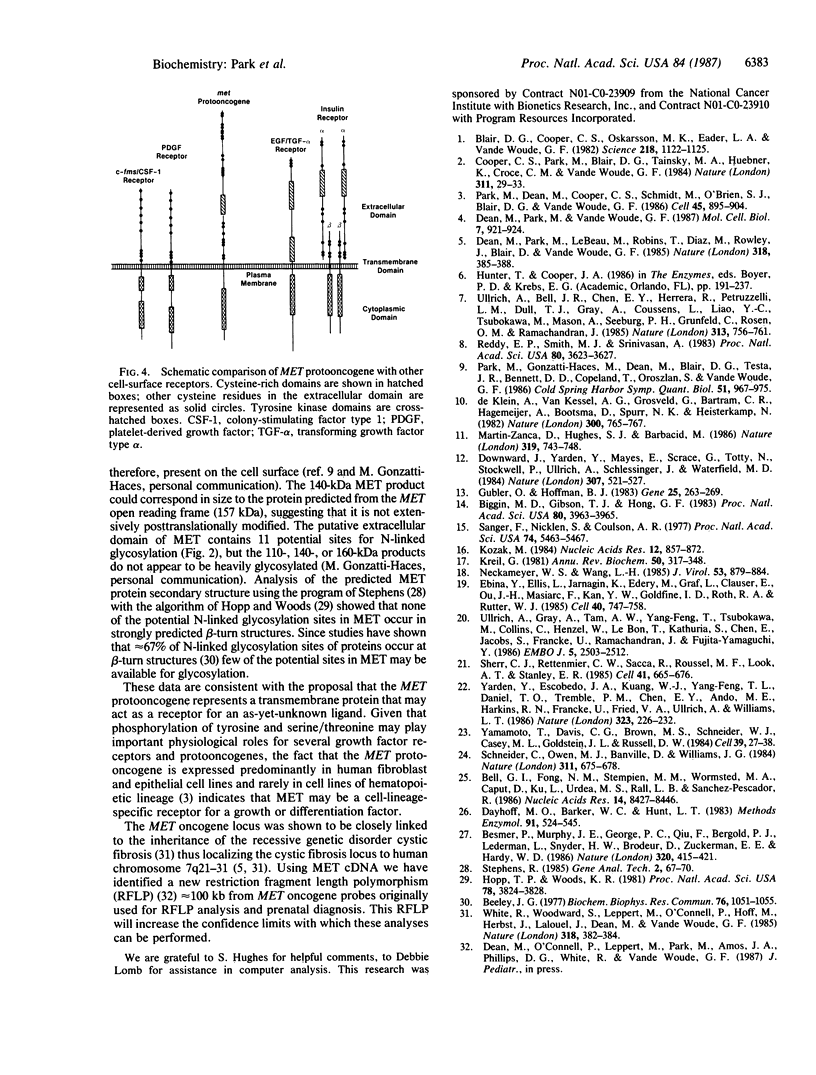
We isolated overlapping cDNA clones corresponding to the major MET protooncogene transcript. The cDNA nucleotide sequence contained an open reading frame of 1408 amino acids with features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth factor receptors. These features include a putative 24-amino acid signal peptide and a candidate, hybrophobic, membrane-spanning segment of 23 amino acids, which defines an extracellular domain of 926 amino acids that could serve as a ligand-binding domain. A putative intracellular domain 435 amino acids long shows high homology with the SRC family of tyrosine kinases and within the kinase domain is most homologous with the human insulin receptor (44%) and v-abl (41%). Despite these similarities, however, we found no apparent sequence homology to other growth factor receptors in the putative ligand-binding domain. We conclude from these results that the MET protooncogene is a cell-surface receptor for an as-yet-unknown ligand.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beeley J. G. Peptide chain conformation and the glycosylation of glycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90962-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Fong N. M., Stempien M. M., Wormsted M. A., Caput D., Ku L. L., Urdea M. S., Rall L. B., Sanchez-Pescador R. Human epidermal growth factor precursor: cDNA sequence, expression in vitro and gene organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8427–8446. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Murphy J. E., George P. C., Qiu F. H., Bergold P. J., Lederman L., Snyder H. W., Jr, Brodeur D., Zuckerman E. E., Hardy W. D. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):415–421. doi: 10.1038/320415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Cooper C. S., Oskarsson M. K., Eader L. A., Vande Woude G. F. New method for detecting cellular transforming genes. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1122–1125. doi: 10.1126/science.6293052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. S., Park M., Blair D. G., Tainsky M. A., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Vande Woude G. F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):29–33. doi: 10.1038/311029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Park M., Le Beau M. M., Robins T. S., Diaz M. O., Rowley J. D., Blair D. G., Vande Woude G. F. The human met oncogene is related to the tyrosine kinase oncogenes. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):385–388. doi: 10.1038/318385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Park M., Vande Woude G. F. Characterization of the rearranged tpr-met oncogene breakpoint. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):921–924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Transfer of proteins across membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:317–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Nucleotide sequence of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming gene with other members of the tyrosine protein kinase oncogene family. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):879–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.879-884.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Cooper C. S., Schmidt M., O'Brien S. J., Blair D. G., Vande Woude G. F. Mechanism of met oncogene activation. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90564-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Gonzatti-Haces M., Dean M., Blair D. G., Testa J. R., Bennett D. D., Copeland T., Oroszlan S., Vande Woude G. The met oncogene: a new member of the tyrosine kinase family and a marker for cystic fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):967–975. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Owen M. J., Banville D., Williams J. G. Primary structure of human transferrin receptor deduced from the mRNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):675–678. doi: 10.1038/311675b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Woodward S., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Hoff M., Herbst J., Lalouel J. M., Dean M., Vande Woude G. A closely linked genetic marker for cystic fibrosis. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):382–384. doi: 10.1038/318382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klein A., van Kessel A. G., Grosveld G., Bartram C. R., Hagemeijer A., Bootsma D., Spurr N. K., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Stephenson J. R. A cellular oncogene is translocated to the Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):765–767. doi: 10.1038/300765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]