Abstract
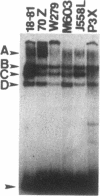
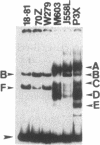
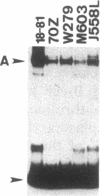
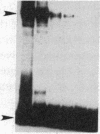
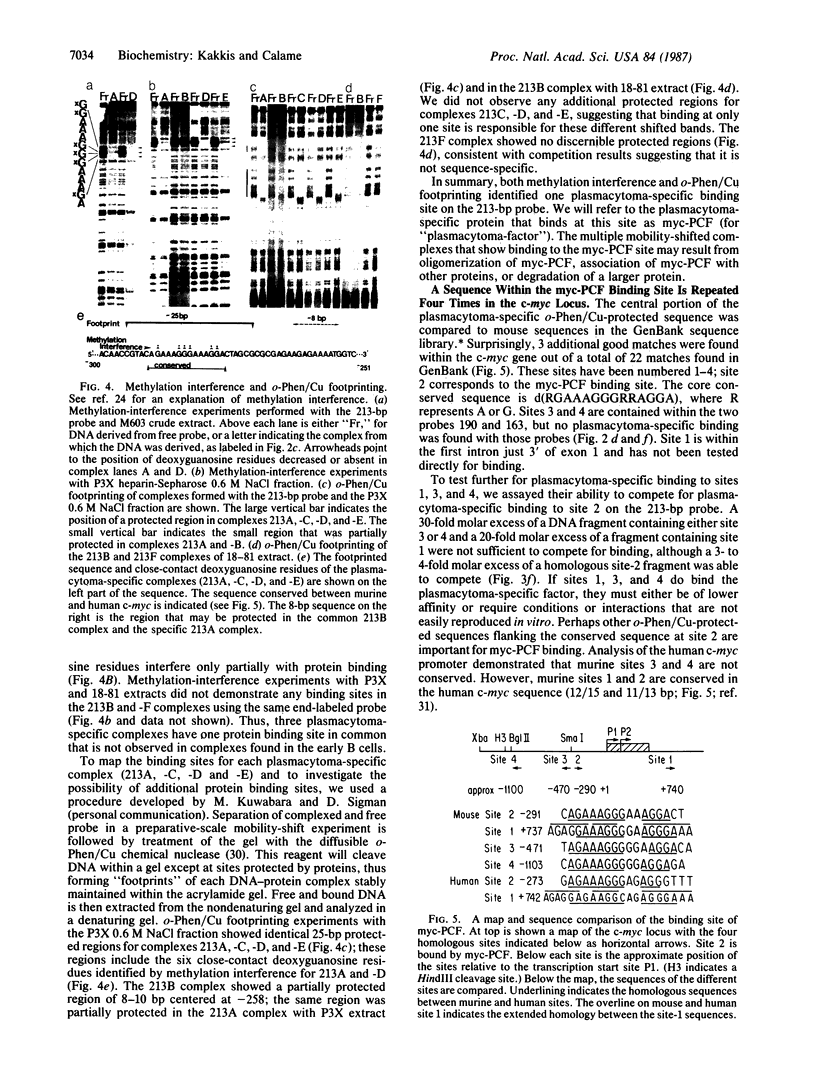
We used an electrophoretic mobility-shift assay to study proteins that bind to sequences in the 5' flanking region of the murine c-myc gene. By comparing the DNA-protein complexes formed with extracts from cells representing earlier stages of B-cell development with those from plasmacytomas, we identified a plasmacytoma-specific protein that binds to a region within the c-myc promoter. Five other regions of this promoter show extensive sequence-specific binding, but the binding is not clearly B-cell stage-specific. Methylation-interference and o-phenanthroline/copper-protection experiments identified a single plasmacytoma-specific protein binding site 290 base pairs 5' of the transcription start site P1. Homologues of a core sequence, d(AGAAAGGGAAAGGA), within the 25-base-pair binding site are found at three additional sites in the murine c-myc locus. The plasmacytoma-specific occurrence of this protein suggests that it may play a role in the transcriptional repression of the normal c-myc gene observed in plasmacytomas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Mitchell J., Bernard O., Cory S. Transcriptionally active DNA region that rearranges frequently in murine lymphoid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6966–6970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. M., Harris A. W., Pinkert C. A., Corcoran L. M., Alexander W. S., Cory S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):533–538. doi: 10.1038/318533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabi F., Neuberger M. S. Chromosome translocation activates heterogeneously initiated, bipolar transcription of a mouse c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):667–674. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sinn E., Reed R. R., Leder P. Trans-acting elements modulate expression of the human c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7918–7922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Cory S., Adams J. M. Transposition of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer to the myc oncogene in a murine plasmacytoma. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S. Activation of cellular oncogenes in hemopoietic cells by chromosome translocation. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:189–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Gerondakis S., Adams J. M. Interchromosomal recombination of the cellular oncogene c-myc with the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is a reciprocal exchange. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):697–703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Erikson J., Huebner K., Nishikura K. Coexpression of translocated and normal c-myc oncogenes in hybrids between Daudi and lymphoblastoid cells. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1235–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.3856319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrlander P. D., Piechaczyk M., Marcu K. B. Chromatin structure of the murine c-myc locus: implications for the regulation of normal and chromosomally translocated genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3195–3202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feo S., ar-Rushdi A., Huebner K., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Clarkson B., Croce C. M. Suppression of the normal mouse c-myc oncogene in human lymphoma cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):493–495. doi: 10.1038/313493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkis E., Prehn J., Calame K. An active chromatin structure acquired by translocated c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1357–1361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. Fibroblast lines expressing activated c-myc oncogenes are tumorigenic in nude mice and syngeneic animals. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in mouse plasmacytomas: similar RNA levels in tumor and proliferating normal cells. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Skoultchi A. I. Expression of c-myc changes during differentiation of mouse erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):592–594. doi: 10.1038/310592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp M., Schilling R., Wiest S., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W. Target sequences for cis-acting regulation within the dual promoter of the human c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K. Sequences involved in accurate and efficient transcription of human c-myc genes microinjected into frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4093–4098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci P. G., Knowles D. M., 2nd, Magrath I., Dalla-Favera R. Chromosomal breakpoints and structural alterations of the c-myc locus differ in endemic and sporadic forms of Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2984–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Orth K., Calame K. L. Binding in vitro of multiple cellular proteins to immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4168–4178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehn J., Mercola M., Calame K. Translocation affects normal c-myc promoter usage and activates fifteen cryptic c-myc transcription starts in plasmacytoma M603. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8987–9007. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J. Deregulated expression of c-myc by murine erythroleukaemia cells prevents differentiation. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):848–850. doi: 10.1038/322848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Yang J. Q., Marcu K. B. A negative transcriptional control element located upstream of the murine c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Yarden A., Zipori D., Kimchi A. Autocrine beta-related interferon controls c-myc suppression and growth arrest during hematopoietic cell differentiation. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90857-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Watt R., Marcu K. B. Translocation, breakage and truncated transcripts of c-myc oncogene in murine plasmacytomas. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):401–406. doi: 10.1038/303401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studzinski G. P., Brelvi Z. S., Feldman S. C., Watt R. A. Participation of c-myc protein in DNA synthesis of human cells. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3532322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Q., Remmers E. F., Marcu K. B. The first exon of the c-myc proto-oncogene contains a novel positive control element. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3553–3562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]