Abstract
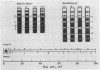
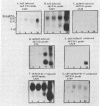
Revertants have been isolated from Ad3hr15, a mutant of human adenovirus type 3 that carries a defective E1A promoter. Transcription of these revertant E1A genes is restored--from nil for Ad3hr15 mutant to levels exceeding that of the wild-type virus. The mutant Ad3hr15 virus and the revertants all have an aberrant E1A promoter that contains two short tandem duplications of viral DNA sequence. The E1A gene-coding region of the mutant is the same as that for wild-type adenovirus type 3, whereas the revertants are characterized by short in-frame deletions within the 5' exon region of their E1A genes. Location of these reverting, second-site deletions is discussed in relation to E1A gene autoregulation and the evolved diversity of E1A-related oncogenic potential among different human adenoviruses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiello L., Guilfoyle R., Huebner K., Weinmann R. Adenovirus 5 DNA sequences present and RNA sequences transcribed in transformed human embryo kidney cells (HEK-Ad-5 or 293). Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):460–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Schrier P. I., Houweling A., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J., Zijlstra M., Melief C. J. Tumorigenicity of cells transformed by adenovirus type 12 by evasion of T-cell immunity. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):776–779. doi: 10.1038/305776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casto B. C. Adenovirus transformation of hamster embryo cells. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.376-383.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Ricciardi R. P. Adenovirus 5 early region 1A host range mutants hr3, hr4, and hr5 contain point mutations which generate single amino acid substitutions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.66-74.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. Sequence-independent autoregulation of the adenovirus type 5 E1A transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochemsen A. G., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. The first exon of region E1a genes of adenoviruses 5 and 12 encodes a separate functional protein domain. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2923–2927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Miller J. S., Porter D., Roberts B. E. E1a regions of the human adenoviruses and of the highly oncogenic simian adenovirus 7 are closely related. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):399–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.399-409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. L., Tibbetts C. Spontaneous reiterations of DNA sequences near the ends of adenovirus type 3 genomes. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C. C., Tibbetts C. Polar encapsidation of adenovirus DNA: evolutionary variants reveal dispensable sequences near the left ends of Ad3 genomes. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Wright S., Quade K., Gallimore P., Cedar H., Grosveld F. Increased MHC H-2K gene transcription in cultured mouse embryo cells after adenovirus infection. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):579–581. doi: 10.1038/315579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Kegler D. M., Ziff E. B. Vector expression of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins: evidence for E1a autoregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2684–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J. The pattern of integration of viral DNA sequences in the adenovirus 5-transformed human cell line 293. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J., Khoury G., Jay G. Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):26–30. doi: 10.1126/science.3975631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C., Larsen P. L., Jones S. N. Autoregulation of adenovirus E1A gene expression. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1055–1064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1055-1064.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C. Physical organization of subgroup B human adenovirus genomes. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):564–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.564-579.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., Israel A., Kourilsky P., van der Eb A. J. Adenovirus E1A-mediated regulation of class I MHC expression. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):335–341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Kern F. G., Basilico C., Ziff E. B. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress expression from polyomavirus early and late promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4019–4025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Shenk T. Dissection of overlapping functions within the adenovirus type 5 E1A gene. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1907–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ormondt H., Maat J., Dijkema R. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of the early E1a regions for subgroups A, B and C of human adenoviruses. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]