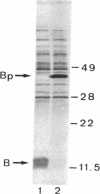
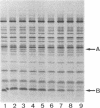
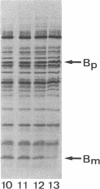
Abstract
The secretion of enterotoxin by Vibrio cholerae is punctuated by the transient entry of the toxin subunits into the periplasm. In this paper, we show that the subunits oligomerize into an assembled holotoxin within the periplasm prior to their secretion across the outer membrane. The rate of toxin assembly was studied by pulse-labeling cells with [35S]-methionine and then monitoring the turnover of radiolabeled subunits as they assembled within the periplasm. The subunits entered the periplasm as monomers and assembled into oligomers with a half-time of approximately 1 min. Since assembly was a rapid event compared to the rate of toxin efflux from the periplasm, which had a half-time of approximately 13 min, we conclude that all of the subunits that pass through the periplasm assemble before they traverse the outer membrane. The average concentration of subunit monomers and assembled holotoxin within the periplasm was calculated to be approximately 20 and approximately 260 micrograms/ml, respectively. This indicates that the periplasm is a suitably concentrated milieu where spontaneous toxin assembly can occur. Our findings suggest that protein movement across bacterial outer membranes, in apparent contrast to export across other biological membranes, involves translocation of polypeptides that have already folded into tertiary and even quaternary conformations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andro T., Chambost J. P., Kotoujansky A., Cattaneo J., Bertheau Y., Barras F., Van Gijsegem F., Coleno A. Mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi defective in secretion of pectinase and cellulase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1199-1203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Baty D., Howard S. P., Verheij H. M., Lazdunski C. Lipoprotein nature of the colicin A lysis protein: effect of amino acid substitutions at the site of modification and processing. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2187–2194. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2187-2194.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S. Conformity between heat-labile toxin genes from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.647-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., McCammon M. T., Vassarotti A. Targeting proteins into mitochondria. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Jun;50(2):166–178. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.2.166-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schatz G. Binding of a specific ligand inhibits import of a purified precursor protein into mitochondria. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):228–232. doi: 10.1038/322228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Clements J. D., Robertson D. C., Finkelstein R. A. Subunit number and arrangement in Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):677–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.677-682.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. The carboxy-terminal region of haemolysin 2001 is required for secretion of the toxin from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02428042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst T. R., Holmgren J. Transient entry of enterotoxin subunits into the periplasm occurs during their secretion from Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1037–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1037-1045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Actions of cholera toxin and the prevention and treatment of cholera. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):413–417. doi: 10.1038/292413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Vinal A. C., Dallas W. S. Nucleotide sequence comparison between heat-labile toxin B-subunit cistrons from Escherichia coli of human and porcine origin. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):73–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.73-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Richardson S. H. Activation of adenylate cyclase by heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity similar to that of choleragen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):281–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI109127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill R. J., Ivins B. E., Holmes R. K. Synthesis and secretion of the plasmid-coded heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli in Vibrio cholerae. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):289–291. doi: 10.1126/science.6857285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Hirst T. R., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J., Randall L. Synthesis of a precursor to the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.325-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlner J., Halter R., Beyreuther K., Meyer T. F. Gene structure and extracellular secretion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae IgA protease. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):458–462. doi: 10.1038/325458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., d'Azzo A., Neufeld E. F. Association of alpha- and beta-subunits during the biosynthesis of beta-hexosaminidase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3350–3354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Schwartz M. Colicin E2 release: lysis, leakage or secretion? Possible role of a phospholipase. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2393–2397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Correlation of competence for export with lack of tertiary structure of the mature species: a study in vivo of maltose-binding protein in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Kornberg R. D. Cell biology. An unfolding story of protein translocation. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):209–210. doi: 10.1038/322209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Maher P. A., Yaffe M. P. On the translocation of proteins across membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1015–1019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wikström M., Lindblad M., Holmgren J. Monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins: neutralising activity and differentiation of human and porcine LTs and cholera toxin. Med Biol. 1986;64(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurn K. K., Chatterjee A. K. Single-site chromosomal Tn5 insertions affect the export of pectolytic and cellulolytic enzymes in Erwinia chrysanthemi EC16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):894–898. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.894-898.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Båga M., Göransson M., Lindberg F. P., Lund B., Norgren M., Normark S. Genes determining adhesin formation in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:163–178. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W., Vogel M., Goebel W. Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):200–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.200-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Gojobori T., Yokota T. Evolutionary origin of pathogenic determinants in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae O1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1352–1357. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1352-1357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]