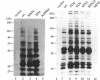
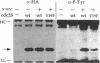
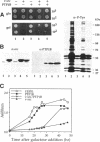
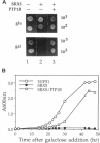
Abstract
Expression of pp60v-src, the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus, arrests the growth of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. To determine the basis of this growth arrest, yeast strains were constructed that expressed either wild-type v-src or various mutant v-src genes under the control of the galactose-inducible, glucose repressible GAL1 promoter. When shifted to galactose medium, cells expressing wild-type v-src ceased growth immediately and lost viability, whereas cells expressing a catalytically inactive mutant (K295M) continued to grow normally, indicating that the kinase activity of pp60v-src is required for its growth inhibitory effect. Mutants of v-src altered in the SH2/SH3 domain (XD4, XD6, SPX1, and SHX13) and a mutant lacking a functional N-terminal myristoylation signal (MM4) caused only a partial inhibition of growth, indicating that complete growth inhibition requires either targeting of the active kinase or binding of the kinase to phosphorylated substrates, or both. Cells arrested by v-src expression displayed aberrant microtubule structures, alterations in DNA content and elevated p34CDC28 kinase activity. Immunoblotting with antiphosphotyrosine antibody showed that many yeast proteins, including the p34CDC28 kinase, became phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells expressing v-src. Both the growth inhibition and the tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation observed following v-src expression were reversed by co-expression of a mammalian phosphotyrosine-specific phosphoprotein phosphatase (PTP1B). However a v-src mutant with a small insertion in the catalytic domain (SRX5) had the same lethal effect as wild-type v-src, yet induced only very low levels of protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. These results indicate that inappropriate phosphorylation at tyrosine is the primary cause of the lethal effect of pp60v-src expression but suggest that only a limited subset of the phosphorylated proteins are involved in this effect.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Rowley R. B., Spana C., Tsygankov A. Y. The Src family of tyrosine protein kinases in hemopoietic signal transduction. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3403–3409. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1281458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschelli F. Expression of p60v-src in Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in elevation of p34CDC28 kinase activity and release of the dependence of DNA replication on mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):5112–5121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.5112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Boschelli F., Uptain S. M., Lightbody J. J. The lethality of p60v-src in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the activation of p34CDC28 kinase are dependent on the integrity of the SH2 domain. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):519–528. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott B. K., Decker S., O'Brien M. C., Jove R. Molecular features of the viral and cellular Src kinases involved in interactions with the GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5059–5067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Jarosik G., Andersen J., Queral-Lustig A., Fedor-Chaiken M., Broach J. R. Expression of Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60v-src in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2180–2187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenevert J., Corrado K., Bender A., Pringle J., Herskowitz I. A yeast gene (BEM1) necessary for cell polarization whose product contains two SH3 domains. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):77–79. doi: 10.1038/356077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Howell B. The when and how of Src regulation. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Pfeuty T., Nouvian-Dooghe Y. Immunolocalization of the cellular src protein in interphase and mitotic NIH c-src overexpresser cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3097–3116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Mulholland J., Zhu Z. M., Botstein D. Homology of a yeast actin-binding protein to signal transduction proteins and myosin-I. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):288–290. doi: 10.1038/343288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., Towler D. A., Heuckeroth R. O., Gordon J. I. Disruption of the yeast N-myristoyl transferase gene causes recessive lethality. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):796–800. doi: 10.1126/science.2644694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Gartner A., Zhou Z., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. MAP kinase-related FUS3 from S. cerevisiae is activated by STE7 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):261–264. doi: 10.1038/362261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., O'Brien M. C., Hanafusa H. Deletions in the SH2 domain of p60v-src prevent association with the detergent-insoluble cellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner A., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. Signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of FUS3 and KSS1. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1280–1292. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Deschenes R. J., Qiu H., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a yeast protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12964–12970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K., Deschenes R. J., Dixon J. E. Isolation and characterization of a second protein tyrosine phosphatase gene, PTP2, from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10024–10030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K., Hakes D. J., Wang Y., Park H. D., Cooper T. G., Dixon J. E. A yeast protein phosphatase related to the vaccinia virus VH1 phosphatase is induced by nitrogen starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12175–12179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Hall B. D., Whelen S., Craig E. A. Multiple protein tyrosine phosphatase-encoding genes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1992 Dec 1;122(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90037-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Kornbluth S., Hanafusa H. Enzymatically inactive p60c-src mutant with altered ATP-binding site is fully phosphorylated in its carboxy-terminal regulatory region. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):937–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90520-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. B., Swedlow J. R., Varmus H. E., Morgan D. O. Association of p60c-src with endosomal membranes in mammalian fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):321–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellie S., Horvath A. R., Elmore M. A. Cytoskeletal targets for oncogenic tyrosine kinases. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):207–211. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Jove R., Hanafusa H. Characterization of avian and viral p60src proteins expressed in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebl E. C., England L. J., DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Host range mutants of v-src: alterations in kinase activity and substrate interactions. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4315–4324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4315-4324.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. Y., Dailey D., Martin G. S., Thorner J. Yeast MCK1 protein kinase autophosphorylates at tyrosine and serine but phosphorylates exogenous substrates at serine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21155–21164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. Dual-specificity protein kinases: will any hydroxyl do? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Cheng H. C., Wang J. H. Purification and characterization of a pp60c-src-related tyrosine kinase that effectively phosphorylates a synthetic peptide derived from p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2557–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclennan A. J., Shaw G. A yeast SH2 domain. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Dec;18(12):464–465. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Russell P. Human Wee1 kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyr15. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):75–85. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., Lenaers G., Russell P. Pyp3 PTPase acts as a mitotic inducer in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4933–4941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05600.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. J., Pendergast A. M., Havlik M. H., Puil L., Pawson T., Witte O. N. A limited set of SH2 domains binds BCR through a high-affinity phosphotyrosine-independent interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5087–5093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. M., Bergman M., Morgan D. O. Suppression of c-Src activity by C-terminal Src kinase involves the c-Src SH2 and SH3 domains: analysis with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5290–5300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Creative blocks: cell-cycle checkpoints and feedback controls. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):599–604. doi: 10.1038/359599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Collins C. A., Hammarback J. A., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the microtubule-associated mechanochemical enzyme dynamin reveals homology with a new family of GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):256–261. doi: 10.1038/347256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottilie S., Chernoff J., Hannig G., Hoffman C. S., Erikson R. L. The fission yeast genes pyp1+ and pyp2+ encode protein tyrosine phosphatases that negatively regulate mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5571–5580. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin M. J., Williams L. T. Triggering signaling cascades by receptor tyrosine kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90003-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodaway A. R., Teahan C. G., Casimir C. M., Segal A. W., Bentley D. L. Characterization of the 47-kilodalton autosomal chronic granulomatous disease protein: tissue-specific expression and transcriptional control by retinoic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5388–5396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Moreno S., Reed S. I. Conservation of mitotic controls in fission and budding yeasts. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90967-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Zheng P., Beidler D. R., Zerillo C. Spk1, a new kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, phosphorylates proteins on serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):987–1001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Fumagalli S., Koegl M., Courtneidge S. A., Draetta G. Csk inhibition of c-Src activity requires both the SH2 and SH3 domains of Src. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2625–2634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarpley W. G., Temin H. M. The location of v-src in a retrovirus vector determines whether the virus is toxic or transforming. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2653–2660. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan J., Xu H., Grunstein M. CDC14 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cloning, sequence analysis, and transcription during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11274–11280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Effects of the src gene product on microfilament and microtubule organization in avian and mammalian cells infected with the same temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasenius V. M., Saraste M., Lehto V. P. From the spectrin gene to the assembly of the membrane skeleton. Int J Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;33(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodford-Thomas T. A., Rhodes J. D., Dixon J. E. Expression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase in normal and v-src-transformed mouse 3T3 fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):401–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Lindquist S. Heat-shock protein hsp90 governs the activity of pp60v-src kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7074–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng P., Fay D. S., Burton J., Xiao H., Pinkham J. L., Stern D. F. SPK1 is an essential S-phase-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that encodes a nuclear serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5829–5842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]