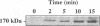Abstract
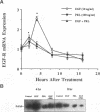
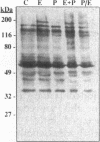
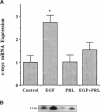
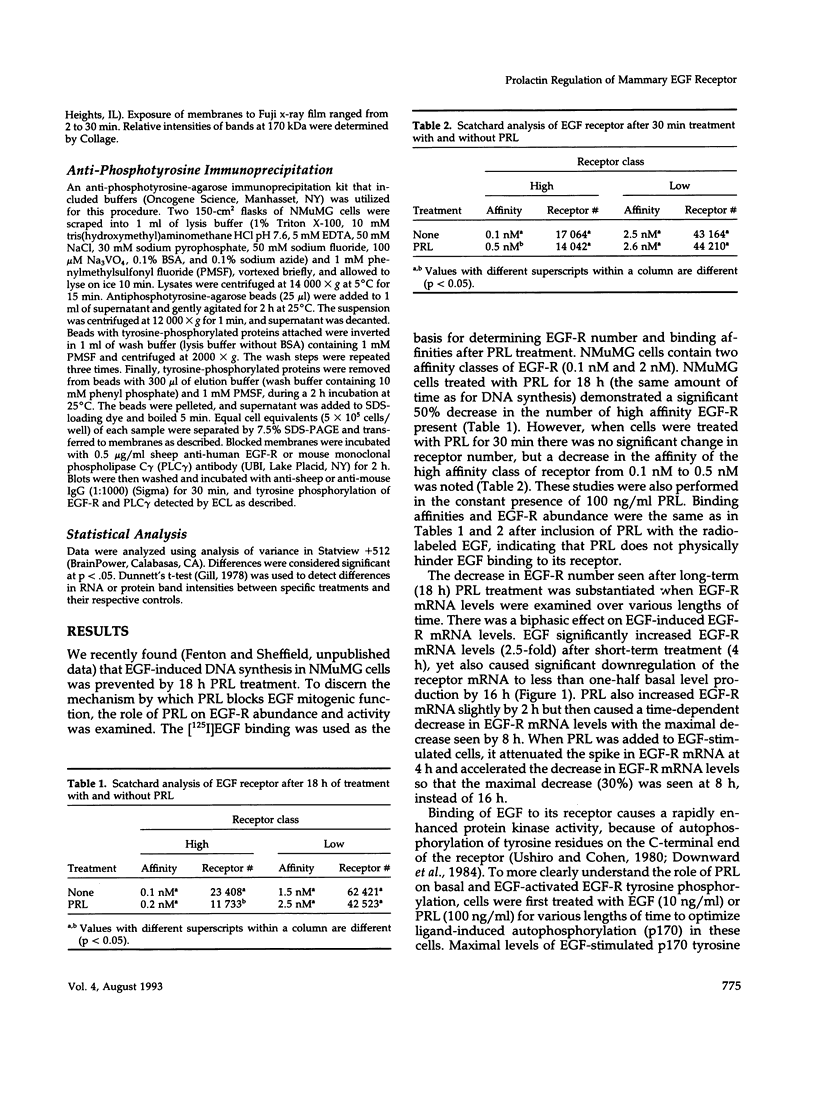
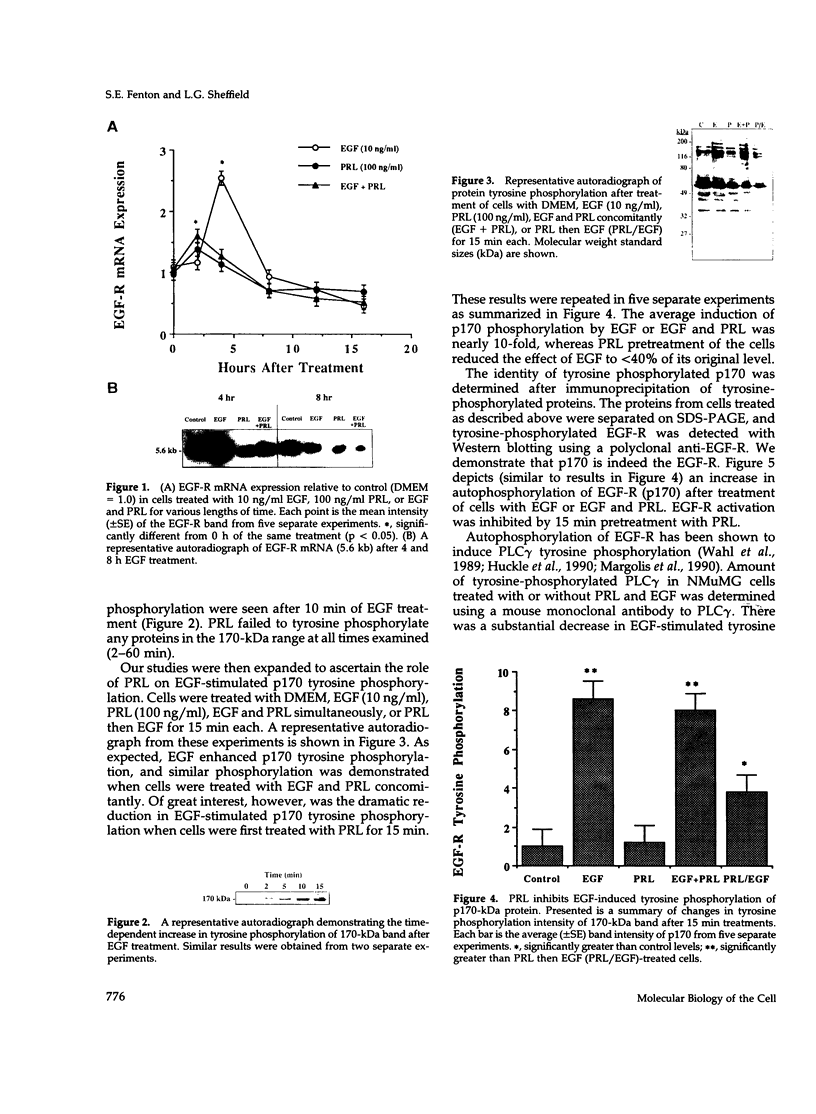
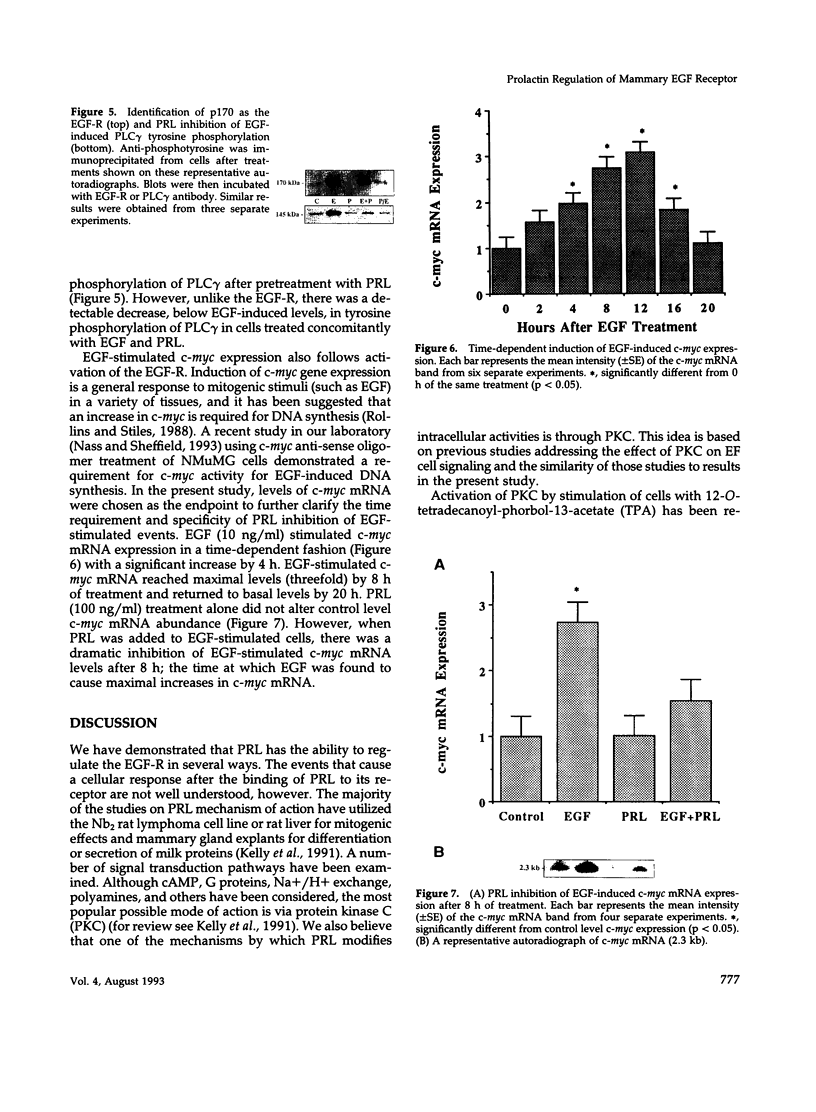
We have previously shown that lactogenic hormones stimulate epidermal growth factor (EGF) mRNA accumulation in mouse mammary glands in vivo and in mouse mammary epithelial cells (NMuMG line). However, our in vitro studies indicate that the lactogenic hormone prolactin (PRL) completely inhibits EGF-stimulated DNA synthesis. PRL does not alter cholera toxin or insulin-like growth factor-1-stimulated cell growth, thus the inhibition appears to be specific for EGF. Our current studies are designed to evaluate the effects of PRL on EGF-stimulated signaling events in the NMuMG cell line. Cells treated with PRL for 30 min demonstrated a loss of high affinity EGF-binding ability. After long-term PRL treatment (18 h) there was a decrease in EGF receptor (R) number, as determined by [125I]EGF binding. PRL treatment (8 h) also decreased EGF-R mRNA levels. An EGF-stimulated increase in EGF-R mRNA observed 2-4 h after treatment was decreased when PRL was added to the cultures. Furthermore, levels of EGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGF-R (170 kDa) and phospholipase C gamma (145 kDa) are dramatically decreased in cells treated with PRL. Also of great interest was a decrease in EGF-stimulated c-myc mRNA in PRL-treated cells. We conclude that PRL is acting to down-regulate the EGF-R, thus limiting EGF-stimulated cell signaling in mammary tissue.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorge J. D., Kudlow J. E. Epidermal growth factor receptor synthesis is stimulated by phorbol ester and epidermal growth factor. Evidence for a common mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6615–6622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borellini F., Oka T. Growth control and differentiation in mammary epithelial cells. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Mar;80:85–99. doi: 10.1289/ehp.898085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. F., Teng C. T., Pentecost B. T., DiAugustine R. P. Epidermal growth factor precursor in mouse lactating mammary gland alveolar cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;3(7):1077–1083. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-7-1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ishii S., Richert N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor regulates the expression of its own receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8374–8378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J. Effects of epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on metabolism of the epidermal growth factor receptor in normal human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1718–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earp H. S., Austin K. S., Blaisdell J., Rubin R. A., Nelson K. G., Lee L. W., Grisham J. W. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates EGF receptor synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4777–4780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earp H. S., Hepler J. R., Petch L. A., Miller A., Berry A. R., Harris J., Raymond V. W., McCune B. K., Lee L. W., Grisham J. W. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and hormones stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and increase EGF receptor protein synthesis and mRNA levels in rat liver epithelial cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13868–13874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery M., Pang K., Larson L., Colosi T., Nandi S. Epidermal growth factor receptor levels in mouse mammary glands in various physiological states. Endocrinology. 1985 Jul;117(1):405–411. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-1-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton S. E., Sheffield L. G. Lactogenic hormones increase epidermal growth factor messenger RNA content of mouse mammary glands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1063–1069. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92045-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O. Enforced expression of the c-myc oncogene inhibits cell differentiation by precluding entry into a distinct predifferentiation state in G0/G1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1614–1624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Santon J. B., Bertics P. J. Regulatory features of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1987;Suppl 5:35–41. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Redner R. L., Nienhuis A. W. An oligomer complementary to c-myc mRNA inhibits proliferation of HL-60 promyelocytic cells and induces differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):963–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckle W. R., Hepler J. R., Rhee S. G., Harden T. K., Earp H. S. Protein kinase C inhibits epidermal growth factor-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma and activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Endocrinology. 1990 Oct;127(4):1697–1705. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-4-1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa W., Bandyopadhyay G. K., Nandi S. Regulation of mammary epithelial cell growth in mice and rats. Endocr Rev. 1990 Nov;11(4):494–523. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-4-494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Djiane J., Postel-Vinay M. C., Edery M. The prolactin/growth hormone receptor family. Endocr Rev. 1991 Aug;12(3):235–251. doi: 10.1210/edrv-12-3-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon W. Y., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. The c-myc oncogene perturbs B lymphocyte development in E-mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K. A., Lazar C. S., Chen W. S., Walsh B. J., Welsh J. B., Herbst J. J., Walton G. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N., Wiley H. S. Phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 654 inhibits ligand-induced internalization and down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20517–20523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P. G., Friedman B., Rosner M. R. Diacylglycerol modulates binding and phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12502–12507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune B. K., Prokop C. A., Earp H. S. Transient epidermal growth factor (EGF)-dependent suppression of EGF receptor autophosphorylation during internalization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9715–9721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Davis R. J. Signal transduction by the epidermal growth factor receptor after functional desensitization of the receptor tyrosine protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6107–6111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. B. Glandular epithelial cells from mice: a method for selective cultivation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1375–1378. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rillema J. A., Campbell G. S., Lawson D. M., Carter-Su C. Evidence for a rapid stimulation of tyrosine kinase activity by prolactin in Nb2 rat lymphoma cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Aug;131(2):973–975. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.2.1639035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Stiles C. D. Regulation of c-myc and c-fos proto-oncogene expression by animal cell growth factors. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Feb;24(2):81–84. doi: 10.1007/BF02623883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rui H., Djeu J. Y., Evans G. A., Kelly P. A., Farrar W. L. Prolactin receptor triggering. Evidence for rapid tyrosine kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24076–24081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran L., Topper Y. J. Is EGF a physiological inhibitor of mouse mammary casein synthesis? Unphysiological responses to pharmacological levels of hormones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90699-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Biologically active phorbol esters specifically alter affinity of epidermal growth factor membrane receptors. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):387–391. doi: 10.1038/279387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha Y. N., Selby F. W., Vanderlaan W. P. Relationship of prolactin and growth hormone to mammary function during pregnancy and lactation in the C3H-ST mouse. J Endocrinol. 1974 May;61(2):219–229. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0610219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snedeker S. M., Brown C. F., DiAugustine R. P. Expression and functional properties of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor during mouse mammary gland ductal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):276–280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketani Y., Oka T. Biological action of epidermal growth factor and its functional receptors in normal mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2647–2650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketani Y., Oka T. Epidermal growth factor stimulates cell proliferation and inhibits functional differentiation of mouse mammary epithelial cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1983 Sep;113(3):871–877. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-3-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketani Y., Oka T. Possible physiological role of epidermal growth factor in the development of the mouse mammary gland during pregnancy. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 21;152(2):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. L., Rosner M. R. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression by retinoic acid and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3230–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderhaar B. K., Nakhasi H. L. Bifunctional activity of epidermal growth factor on alpha- and kappa-casein gene expression in rodent mammary glands in vitro. Endocrinology. 1986 Sep;119(3):1178–1184. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-3-1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]