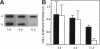Abstract
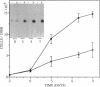
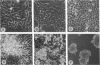
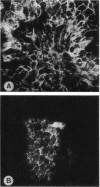
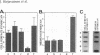
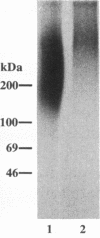
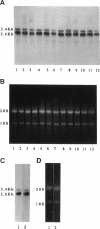
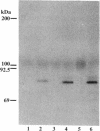
A cell surface proteoglycan, syndecan-1, has been shown to participate in the maintenance of the epithelial cell morphology. A point mutated activated c-Ha-ras gene under the control of the glucocorticoid inducible MMTV-LTR promoter was transfected into the mouse mammary epithelial cell line, NOG-8. The NOG-8 ras cells were used to study changes in syndecan-1 expression during epithelial transformation. NOG-8 ras cells, when induced to express Ha-ras, transformed and formed foci in monolayer cultures and colonies in suspension cultures. Expression of syndecan-1 at the cell surface was markedly reduced in cells showing the transformed phenotype. The accumulation of newly synthesized core protein of syndecan-1 was suppressed in these cells, whereas mRNA levels remained unchanged. This novel finding indicates that syndecan-1 expression is translationally suppressed in the Ha-ras-transformed epithelial cells. Hence, syndecan-1 loss during epithelial transformation could take place without altering syndecan gene transcription and, on the other hand, could be one of the critical events involved in malignant transformation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardiello F., Kim N., Hynes N., Jaggi R., Redmond S., Liscia D. S., Sanfilippo B., Merlo G., Callahan R., Kidwell W. R. Induction of transforming growth factor alpha expression in mouse mammary epithelial cells after transformation with a point-mutated c-Ha-ras protooncogene. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1202–1216. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Mättä A., Salmivirta M., Jalkanen M. Growth factors induce 3T3 cells to express bFGF-binding syndecan. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6435–6441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Vainio S., Laato M., Salmivirta M., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Induced expression of syndecan in healing wounds. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):585–595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., DeFeo D., Maryak J. M., Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Chang E. H., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. Dual evolutionary origin for the rat genetic sequences of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):408–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.408-420.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai Y., Takebe K., Takashina M., Kobayashi S., Takeichi M. Epimorphin: a mesenchymal protein essential for epithelial morphogenesis. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90448-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Gomez M., Quintanilla M., Cano A., Jalkanen M. Expression of syndecan in transformed mouse keratinocytes. Lab Invest. 1992 Aug;67(2):225–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Kujari H., Jalkanen M. Syndecan in carcinomas produced from transformed epithelial cells in nude mice. Lab Invest. 1992 Mar;66(3):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Stenbäck F., Talve L., Jalkanen M. Immunohistochemical localization of syndecan in mouse skin tumors induced by UV irradiation. Loss of expression associated with malignant transformation. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1333–1340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Nguyen H., Rapraeger A., Kurn N., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells: localization on the cell surface with a monoclonal antibody. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):976–984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Rapraeger A., Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mouse mammary epithelial cells is shed by cleavage of its matrix-binding ectodomain from its membrane-associated domain. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):3087–3096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Stephans J. C., Crawford K., Okino K., Barr P. J. Ligand-affinity cloning and structure of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan that binds basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda J. E., Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells. Cell surface proteoglycan as a receptor for interstitial collagens. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8157–8162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppä S., Härkönen P., Jalkanen M. Steroid-induced epithelial-fibroblastic conversion associated with syndecan suppression in S115 mouse mammary tumor cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Jan;2(1):1–11. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppä S., Mali M., Miettinen H. M., Jalkanen M. Syndecan expression regulates cell morphology and growth of mouse mammary epithelial tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):932–936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mali M., Jaakkola P., Arvilommi A. M., Jalkanen M. Sequence of human syndecan indicates a novel gene family of integral membrane proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6884–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pienta K. J., Partin A. W., Coffey D. S. Cancer as a disease of DNA organization and dynamic cell structure. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2525–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. C., Krufka A., Olwin B. B. Requirement of heparan sulfate for bFGF-mediated fibroblast growth and myoblast differentiation. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1705–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.1646484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mammary epithelial cells. Protease releases a heparan sulfate-rich ectodomain from a putative membrane-anchored domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4103–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan associates with the cytoskeleton at the basolateral cell surface of mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2683–2696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen S., Rapraeger A. Altered structure of the hybrid cell surface proteoglycan of mammary epithelial cells in response to transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1959–1967. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D. Post-transcriptional steps in the expression of chloroplast genes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Elenius K., Vainio S., Hofer U., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Syndecan from embryonic tooth mesenchyme binds tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Heino J., Jalkanen M. Basic fibroblast growth factor-syndecan complex at cell surface or immobilized to matrix promotes cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17606–17610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Bernfield M. Molecular polymorphism of a cell surface proteoglycan: distinct structures on simple and stratified epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9562–9566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Lalor P., Bernfield M. B lymphocytes express and lose syndecan at specific stages of differentiation. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):27–35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan binds mouse mammary epithelial cells to fibronectin and behaves as a receptor for interstitial matrix. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):423–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Jalkanen M., O'Farrell S., Bernfield M. Molecular cloning of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1547–1556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solursh M., Reiter R. S., Jensen K. L., Kato M., Bernfield M. Transient expression of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan (syndecan) during limb development. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90055-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. C., Freeze H. H., Sampath D., Garcia J. A. Uncoupling of chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan synthesis by brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1463–1473. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland A. E., Sanderson R. D., Mayes M., Seibert M., Calarco P. G., Bernfield M., Damsky C. H. Expression of syndecan, a putative low affinity fibroblast growth factor receptor, in the early mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):339–351. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Jalkanen M., Vainio S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan expression correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautman M. S., Kimelman J., Bernfield M. Developmental expression of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan, correlates with cell differentiation. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):213–220. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M., Saxén L. Transient expression of syndecan in mesenchymal cell aggregates of the embryonic kidney. Dev Biol. 1992 Aug;152(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Thesleff I. Syndecan and tenascin expression is induced by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in embryonic tooth mesenchyme. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1945–1953. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Vaahtokari A., Sahlberg C., Mali M., Bernfield M., Thesleff I. Expression of syndecan gene is induced early, is transient, and correlates with changes in mesenchymal cell proliferation during tooth organogenesis. Dev Biol. 1991 Oct;147(2):322–333. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90290-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]