Abstract
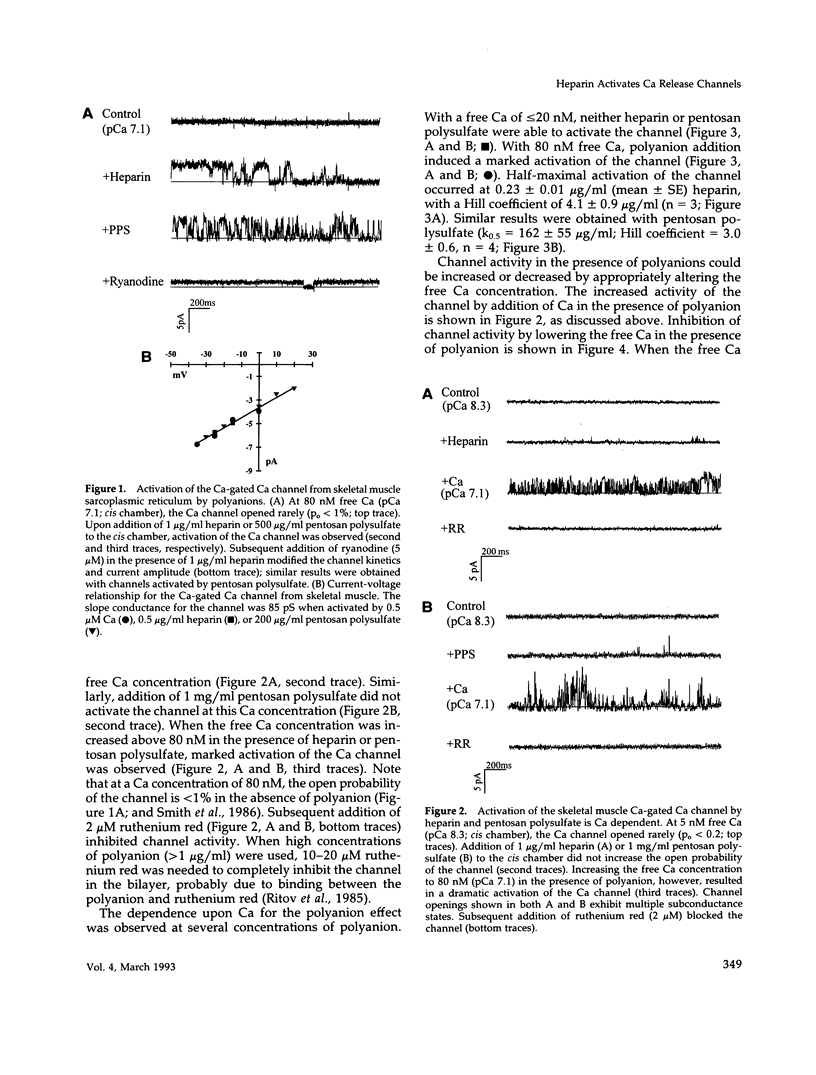
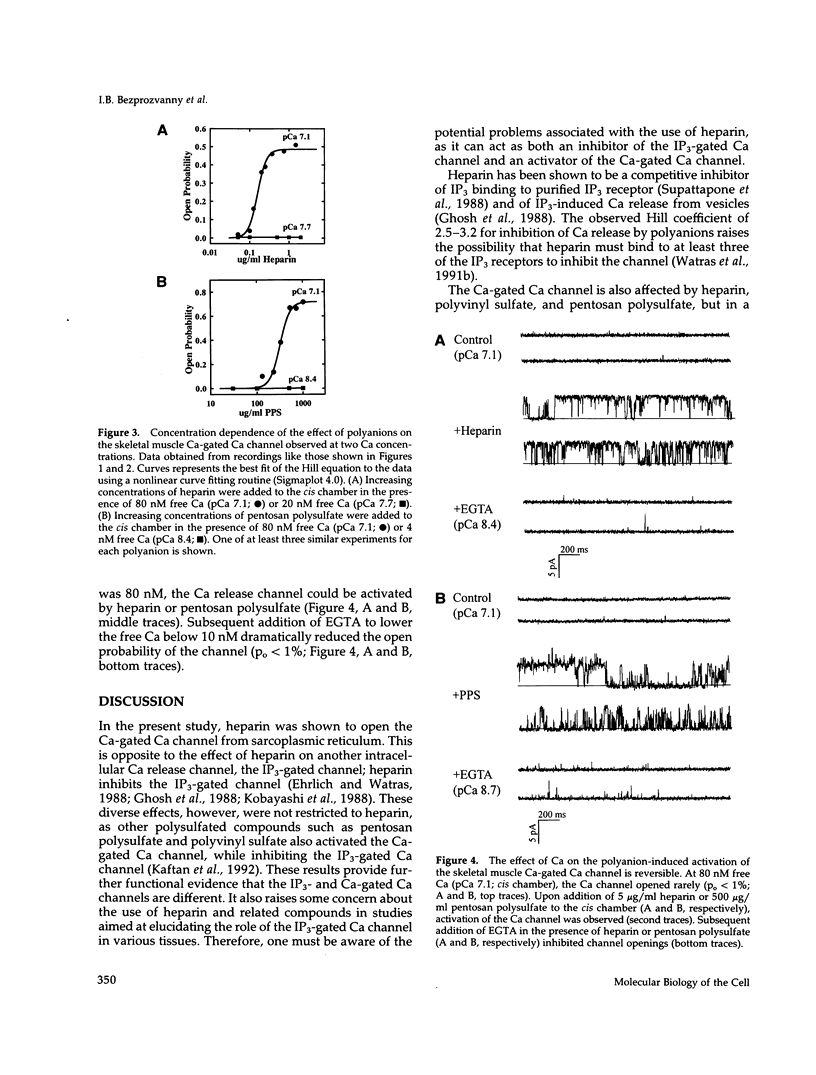
Heparin has been used as a potent competitive inhibitor of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)-binding to IP3 receptors and to block IP3-gated calcium channels in bilayer experiments. In contrast to the effect on the IP3-gated channel, heparin (0.1-1 micrograms/ml) opened the Ca release channel (ryanodine receptor). Other polyanions such as pentosan polysulfate and polyvinyl sulfate also activated the Ca release channel. The effect of polyanions on the Ca release channel was Ca dependent. Polyanion addition activated the Ca release channel when free Ca was > 80 nM, but was ineffective when free Ca was < 20 nM. The level of channel activation could be altered by manipulating the free Ca concentration. These results suggest that the polyanions act by increasing the local concentration of Ca near regulatory sites on the channel complex. As most cells have both types of intracellular channels, the opposite effects of the polyanions on the two channel types suggests that addition of polyanions to intact cells may produce multiple effects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgatta L., Watras J., Katz A. M., Ehrlich B. E. Regional differences in calcium-release channels from heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2486–2489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick C. C., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation and characterization of the inositol trisphosphate receptor from smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Watras J. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):583–586. doi: 10.1038/336583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Deerinck T. J., Ouyang Y., Beck C. F., Tanksley S. J., Walton P. D., Airey J. A., Sutko J. L. Identification and localization of ryanodine binding proteins in the avian central nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Aug;5(2):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Inui M. Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Yoshikawa S., Miyawaki A., Wada K., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):32–38. doi: 10.1038/342032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T. K., Eis P. S., Mullaney J. M., Ebert C. L., Gill D. L. Competitive, reversible, and potent antagonism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated calcium release by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11075–11079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. H., Ohnishi S. T., Ikemoto N. Kinetic studies of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9662–9668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Heparin inhibits the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent, but not the independent, calcium release induced by guanine nucleotide in vascular smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):625–631. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Niinobe M., Mikoshiba K. A cerebellar Purkinje cell marker P400 protein is an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor protein. Purification and characterization of InsP3 receptor complex. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C., Takei K., De Camilli P. Putative receptor for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate similar to ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):192–195. doi: 10.1038/342192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai J., Imagawa T., Hakamat Y., Shigekawa M., Takeshima H., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNA of the cardiac ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P., Dettbarn C., Alderson B., Volpe P. Pharmacologic differentiation between inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release and Ca2+- or caffeine-induced Ca2+ release from intracellular membrane systems. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;36(4):673–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritov V. B., Men'shikova E. V., Kozlov Y. P. Heparin induces Ca2+ release from the terminal cisterns of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 19;188(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80878-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Meldolesi J., Milner T. A., Satoh T., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor localized to endoplasmic reticulum in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):468–470. doi: 10.1038/339468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Isla B. A., Irribarra V., Oberhauser A., Larralde L., Bull R., Hidalgo C., Jaimovich E. Inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate activates a calcium channel in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):737–741. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83009-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watras J., Benevolensky D. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release from canine aortic sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 10;931(3):354–363. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watras J., Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated channels in cerebellum: presence of multiple conductance states. J Neurosci. 1991 Oct;11(10):3239–3245. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-10-03239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


