Abstract
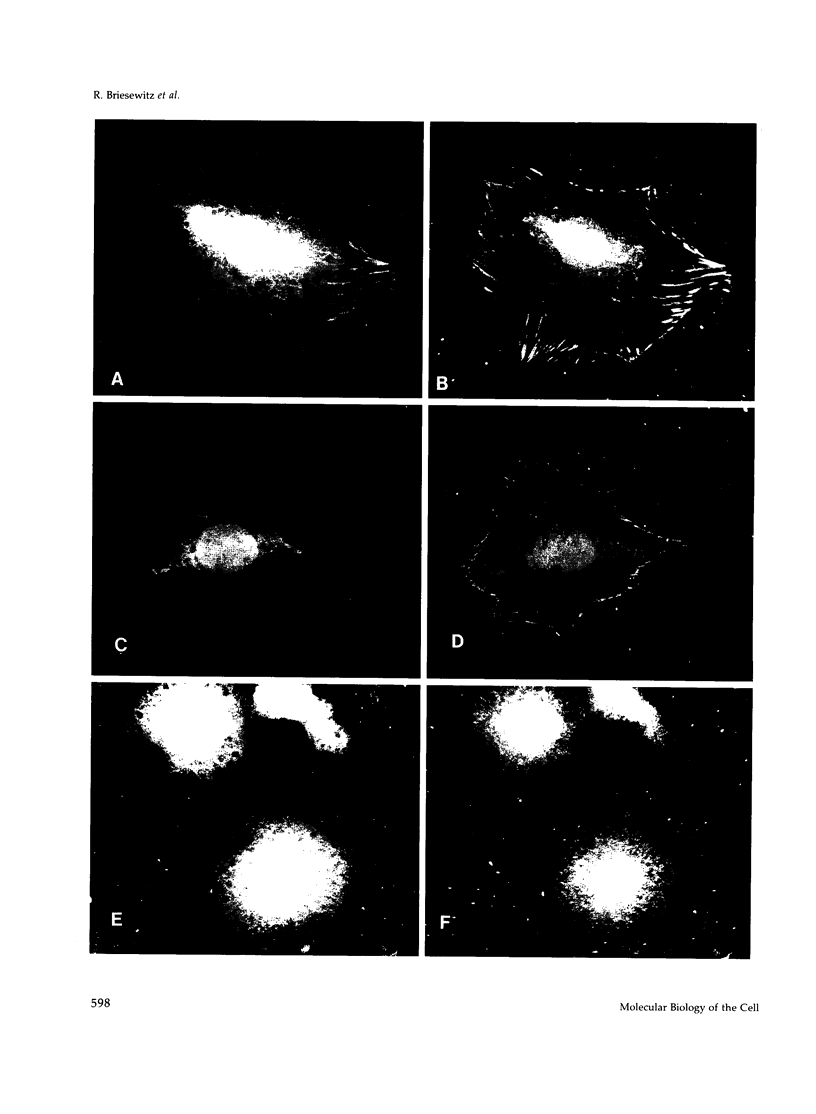
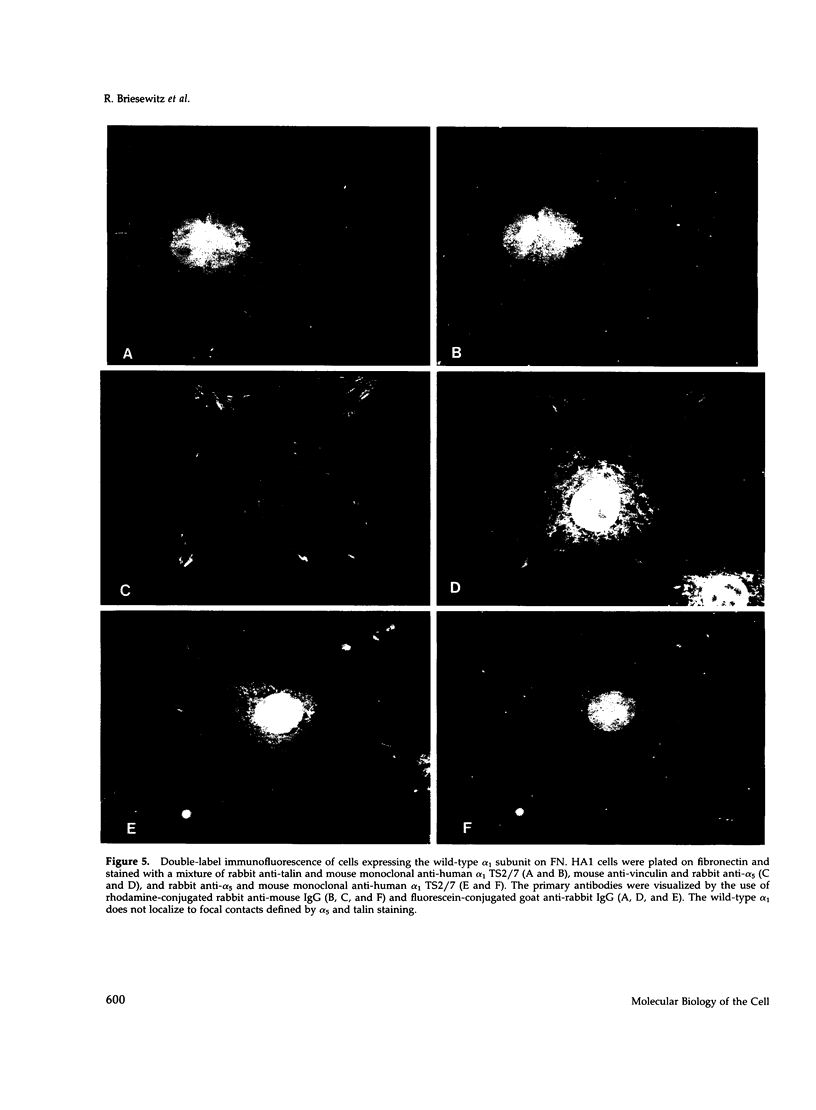
Many integrin receptors localize to focal contact sites upon binding their ligand. However, unoccupied integrin receptors do not localize to focal contact sites. Because the integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain appears to have a focal contact localization signal, there must be a mechanism by which this domain is kept inactive in the unoccupied state and becomes exposed or activated in the occupied receptor. We considered that this mechanism involves the alpha subunit cytoplasmic domain. To test this hypothesis, we have established two NIH 3T3 cell lines that express either the human alpha 1 wild-type subunit (HA1 cells) or the cytoplasmic domain deleted alpha 1 subunit (CYT cells). Both cell lines express similar levels of the human alpha 1 subunit, and there is no significant effect of the deletion on the dimerization and surface expression of the receptor. Furthermore, the deletion had no effect on the binding or adhesion via alpha 1 beta 1 to its ligand collagen IV. However, when these two cell lines are plated on fibronectin (FN), which is a ligand for alpha 5 beta 1 but not for alpha 1 beta 1, there is a striking difference in the cellular localization of alpha 1 beta 1. The HA1 cells show only alpha 5 in focal contacts, without alpha 1, demonstrating that all of the integrin localization is ligand dependent. In contrast, when the CYT cells are plated on FN, the mutant alpha 1 appears in focal contacts along with the alpha 5/beta 1. Thus, there is both ligand-dependent (alpha 5/beta 1) and ligand-independent (alpha 1/beta 1) focal contact localization in these cells. The truncated alpha 1 also localized to focal contacts in a ligand-independent manner on vitronectin. We conclude that the mutant alpha 1 no longer requires ligand occupancy for focal contact localization. These data strongly suggest that the alpha cytoplasmic domain plays a role in the normal ligand-dependent integrin focal contact localization.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aumailley M., Mann K., von der Mark H., Timpl R. Cell attachment properties of collagen type VI and Arg-Gly-Asp dependent binding to its alpha 2(VI) and alpha 3(VI) chains. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank I., Hemler M., Brenner M. B., Cohen D., Levy V., Belko J., Crouse C., Chess L. A novel monoclonal antibody, 1B3.1, binds to a new epitope of the VLA-1 molecule. Cell Immunol. 1989 Sep;122(2):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briesewitz R., Epstein M. R., Marcantonio E. E. Expression of native and truncated forms of the human integrin alpha 1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2989–2996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyon J. P., Slade S. G., Reibman J., Abramson S. B., Philips M. R., Weissmann G., Winchester R. Constitutive and induced phosphorylation of the alpha- and beta-chains of the CD11/CD18 leukocyte integrin family. Relationship to adhesion-dependent functions. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):191–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B. M., Kassner P. D., Schiro J. A., Byers H. R., Kupper T. S., Hemler M. E. Distinct cellular functions mediated by different VLA integrin alpha subunit cytoplasmic domains. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1051–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90077-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. T., Hasegawa E., Hasegawa T., Weinstock C., Yamada K. M. Development of cell surface linkage complexes in cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damsky C. H., Knudsen K. A., Bradley D., Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Distribution of the cell substratum attachment (CSAT) antigen on myogenic and fibroblastic cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1528–1539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone D. W., Hynes R. O. Xenopus laevis integrins. Structural conservation and evolutionary divergence of integrin beta subunits. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5333–5340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Colella S., Conforti G., Abbadini M., Gaboli M., Marchisio P. C. Fibronectin and vitronectin regulate the organization of their respective Arg-Gly-Asp adhesion receptors in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1215–1223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Salomon D., Takeichi M., Hynes R. O. A chimeric N-cadherin/beta 1-integrin receptor which localizes to both cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesions. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):943–951. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. E., Reichardt L. F., Crowley E., Holley B., Moezzi H., Sonnenberg A., Damsky C. H. The alpha 1/beta 1 and alpha 6/beta 1 integrin heterodimers mediate cell attachment to distinct sites on laminin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2175–2184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Haimovich B., Reszka A., Boettiger D., Horwitz A. Expression and function of chicken integrin beta 1 subunit and its cytoplasmic domain mutants in mouse NIH 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):175–184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., van Kessel A. G., Sonnenberg A. Molecular cloning of the human alpha 6 integrin subunit. Alternative splicing of alpha 6 mRNA and chromosomal localization of the alpha 6 and beta 4 genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):425–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Buck C., Beckerle M. C., Burridge K. Interaction of plasma membrane fibronectin receptor with talin--a transmembrane linkage. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):531–533. doi: 10.1038/320531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Marcantonio E. E., Stepp M. A., Urry L. A., Yee G. H. Integrin heterodimer and receptor complexity in avian and mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):409–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Marks N. Identification of integrin collagen receptors on human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4684–4688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFlamme S. E., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Regulation of fibronectin receptor distribution. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):437–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Guan J. L., Trevithick J. E., Hynes R. O. Mapping of the functional determinants of the integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain by site-directed mutagenesis. Cell Regul. 1990 Jul;1(8):597–604. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.8.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Du X. P., Glass A. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of the alpha IIb beta 3 integrin (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) is an intrinsic property of the receptor. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):883–893. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Mandelman D., Forsyth J., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Modulation of the affinity of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (GPIIb-IIIa) by the cytoplasmic domain of alpha IIb. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):845–847. doi: 10.1126/science.1948065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otey C. A., Pavalko F. M., Burridge K. An interaction between alpha-actinin and the beta 1 integrin subunit in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):721–729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reszka A. A., Hayashi Y., Horwitz A. F. Identification of amino acid sequences in the integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain implicated in cytoskeletal association. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Messier J. M., Mercurio A. M. The activation dependent adhesion of macrophages to laminin involves cytoskeletal anchoring and phosphorylation of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2167–2174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Scott S., Kawka D. W., Kazazis D. M., Gailit J., Ruoslahti E. Cell surface distribution of fibronectin and vitronectin receptors depends on substrate composition and extracellular matrix accumulation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2171–2182. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solowska J., Guan J. L., Marcantonio E. E., Trevithick J. E., Buck C. A., Hynes R. O. Expression of normal and mutant avian integrin subunits in rodent cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):853–861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada Y., Ylänne J., Mandelman D., Puzon W., Ginsberg M. H. A point mutation of integrin beta 1 subunit blocks binding of alpha 5 beta 1 to fibronectin and invasin but not recruitment to adhesion plaques. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):913–921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Cooper H. M., Collo G., Quaranta V. Cell type-specific integrin variants with alternative alpha chain cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10183–10187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P., Horwitz A., Buck C., Duggan K., Rohrschneider L. Integrins isolated from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):325–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. C., Flier L. A., Carbonetto S. Identification of a cell-surface protein involved in PC12 cell-substratum adhesion and neurite outgrowth on laminin and collagen. J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;9(9):3287–3296. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-03287.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg P., Kern A., Ries A., Luckenbill-Edds L., Mann K., Kühn K. Characterization of a type IV collagen major cell binding site with affinity to the alpha 1 beta 1 and the alpha 2 beta 1 integrins. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1475–1483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R., Johansson S., Hök M. Adhesion and cytoskeletal organisation of fibroblasts in response to fibronectin fragments. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):665–670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R. Protein kinase C involvement in focal adhesion formation. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):277–290. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]