Abstract
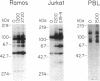
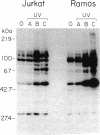
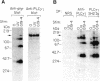
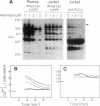
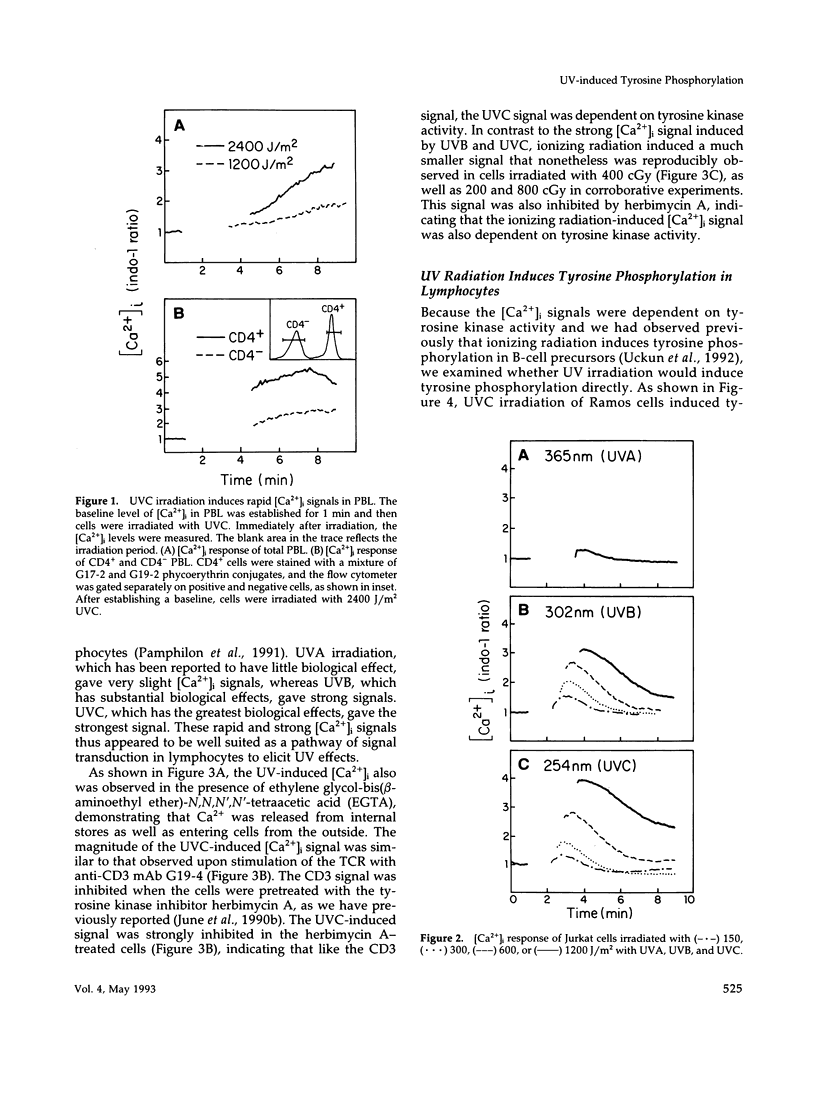
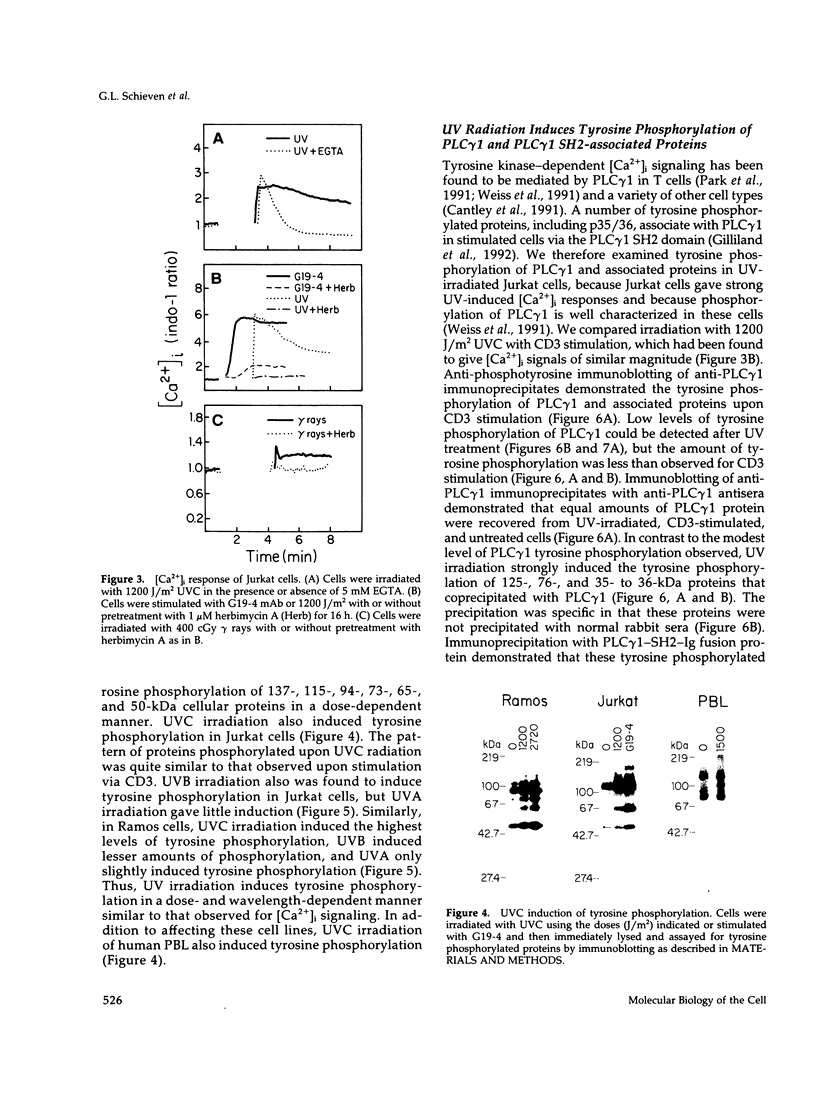
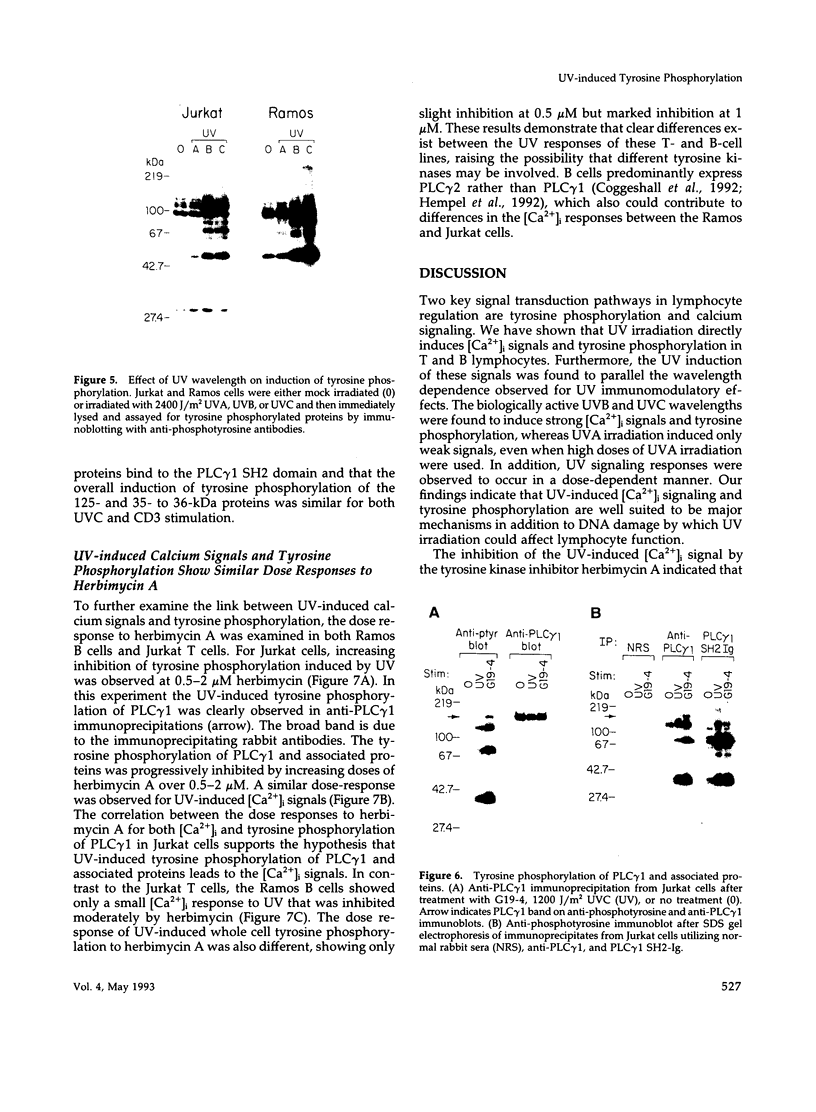
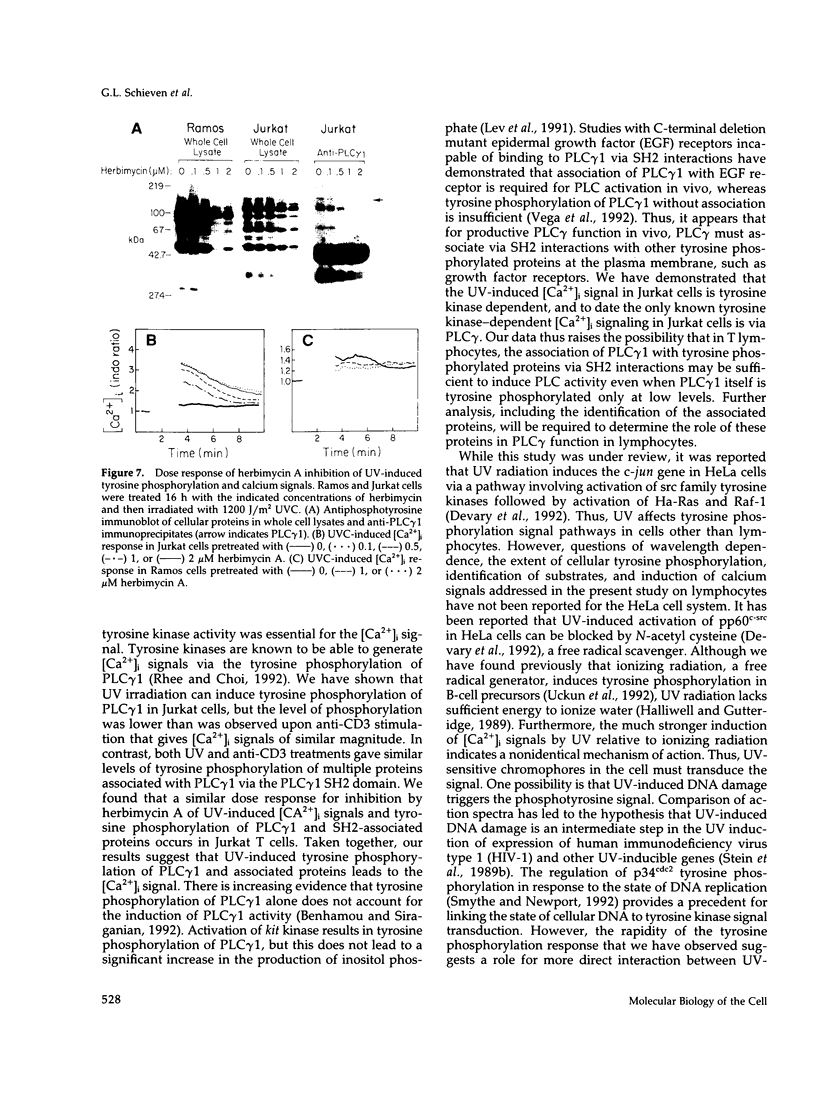
UV radiation is known to induce lymphocyte nonresponsiveness both in vitro and in vivo. We have found that UV radiation rapidly induced tyrosine phosphorylation and calcium signaling in normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes. In the leukemic T cell line Jurkat and the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Ramos, UV rapidly induced tyrosine phosphorylation in a wavelength-dependent manner, giving strong signals after UVB and UVC, but not UVA, irradiation. Similarly, in Jurkat cells UV-induced calcium signals were dependent on the dose of UVB or UVC irradiation over a range of 150-1200 J/m2, but only a small signal was observed for UVA at a dose of 1200 J/m2. The UV-induced calcium signals were blocked by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor herbimycin A, indicating that they were dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. Phospholipase C (PLC) gamma 1 was tyrosine phosphorylated in response to UV irradiation but to a lesser extent than observed after CD3 cross-linking. However, PLC gamma 1-associated proteins demonstrated to bind to the PLC gamma 1 SH2 domain were tyrosine phosphorylated strongly after UV irradiation. A similar dose response was observed for the inhibition by herbimycin A of UV-induced calcium signals and UV-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of PLC gamma 1 and associated proteins. We propose that in contrast to CD3/Ti stimulation, UV aberrantly triggers lymphocyte signal transduction pathways by a mechanism that bypasses normal receptor control.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benhamou M., Siraganian R. P. Protein-tyrosine phosphorylation: an essential component of Fc epsilon RI signaling. Immunol Today. 1992 Jun;13(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90152-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black H. S. Potential involvement of free radical reactions in ultraviolet light-mediated cutaneous damage. Photochem Photobiol. 1987 Aug;46(2):213–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1987.tb04759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Rowley R. B., Spana C., Tsygankov A. Y. The Src family of tyrosine protein kinases in hemopoietic signal transduction. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3403–3409. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1281458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chae H. P., Jarvis L. J., Uckun F. M. Role of tyrosine phosphorylation in radiation-induced activation of c-jun protooncogene in human lymphohematopoietic precursor cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 1;53(3):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., McHugh J. C., Altman A. Predominant expression and activation-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5660–5664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey D., Schieven G. L., Lim M. Y., Marquardt H., Gilmore T., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Novel yeast protein kinase (YPK1 gene product) is a 40-kilodalton phosphotyrosyl protein associated with protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6244–6256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. S., Wacholtz M. C., Lipsky P. E. The induction of T cell unresponsiveness by rapidly modulating CD3. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1084–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeg H. J., Bazar L., Sigaroudinia M., Cottler-Fox M. Ultraviolet B light inactivates bone marrow T lymphocytes but spares hematopoietic precursor cells. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):369–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeg H. J. Ultraviolet irradiation in transplantation biology. Manipulation of immunity and immunogenicity. Transplantation. 1988 May;45(5):845–851. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198805000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland L. K., Schieven G. L., Norris N. A., Kanner S. B., Aruffo A., Ledbetter J. A. Lymphocyte lineage-restricted tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins that bind PLC gamma 1 SH2 domains. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13610–13616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel W. M., Schatzman R. C., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 upon cross-linking of membrane Ig on murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Mallick U., Pöting A., Hieber L., Lücke-Huhle C., Schorpp M. The mammalian genetic stress response. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1986;25:485–504. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(86)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Pardoll D. M., Mizuguchi J., Chused T. M., Schwartz R. H. Molecular events in the induction of a nonresponsive state in interleukin 2-producing helper T-lymphocyte clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5409–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Samelson L. E. Increases in tyrosine phosphorylation are detectable before phospholipase C activation after T cell receptor stimulation. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1591–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Damle N. K., Blake J., Aruffo A., Ledbetter J. A. CD2/LFA-3 ligation induces phospholipase-C gamma 1 tyrosine phosphorylation and regulates CD3 signaling. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2023–2029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L. Immunological unresponsiveness induced by ultraviolet radiation. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:87–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. J., Ledbetter J. A., McConnell F. M., Draves K., Deans J., Schieven G. L., Clark E. A. The role of tyrosine phosphorylation in signal transduction through surface Ig in human B cells. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents intracellular calcium release. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):715–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Kuebelbeck V. M., Uckun F. M. Accessory receptors regulate coupling of the T-cell receptor complex to tyrosine kinase activation and mobilization of cytoplasmic calcium in T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1991 Mar 15;77(6):1271–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Givol D., Yarden Y. A specific combination of substrates is involved in signal transduction by the kit-encoded receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):647–654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07993.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. H., Gurish M. F., Daynes R. A. The effects of ultraviolet irradiation on the generation of anti-tumor cytotoxic effector cell responses in vitro. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1163–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamphilon D. H., Alnaqdy A. A., Wallington T. B. Immunomodulation by ultraviolet light: clinical studies and biological effects. Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90095-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Rho H. W., Rhee S. G. CD3 stimulation causes phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 on serine and tyrosine residues in a human T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5453–5456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch P. S., June C. H., Grossmann A., Ledbetter J. A. Heterogeneity among T cells in intracellular free calcium responses after mitogen stimulation with PHA or anti-CD3. Simultaneous use of indo-1 and immunofluorescence with flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):952–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay D. L., Lish K. M., Yalowitz C. B., Soter N. A. Ultraviolet-B phototherapy for early-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 1992 Jul;128(7):931–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronai Z. A., Lambert M. E., Weinstein I. B. Inducible cellular responses to ultraviolet light irradiation and other mediators of DNA damage in mammalian cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1990 Jan;6(1):105–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00135030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. L., Datta R., Hallahan D. E., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Ionizing radiation regulates expression of the c-jun protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5663–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Krämer M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H., Herrlich P. UV-induced transcription from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat and UV-induced secretion of an extracellular factor that induces HIV-1 transcription in nonirradiated cells. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4540–4544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4540-4544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Rahmsdorf H. J., Steffen A., Litfin M., Herrlich P. UV-induced DNA damage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5169–5181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Schieven G. L., Tuel-Ahlgren L. M., Dibirdik I., Myers D. E., Ledbetter J. A., Song C. W. Tyrosine phosphorylation is a mandatory proximal step in radiation-induced activation of the protein kinase C signaling pathway in human B-lymphocyte precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):252–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Tuel-Ahlgren L., Song C. W., Waddick K., Myers D. E., Kirihara J., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L. Ionizing radiation stimulates unidentified tyrosine-specific protein kinases in human B-lymphocyte precursors, triggering apoptosis and clonogenic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9005–9009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega Q. C., Cochet C., Filhol O., Chang C. P., Rhee S. G., Gill G. N. A site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the C terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor is required to activate phospholipase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Koretzky G., Schatzman R. C., Kadlecek T. Functional activation of the T-cell antigen receptor induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5484–5488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Prooijen H. C., Aarts-Riemens M. I., Grijzenhout M. A., van Weelden H. Ultraviolet irradiation modulates MHC-alloreactive cytotoxic T-cell precursors involved in the onset of graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 1992 May;81(1):73–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb08174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]