Abstract
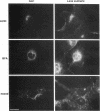
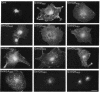
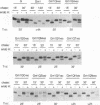
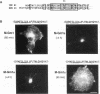
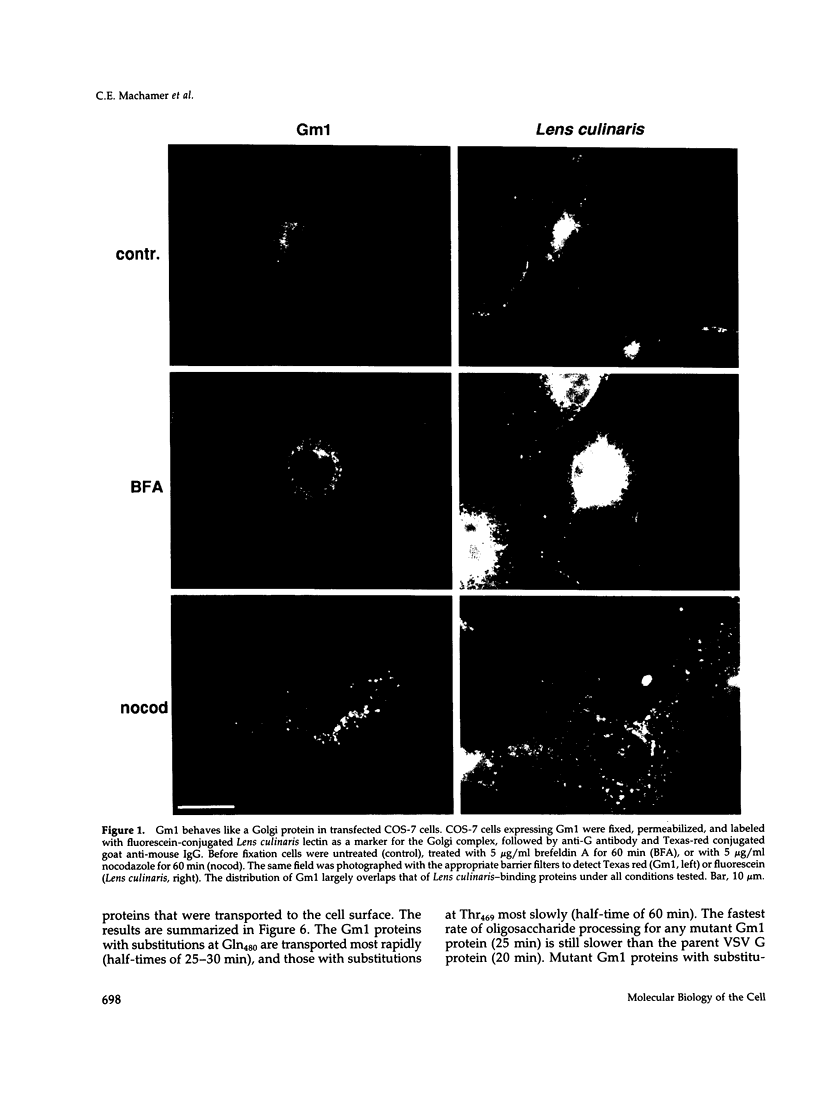
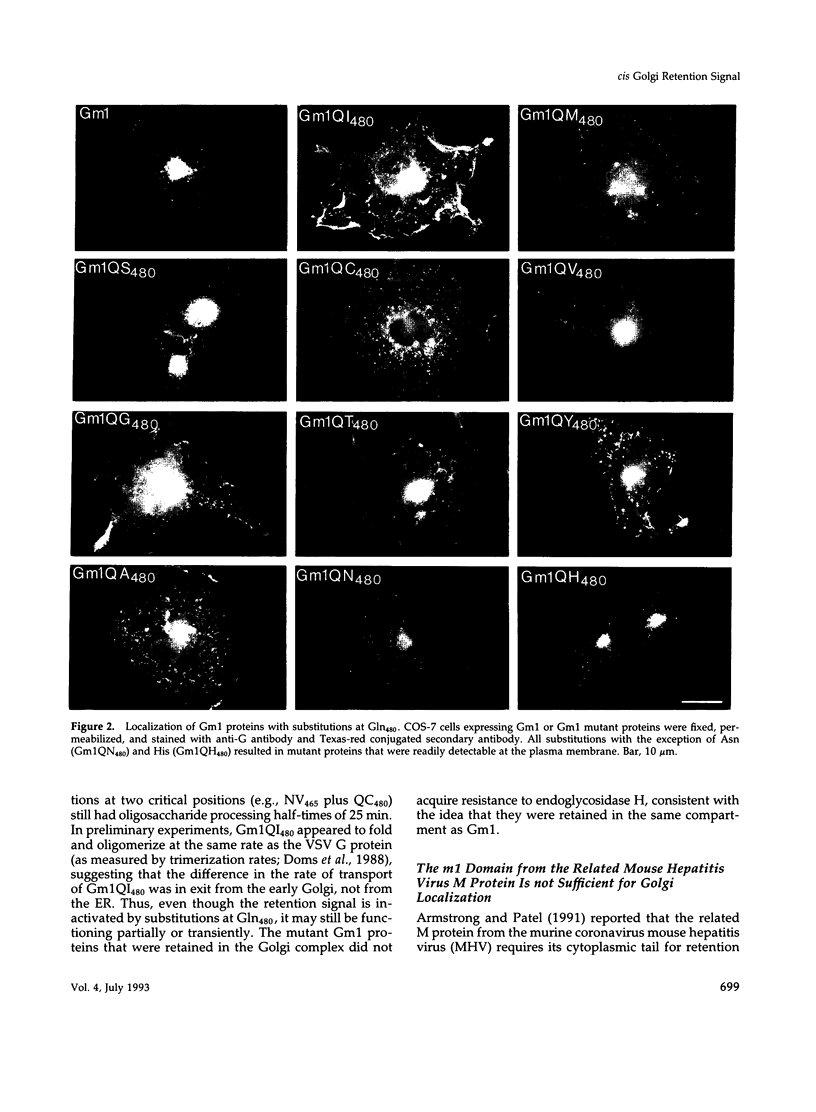
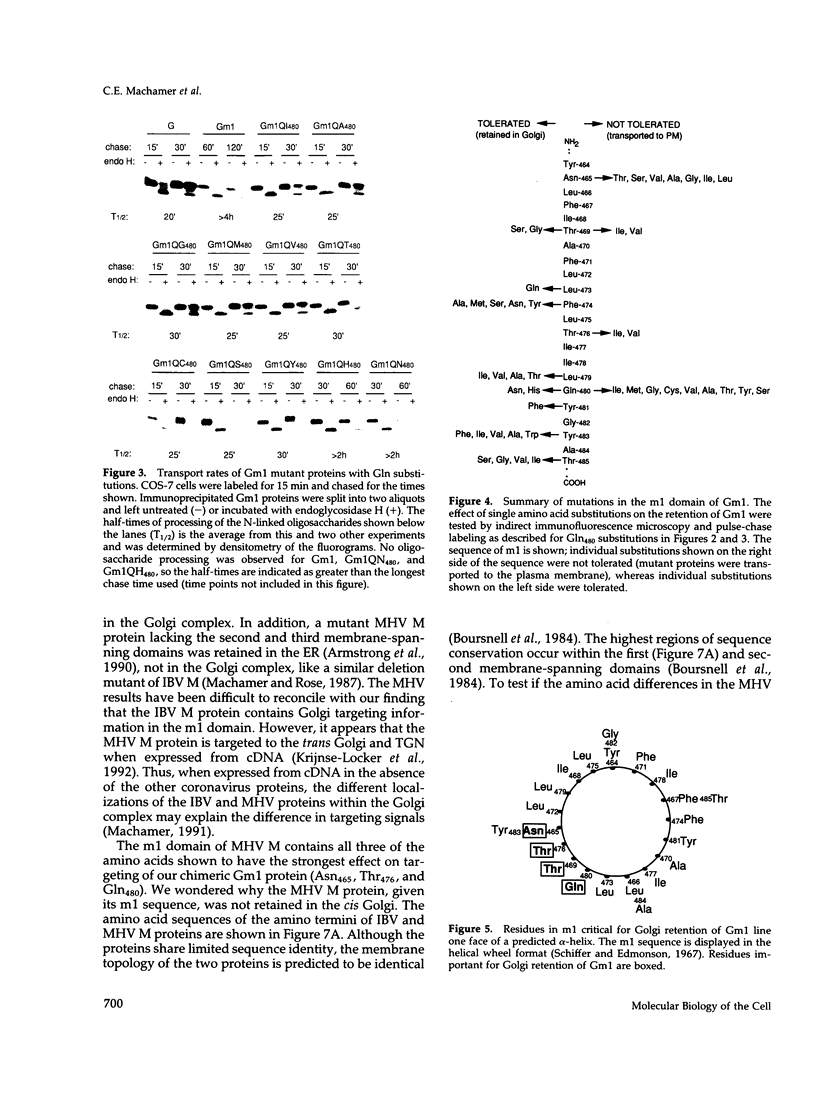
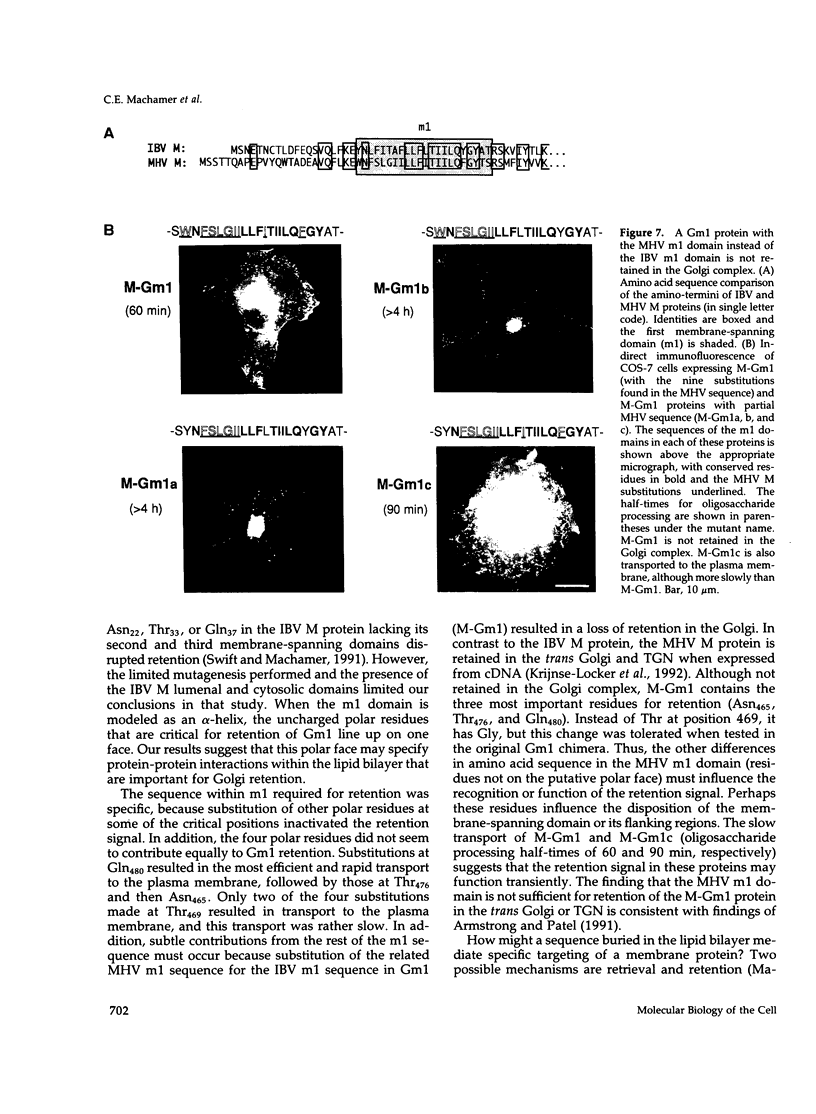
The first membrane-spanning domain (m1) of the model cis Golgi protein M (formerly called E1) from the avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus is required for targeting to the Golgi complex. When inserted in place of the membrane-spanning domain of a plasma membrane protein (vesicular stomatitis virus G protein), the chimeric protein ("Gm1") is retained in the Golgi complex of transfected cells. To determine the precise features of the m1 domain responsible for Golgi targeting, we produced single amino acid substitutions in m1 and analyzed their effects on localization of Gm1. Expression at the plasma membrane was used as the criterion for loss of Golgi retention. Rates of oligosaccharide processing were used as a measure of rate and efficiency of transport through the Golgi complex. We identified four uncharged polar residues that are critical for Golgi retention of Gm1 (Asn465, Thr469, Thr476, and Gln480). These residues line one face of a predicted alpha-helix. Interestingly, when the m1 domain of the homologous M protein from mouse hepatitis virus is inserted into the G protein reporter, the chimeric protein is not efficiently retained in the Golgi complex, but transported to the cell surface. Although it possesses three of the four residues we identified as important in the avian m1 sequence, other residues in the membrane-spanning domain from the mouse protein must prevent efficient recognition of the polar face within the lipid bilayer of the cis Golgi.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki D., Lee N., Yamaguchi N., Dubois C., Fukuda M. N. Golgi retention of a trans-Golgi membrane protein, galactosyltransferase, requires cysteine and histidine residues within the membrane-anchoring domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4319–4323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J., Patel S., Riddle P. Lysosomal sorting mutants of coronavirus E1 protein, a Golgi membrane protein. J Cell Sci. 1990 Feb;95(Pt 2):191–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J., Patel S. The Golgi sorting domain of coronavirus E1 protein. J Cell Sci. 1991 Apr;98(Pt 4):567–575. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell M. E., Brown T. D., Binns M. M. Sequence of the membrane protein gene from avian coronavirus IBV. Virus Res. 1984;1(4):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90019-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J., Pettitt J. M., Schachter H., Sarkar M., Gleeson P. A. The transmembrane and flanking sequences of beta 1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I specify medial-Golgi localization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24433–24440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley K. J., Lee E. U., Paulson J. C. The signal anchor and stem regions of the beta-galactoside alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase may each act to localize the enzyme to the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7784–7793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu V. W., Shah N., Klausner R. D. A brefeldin A-like phenotype is induced by the overexpression of a human ERD-2-like protein, ELP-1. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90226-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu V. W., Yuan L. C., Nuchtern J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Hammerling G. J., Klausner R. D. A recycling pathway between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus for retention of unassembled MHC class I molecules. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):441–444. doi: 10.1038/352441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Tooze S. A. Biosynthetic protein transport in the secretory pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;1(4):648–654. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld K., Reitman M. L., Kornfeld R. The carbohydrate-binding specificity of pea and lentil lectins. Fucose is an important determinant. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6633–6640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E. Role of microtubules in the organisation of the Golgi apparatus. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;15(2):67–70. doi: 10.1002/cm.970150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L., Lyles D. S. The interaction of antibody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Monoclonal antibodies of nonneutralizing and cross-reactive epitopes of Indiana and New Jersey serotypes. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. K., Griffiths G., Horzinek M. C., Rottier P. J. O-glycosylation of the coronavirus M protein. Differential localization of sialyltransferases in N- and O-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14094–14101. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)49683-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Florkiewicz R. Z., Rose J. K. A single N-linked oligosaccharide at either of the two normal sites is sufficient for transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein to the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3074–3083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E. Golgi retention signals: do membranes hold the key? Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90001-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Mentone S. A., Rose J. K., Farquhar M. G. The E1 glycoprotein of an avian coronavirus is targeted to the cis Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. A specific transmembrane domain of a coronavirus E1 glycoprotein is required for its retention in the Golgi region. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1205–1214. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S. Sequences within and adjacent to the transmembrane segment of alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase specify Golgi retention. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3577–3588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Lucocq J. M., Mackay D., Warren G. The membrane spanning domain of beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase specifies trans Golgi localization. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3567–3575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Pypaert M., Hoe M. H., Slusarewicz P., Berger E. G., Warren G. Overlapping distribution of two glycosyltransferases in the Golgi apparatus of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):5–13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Recycling of proteins between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Protein sorting by selective retention in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):521–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90024-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo R. N., Shaper N. L., Taatjes D. J., Shaper J. H. Beta 1,4-galactosyltransferase: a short NH2-terminal fragment that includes the cytoplasmic and transmembrane domain is sufficient for Golgi retention. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9241–9247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift A. M., Machamer C. E. A Golgi retention signal in a membrane-spanning domain of coronavirus E1 protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):19–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B. L., Wong S. H., Low S. H., Hong W. The transmembrane domain of N-glucosaminyltransferase I contains a Golgi retention signal. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10122–10126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale R. D., D'Agostaro G., Gleeson P. A. The signal for Golgi retention of bovine beta 1,4-galactosyltransferase is in the transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4084–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. H., Low S. H., Hong W. The 17-residue transmembrane domain of beta-galactoside alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase is sufficient for Golgi retention. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):245–258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]