Abstract
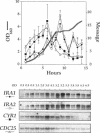
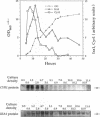
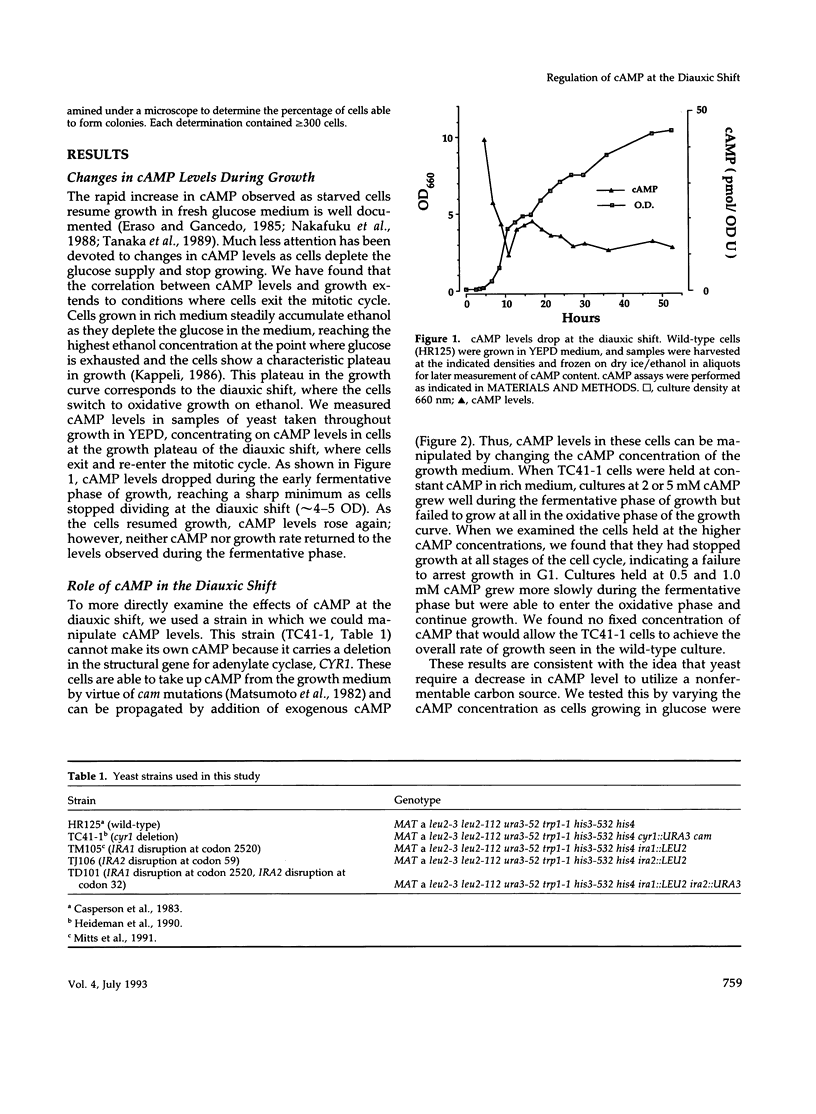
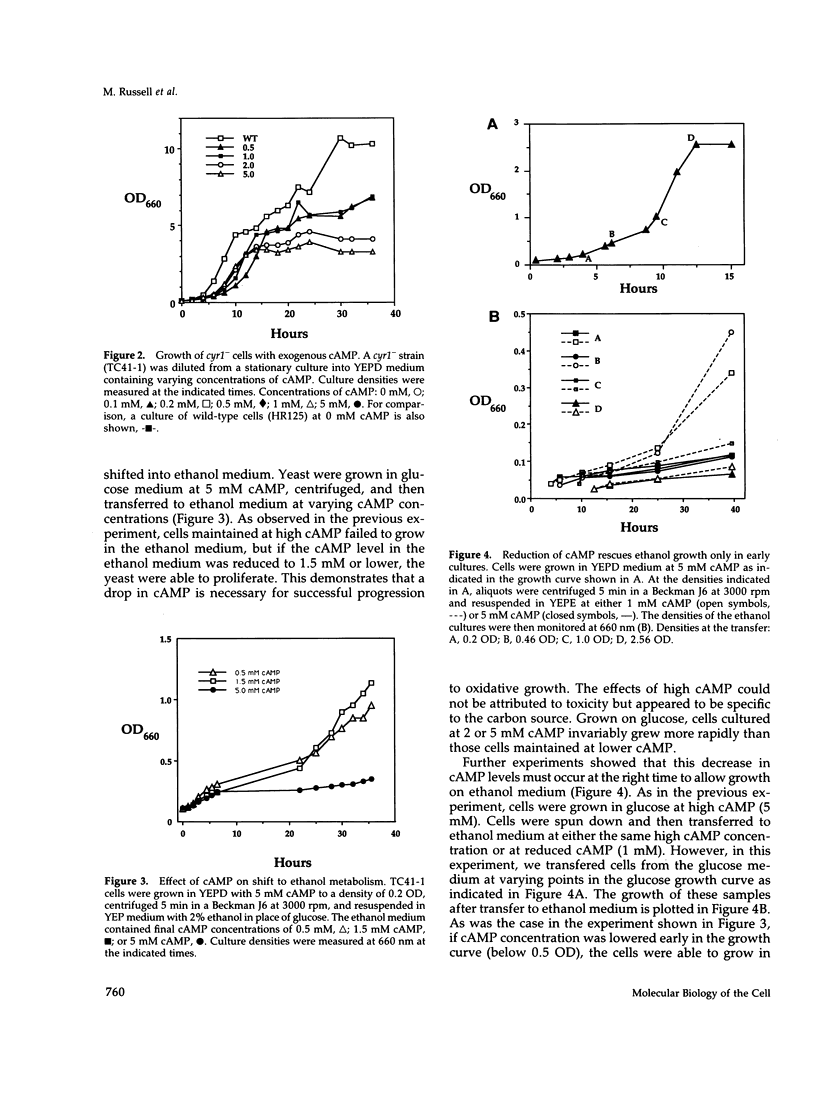
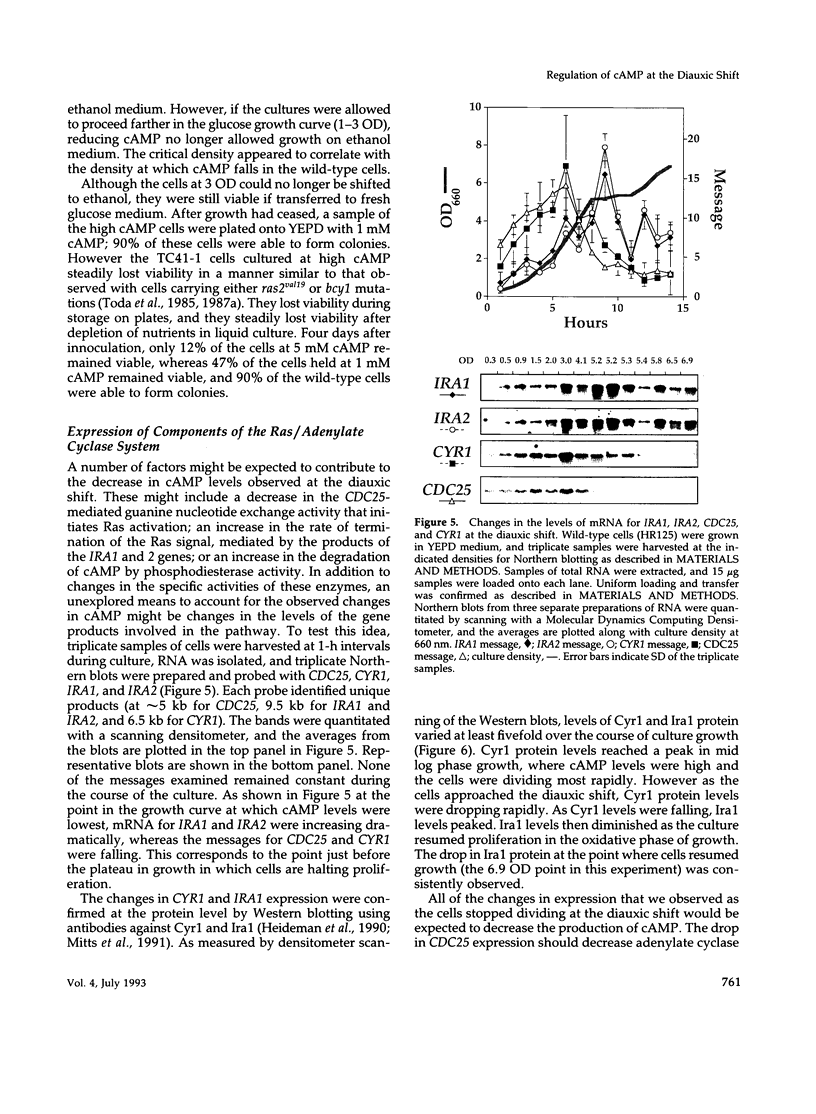
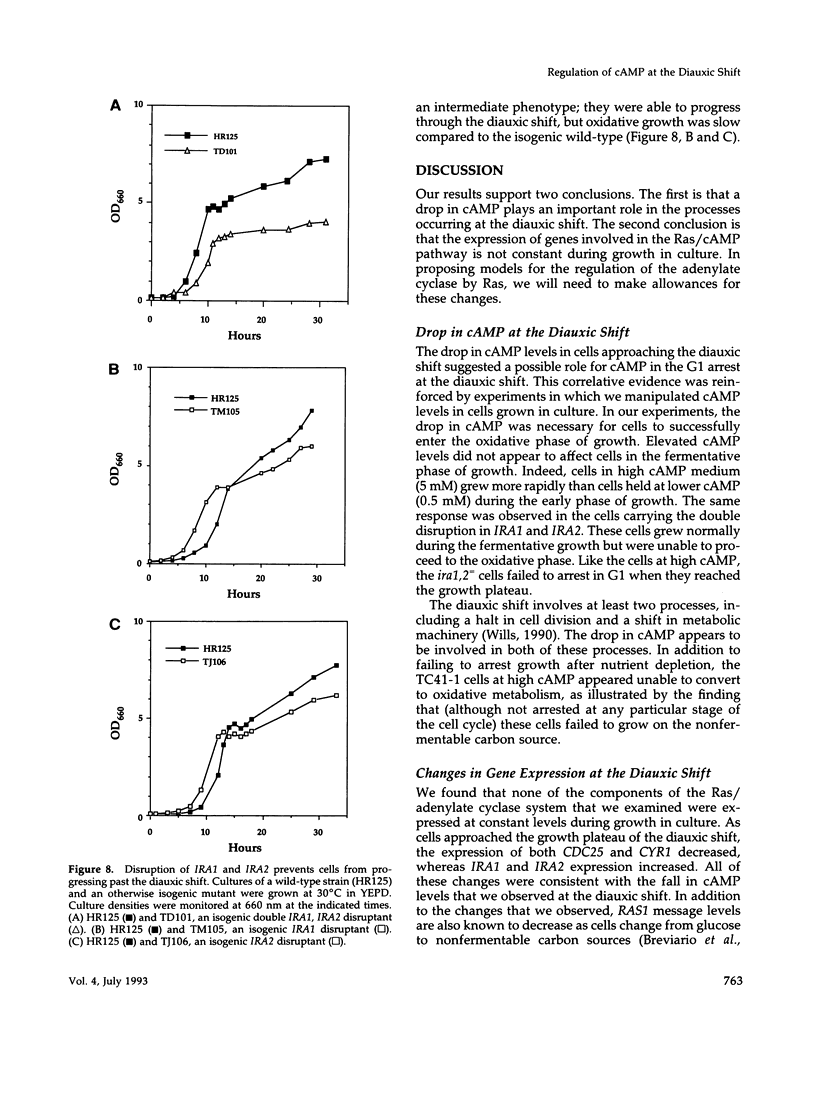
Levels of cyclic 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) play an important role in the decision to enter the mitotic cycle in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In addition to growth arrest at stationary phase, S. cerevisiae transiently arrest growth as they shift from fermentative to oxidative metabolism (the diauxic shift). Experiments examining the role of cAMP in growth arrest at the diauxic shift show the following: 1) yeast lower cAMP levels as they exhaust their glucose supply and shift to oxidative metabolism of ethanol, 2) a reduction in cAMP is essential for traversing the diauxic shift, 3) the decrease in adenylate cyclase activity is associated with a decrease in the expression of CYR1 and CDC25, two positive regulators of cAMP levels and an increase in the expression of IRA1 and IRA2, two negative regulators of intracellular cAMP, 4) mutants carrying disruptions in IRA1 and IRA2 were unable to arrest cell division at the diauxic shift and were unable to progress into the oxidative phase of growth. These results indicate that changes cAMP levels are important in regulation of growth arrest at the diauxic shift and that changes in gene expression plays a role in the regulation of the Ras/adenylate cyclase system.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breviario D., Hinnebusch A., Cannon J., Tatchell K., Dhar R. Carbon source regulation of RAS1 expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the phenotypes of ras2- cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4152–4156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Walker N., Bourne H. R. Isolation of the gene encoding adenylate cyclase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5060–5063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Walker N., Brasier A. R., Bourne H. R. A guanine nucleotide-sensitive adenylate cyclase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7911–7914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M. S., Craig E. A. Differential regulation of the 70K heat shock gene and related genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1454–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heideman W., Casperson G. F., Bourne H. R. Adenylyl cyclase in yeast. Hydrodynamic properties and activation by trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7087–7091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heideman W., Casperson G. F., Bourne H. R. Adenylyl cyclase in yeast: antibodies and mutations identify a regulatory domain. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Apr;42(4):229–242. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240420406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Tackling the protease problem in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:428–453. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94034-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Vignais M. L., Broach J. R. The CDC25 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae promotes exchange of guanine nucleotides bound to ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2641–2646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käppeli O. Regulation of carbon metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and related yeasts. Adv Microb Physiol. 1986;28:181–209. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Genetic analysis of the role of cAMP in yeast. Yeast. 1985 Sep;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Oshima Y., Ishikawa T. Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants deficient in adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2355–2359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitts M. R., Bradshaw-Rouse J., Heideman W. Interactions between adenylate cyclase and the yeast GTPase-activating protein IRA1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4591–4598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Obara T., Kaibuchi K., Miyajima I., Miyajima A., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Arai K., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y. Isolation of a second yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene (GPA2) coding for guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein: studies on its structure and possible functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikawa J., Cameron S., Toda T., Ferguson K. M., Wigler M. Rigorous feedback control of cAMP levels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):931–937. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Matsumoto K., Toh-E A. IRA1, an inhibitory regulator of the RAS-cyclic AMP pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):757–768. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Nakafuku M., Satoh T., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y., Toh-e A. S. cerevisiae genes IRA1 and IRA2 encode proteins that may be functionally equivalent to mammalian ras GTPase activating protein. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):803–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90094-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Scott J. D., McMullen B., Hurwitz M., Krebs E. G., Wigler M. Cloning and characterization of BCY1, a locus encoding a regulatory subunit of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1371–1377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills C. Regulation of sugar and ethanol metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(4):245–280. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]