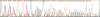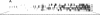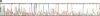Abstract
Two cDNA clones, lambda RHM-MF and lambda RHB-DAR, encoding the muscarinic cholinergic receptor and the beta-adrenergic receptor, respectively, have been isolated from a rat heart cDNA library. The cDNA clones were characterized by restriction mapping and automated DNA sequence analysis utilizing fluorescent dye primers. The rat heart muscarinic receptor consists of 466 amino acids and has a calculated molecular weight of 51,543. The rat heart beta-adrenergic receptor consists of 418 amino acids and has a calculated molecular weight of 46,890. The two cardiac receptors have substantial amino acid homology (27.2% identity, 50.6% with favored substitutions). The rat cardiac beta receptor has 88.0% homology (92.5% with favored substitutions) with the human brain beta receptor and the rat cardiac muscarinic receptor has 94.6% homology (97.6% with favored substitutions) with the porcine cardiac muscarinic receptor. The muscarinic cholinergic and beta-adrenergic receptors appear to be as conserved as hemoglobin and cytochrome c but less conserved than histones and are clearly members of a multigene family. These data support our hypothesis, based upon biochemical and immunological evidence, that suggests considerable structural homology and evolutionary conservation between adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors. To our knowledge, this is the first report utilizing automated DNA sequence analysis to determine the structure of a gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung F. Z., Lentes K. U., Gocayne J., Fitzgerald M., Robinson D., Kerlavage A. R., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human brain beta-adrenergic receptor. Evolutionary relationship to rodent and avian beta-receptors and porcine muscarinic receptors. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R., McCoy J., Simsek M., Majumdar A., Chang S. H., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. The bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6744–6748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Monoclonal antibodies to beta-adrenergic receptors: use in purification and molecular characterization of beta receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7034–7038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlavage A. R., Fraser C. M., Chung F. Z., Venter J. C. Molecular structure and evolution of adrenergic and cholinergic receptors. Proteins. 1986 Dec;1(4):287–301. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Fukuda K., Mikami A., Maeda A., Takahashi H., Mishina M., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Cloning, sequencing and expression of complementary DNA encoding the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):411–416. doi: 10.1038/323411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Maeda A., Sugimoto K., Akiba I., Mikami A., Takahashi H., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of porcine cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptor deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding human rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Peterson G. L., Smith D. H., Ashkenazi A., Ramachandran J., Schimerlik M. I., Capon D. J. Primary structure and biochemical properties of an M2 muscarinic receptor. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):600–605. doi: 10.1126/science.3107123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreeve S. M., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Molecular comparison of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors suggests that these proteins are structurally related "isoreceptors". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4842–4846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mammalian beta-adrenergic receptors. Structural differences in beta 1 and beta 2 subtypes revealed by peptide maps. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10689–10694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter J. C. Muscarinic cholinergic receptor structure. Receptor size, membrane orientation, and absence of major phylogenetic structural diversity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4842–4848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter J. C., di Porzio U., Robinson D. A., Shreeve S. M., Lai J., Kerlavage A. R., Fracek S. P., Jr, Lentes K. U., Fraser C. M. Evolution of neurotransmitter receptor systems. Prog Neurobiol. 1988;30(2-3):105–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(88)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Rodriguez H., Wong S. K., Brandt D. R., May D. C., Burnier J., Harkins R. N., Chen E. Y., Ramachandran J., Ullrich A. The avian beta-adrenergic receptor: primary structure and membrane topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Waitches G., Birchmeier C., Fasano O., Wigler M. Isolation and characterization of a new cellular oncogene encoding a protein with multiple potential transmembrane domains. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90785-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]