Abstract
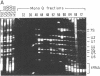
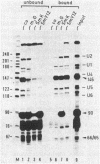
Upon chromatographic fractionation of HeLa cell nuclear extracts, small RNAs of 145 and 66/65 nucleotides, respectively, were detected that are distinct from the abundant small RNAs present in the extract. These RNAs are precipitated by antibodies directed against the trimethylguanosine cap structure, characteristic for small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) of the U type. The RNAs of 145 and 66/65 nucleotides appear to be associated with at least one of the proteins common to the major small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles U1 to U6, since they are specifically bound by anti-Sm antibodies. These criteria characterize the RNAs that are 145 and 66/65 nucleotides in length as U-type snRNAs. Upon gel filtration, the RNAs are found within particles of molecular weights approximately equal to 150,000 and 115,000, respectively. The RNA of 145 nucleotides represents a different minor snRNA, designated U11, whereas the RNA of 66/65 nucleotides may correspond to either mammalian U7 or U10 RNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr U2 RNA from yeast is unexpectedly large and contains homology to vertebrate U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear RNAs. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann P., Appel B., Rinke J., Reuter R., Theissen H., Lührmann R. Evidence for the existence of snRNAs U4 and U6 in a single ribonucleoprotein complex and for their association by intermolecular base pairing. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1357–1363. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann P., Reuter R., Rinke J., Appel B., Bald R., Lührmann R. 5'-terminal caps of snRNAs are accessible for reaction with 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine-specific antibody in intact snRNPs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2745–2747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A., Parisot R., Newmeyer D., De Robertis E. M. Small nuclear U-ribonucleoproteins in Xenopus laevis development. Uncoupled accumulation of the protein and RNA components. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein associates with the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. U4 and U6 RNAs coexist in a single small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3283–3293. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Rymond B. C., Rosbash M. S. cerevisiae U1 RNA is large and has limited primary sequence homology to metazoan U1 snRNA. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrmann R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Reuter R., Rothe S., Bald R. Isolation and characterization of rabbit anti-m3 2,2,7G antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7103–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson B., Guthrie C. An essential yeast snRNA with a U5-like domain is required for splicing in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):613–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90537-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Mimori T., Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The structure of mammalian small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Identification of multiple protein components reactive with anti-(U1)ribonucleoprotein and anti-Sm autoantibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5907–5914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R. Compilation of small RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r61–r72. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. Primary and secondary structure of U8 small nuclear RNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10930–10935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter R., Lührmann R. Immunization of mice with purified U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RNP) induces a pattern of antibody specificities characteristic of the anti-Sm and anti-RNP autoimmune response of patients with lupus erythematosus, as measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8689–8693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wise J. A., Swerdlow H., Mak A., Guthrie C. Small nuclear RNAs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: unexpected diversity in abundance, size, and molecular complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8097–8101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., Gilmartin G. M., Bannwarth W., Birnstiel M. L. Compensatory mutations suggest that base-pairing with a small nuclear RNA is required to form the 3' end of H3 messenger RNA. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):777–781. doi: 10.1038/323777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Brow D. A., Roiha H., Guthrie C. An essential snRNA from S. cerevisiae has properties predicted for U4, including interaction with a U6-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Jones M. H., Guthrie C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a U1-like small nuclear RNA with unexpected properties. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1484–1487. doi: 10.1126/science.3306922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. H., Eliceiri G. L. Antibodies elicited by N2,N2-7-trimethylguanosine react with small nuclear RNAs and ribonucleoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4636–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Birnstiel M. L. Genetic complementation in the Xenopus oocyte: co-expression of sea urchin histone and U7 RNAs restores 3' processing of H3 pre-mRNA in the oocyte. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1675–1682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D. High level of complexity of small nuclear RNAs in fungi and plants. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90696-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Tollervey D., Maloney D., Swerdlow H., Dunn E. J., Guthrie C. Yeast contains small nuclear RNAs encoded by single copy genes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):743–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]