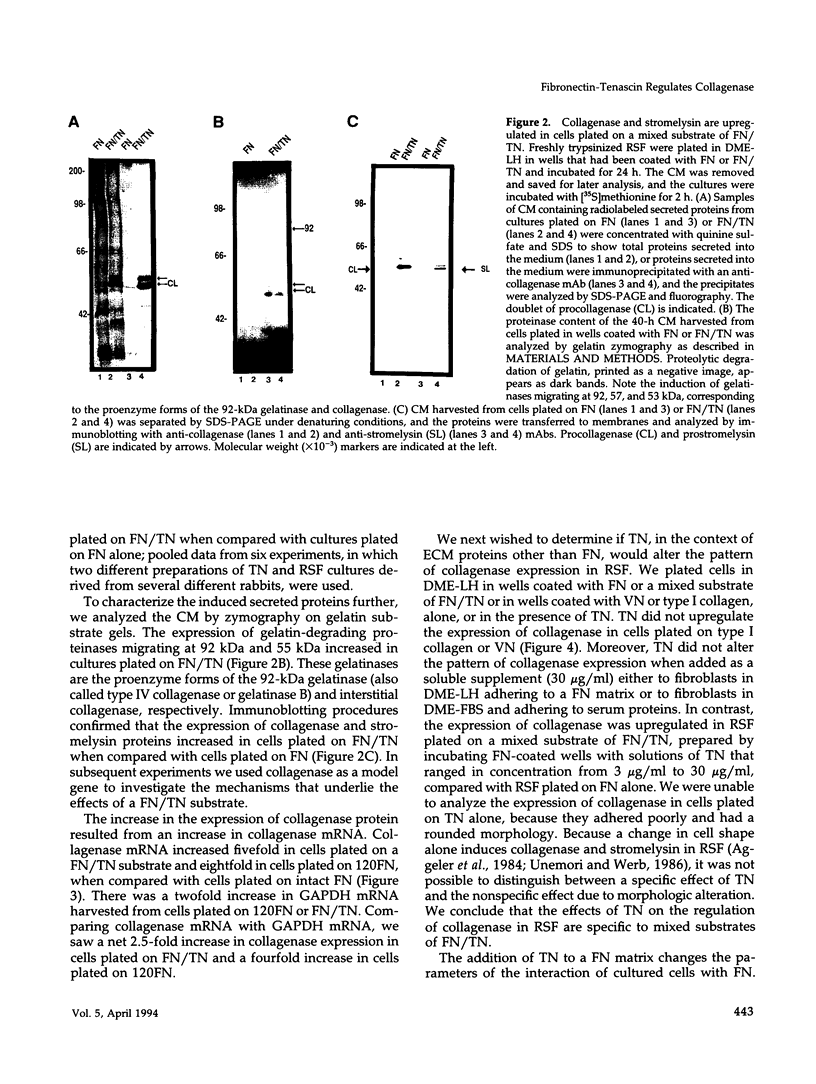
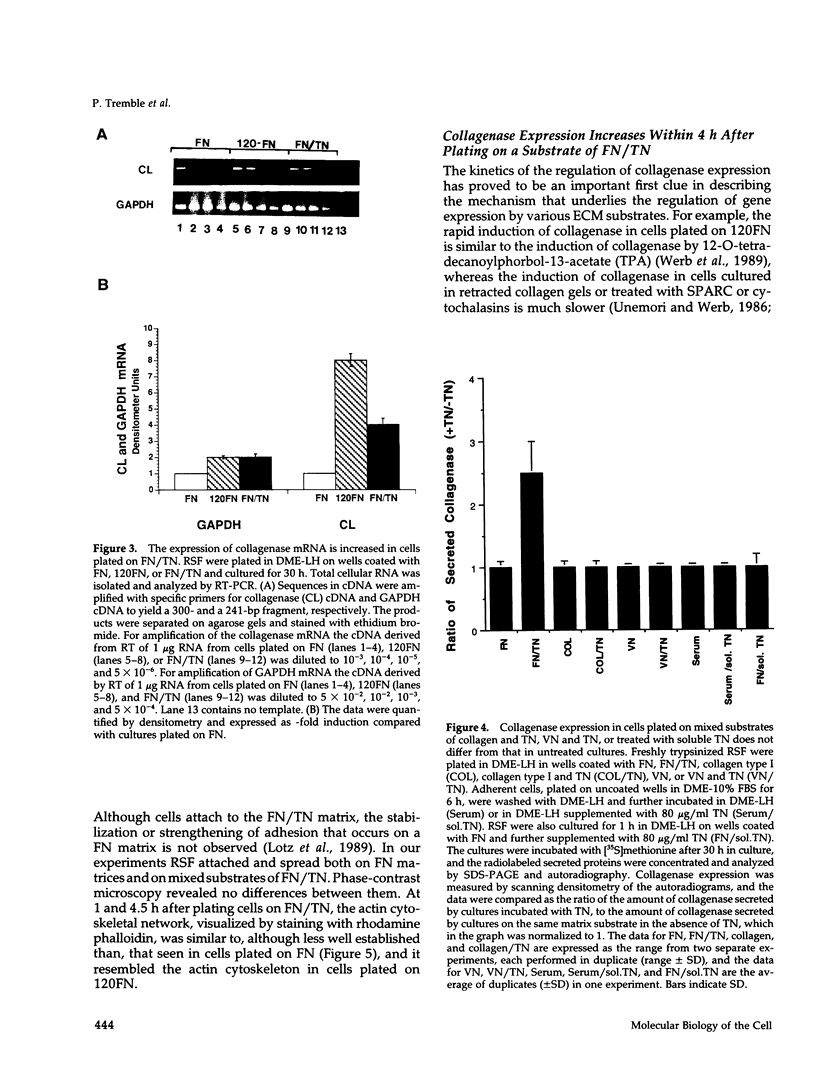
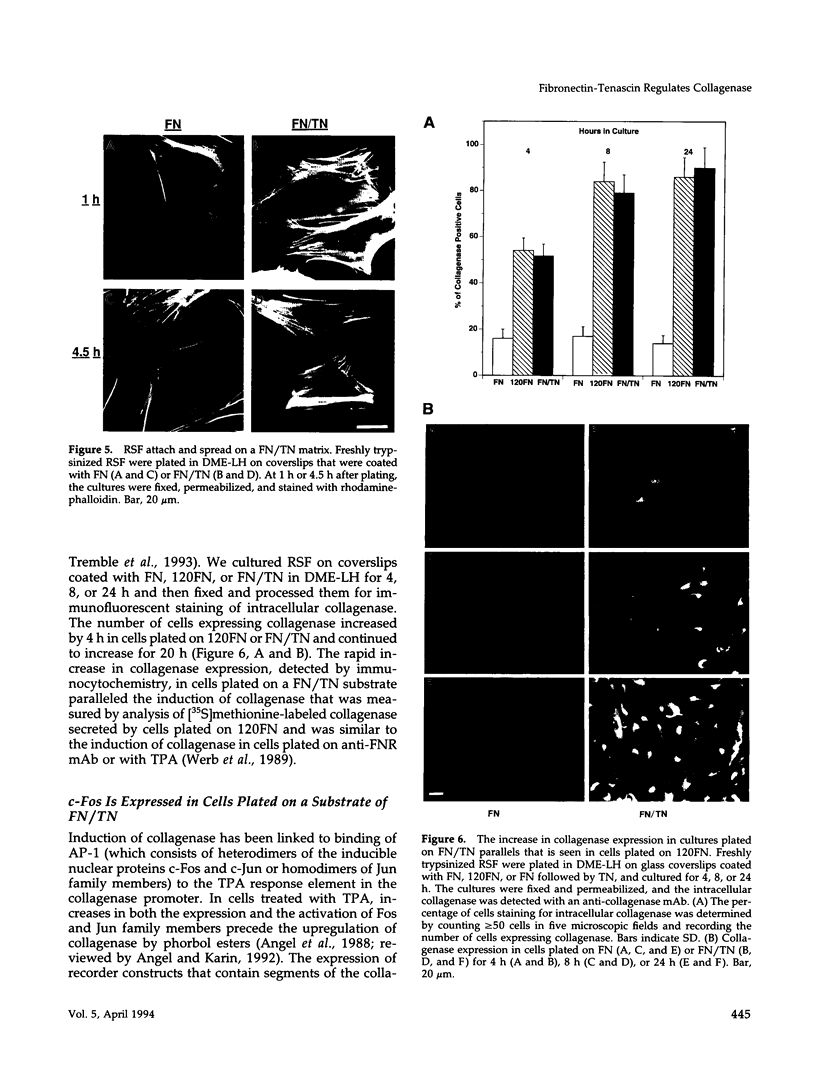
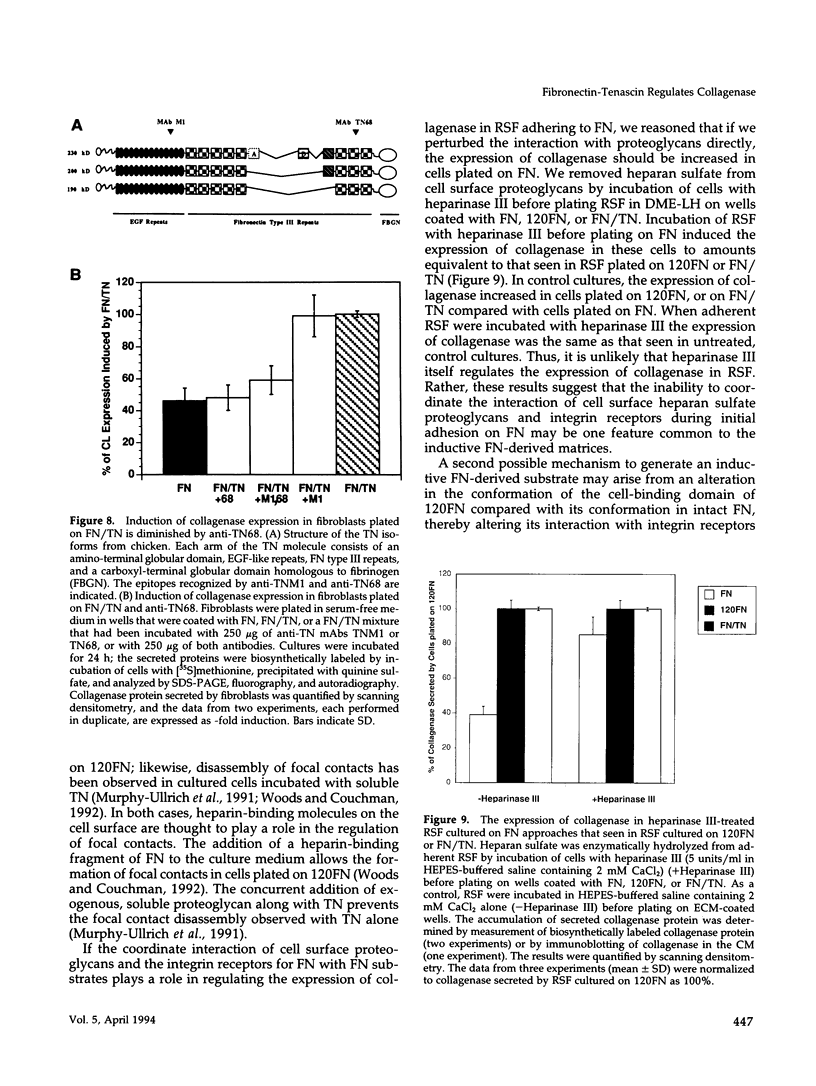
Abstract
Tenascin (TN) is a large oligomeric glycoprotein that is present transiently in the extracellular matrix (ECM) of cells and is involved in morphogenetic movements, tissue patterning, and tissue repair. It has multiple domains, both adhesive and anti-adhesive, that interact with cells and with fibronectin (FN) and other ECM macromolecules. We have studied the consequences of the interaction of TN with a FN matrix on gene expression in rabbit synovial fibroblasts. Fibroblasts plated on a mixed substrate of FN and TN, but not on FN alone, upregulated synthesis of four genes: collagenase, stromelysin, the 92-kDa gelatinase, and c-fos. Although the fibroblasts spread well on both FN and FN/TN substrates, nuclear c-Fos increased within 1 h only in cells that were plated on FN/TN. TN did not induce the expression of collagenase in cells plated on substrates of type I collagen or vitronectin (VN). Moreover, soluble TN added to cells adhering to a FN substrate or to serum proteins had no effect, suggesting that TN has an effect only in the context of mixed substrates of FN and TN. Collagenase increased within 4 h of plating on a FN/TN substrate and exhibited kinetics similar to those for induction of collagenase gene expression by signaling through the integrin FN receptor. Arg-Gly-Asp peptide ligands that recognize either the FN receptor or the VN receptor and function-perturbing anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies diminished the interaction of fibroblasts with a mixed substrate of FN, TN, and VN, but had no effect on the adhesion of fibroblasts to a substrate of FN and VN, suggesting that both receptors recognize the complex. Anti-TN68, an antibody that recognizes an epitope in the carboxyl-terminal type III repeats involved in the interaction of TN with both FN and cells, blocked the inductive effect of the FN/TN substrate, whereas anti-TNM1, an antibody that recognizes an epitope in the amino-terminal anti-adhesive region of epidermal growth factor-like repeats, had no effect. These data suggest that transient alteration of the composition of ECM by addition of proteins like TN may regulate the expression of genes involved in cell migration, tissue remodeling, and tissue invasion, in regions of tissue undergoing phenotypic changes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggeler J., Frisch S. M., Werb Z. Collagenase is a major gene product of induced rabbit synovial fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1656–1661. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander C. M., Werb Z. Targeted disruption of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases gene increases the invasive behavior of primitive mesenchymal cells derived from embryonic stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):727–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. Specific members of the Jun protein family regulate collagenase expression in response to various extracellular stimuli. Matrix Suppl. 1992;1:156–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auble D. T., Brinckerhoff C. E. The AP-1 sequence is necessary but not sufficient for phorbol induction of collagenase in fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4629–4635. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C. A., Adler R. R., Rappolee D. A., Pedersen R. A., Werb Z. Genes for extracellular-matrix-degrading metalloproteinases and their inhibitor, TIMP, are expressed during early mammalian development. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):848–859. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Anti-adhesive molecules of the extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):800–804. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Kalla P., Pearson C. A., Beck K., Chiquet M. Tenascin interferes with fibronectin action. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Mackie E. J., Pearson C. A., Sakakura T. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein involved in tissue interactions during fetal development and oncogenesis. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Matsuoka Y., Hofer U., Spring J., Bernasconi C., Chiquet M. Tenascin variants: differential binding to fibronectin and distinct distribution in cell cultures and tissues. Cell Regul. 1991 Nov;2(11):927–938. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.11.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Fambrough D. M. Chick myotendinous antigen. I. A monoclonal antibody as a marker for tendon and muscle morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1926–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Vrucinić-Filipi N., Schenk S., Beck K., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Isolation of chick tenascin variants and fragments. A C-terminal heparin-binding fragment produced by cleavage of the extra domain from the largest subunit splicing variant. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damsky C. H., Werb Z. Signal transduction by integrin receptors for extracellular matrix: cooperative processing of extracellular information. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):772–781. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90100-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Aufderheide E. Stimulation of tenascin expression in mesenchyme by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Int J Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;33(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. Domains in proteins and proteoglycans of the extracellular matrix with functions in assembly and cellular activities. Int J Biol Macromol. 1991 Jun;13(3):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(91)90039-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Bourdon M. A. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein prominent in specialized embryonic tissues and tumors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:71–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ffrench-Constant C., Van de Water L., Dvorak H. F., Hynes R. O. Reappearance of an embryonic pattern of fibronectin splicing during wound healing in the adult rat. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander D. R., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Functional mapping of cytotactin: proteolytic fragments active in cell-substrate adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2329–2340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatchalian C. L., Schachner M., Sanes J. R. Fibroblasts that proliferate near denervated synaptic sites in skeletal muscle synthesize the adhesive molecules tenascin(J1), N-CAM, fibronectin, and a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1873–1890. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Plow E. Inhibition of fibronectin binding to platelets by proteolytic fragments and synthetic peptides which support fibroblast adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):3931–3936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulcher J. R., Nies D. E., Alexakos M. J., Ravikant N. A., Sturgill M. E., Marton L. S., Stefansson K. Structure of the human hexabrachion (tenascin) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9438–9442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter W., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Tucker R. P. The effect of tenascin and embryonic basal lamina on the behavior and morphology of neural crest cells in vitro. Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;132(1):14–25. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Molecular forms, binding functions, and developmental expression patterns of cytotactin and cytotactin-binding proteoglycan, an interactive pair of extracellular matrix molecules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):519–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. E., Arumugham R. G., Tanzer M. L. Fibronectin glycosylation modulates fibroblast adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi P., Chung C. Y., Aukhil I., Erickson H. P. Endothelial cells adhere to the RGD domain and the fibrinogen-like terminal knob of tenascin. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):389–400. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Herbst H., Hummel M., Dürkop H., Tripier D., Stein H., Schuppan D. Undulin is a novel member of the fibronectin-tenascin family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17326–17332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner V. A., Erickson H. P. Binding of hexabrachion (tenascin) to the extracellular matrix and substratum and its effect on cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1990 Feb;95(Pt 2):263–277. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochter A., Vaughan L., Kaplony A., Prochiantz A., Schachner M., Faissner A. J1/tenascin in substrate-bound and soluble form displays contrary effects on neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1159–1171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M. M., Burdsal C. A., Erickson H. P., McClay D. R. Cell adhesion to fibronectin and tenascin: quantitative measurements of initial binding and subsequent strengthening response. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1795–1805. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. J., Halfter W., Liverani D. Induction of tenascin in healing wounds. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2757–2767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Arai M., Ishihara N., Ando A., Inoko H., Ikemura T. Cluster of fibronectin type III repeats found in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region shows the highest homology with the repeats in an extracellular matrix protein, tenascin. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):485–491. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Lightner V. A., Aukhil I., Yan Y. Z., Erickson H. P., Hök M. Focal adhesion integrity is downregulated by the alternatively spliced domain of human tenascin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1127–1136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. E., Hemesath T. J., Kim J. H., Gulcher J. R., Stefansson K. The complete cDNA sequence of human hexabrachion (Tenascin). A multidomain protein containing unique epidermal growth factor repeats. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2818–2823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Weinstein J., Gillespie W. M., Paulson J. C. Complete primary structure of porcine tenascin. Detection of tenascin transcripts in adult submaxillary glands. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):643–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nörenberg U., Wille H., Wolff J. M., Frank R., Rathjen F. G. The chicken neural extracellular matrix molecule restrictin: similarity with EGF-, fibronectin type III-, and fibrinogen-like motifs. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):849–863. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90199-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto A. L., Andersson-Fisone C., Crossin K. L. Characterization of multiple adhesive and counteradhesive domains in the extracellular matrix protein cytotactin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):663–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto A. L., Jones F. S., Cunningham B. A., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Localization during development of alternatively spliced forms of cytotactin mRNA by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):685–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Sturm K. S., Behrendtsen O., Schultz G. A., Pedersen R. A., Werb Z. Insulin-like growth factor II acts through an endogenous growth pathway regulated by imprinting in early mouse embryos. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):939–952. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. F., Shi D. L., Chiquet M., Boucaut J. C. Exogenous tenascin inhibits mesodermal cell migration during amphibian gastrulation. Dev Biol. 1990 Feb;137(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90256-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saga Y., Yagi T., Ikawa Y., Sakakura T., Aizawa S. Mice develop normally without tenascin. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1821–1831. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E. H., Bornstein P. Extracellular proteins that modulate cell-matrix interactions. SPARC, tenascin, and thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14831–14834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Elenius K., Vainio S., Hofer U., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Syndecan from embryonic tooth mesenchyme binds tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siri A., Carnemolla B., Saginati M., Leprini A., Casari G., Baralle F., Zardi L. Human tenascin: primary structure, pre-mRNA splicing patterns and localization of the epitopes recognized by two monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):525–531. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring J., Beck K., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Two contrary functions of tenascin: dissection of the active sites by recombinant tenascin fragments. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriramarao P., Mendler M., Bourdon M. A. Endothelial cell attachment and spreading on human tenascin is mediated by alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 integrins. J Cell Sci. 1993 Aug;105(Pt 4):1001–1012. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.4.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steindler D. A., Cooper N. G., Faissner A., Schachner M. Boundaries defined by adhesion molecules during development of the cerebral cortex: the J1/tenascin glycoprotein in the mouse somatosensory cortical barrel field. Dev Biol. 1989 Jan;131(1):243–260. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talhouk R. S., Bissell M. J., Werb Z. Coordinated expression of extracellular matrix-degrading proteinases and their inhibitors regulates mammary epithelial function during involution. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1271–1282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremble P. M., Lane T. F., Sage E. H., Werb Z. SPARC, a secreted protein associated with morphogenesis and tissue remodeling, induces expression of metalloproteinases in fibroblasts through a novel extracellular matrix-dependent pathway. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1433–1444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. P., McKay S. E. The expression of tenascin by neural crest cells and glia. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):1031–1039. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemori E. N., Werb Z. Reorganization of polymerized actin: a possible trigger for induction of procollagenase in fibroblasts cultured in and on collagen gels. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrle B., Chiquet M. Tenascin is accumulated along developing peripheral nerves and allows neurite outgrowth in vitro. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):401–415. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller A., Beck S., Ekblom P. Amino acid sequence of mouse tenascin and differential expression of two tenascin isoforms during embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):355–362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
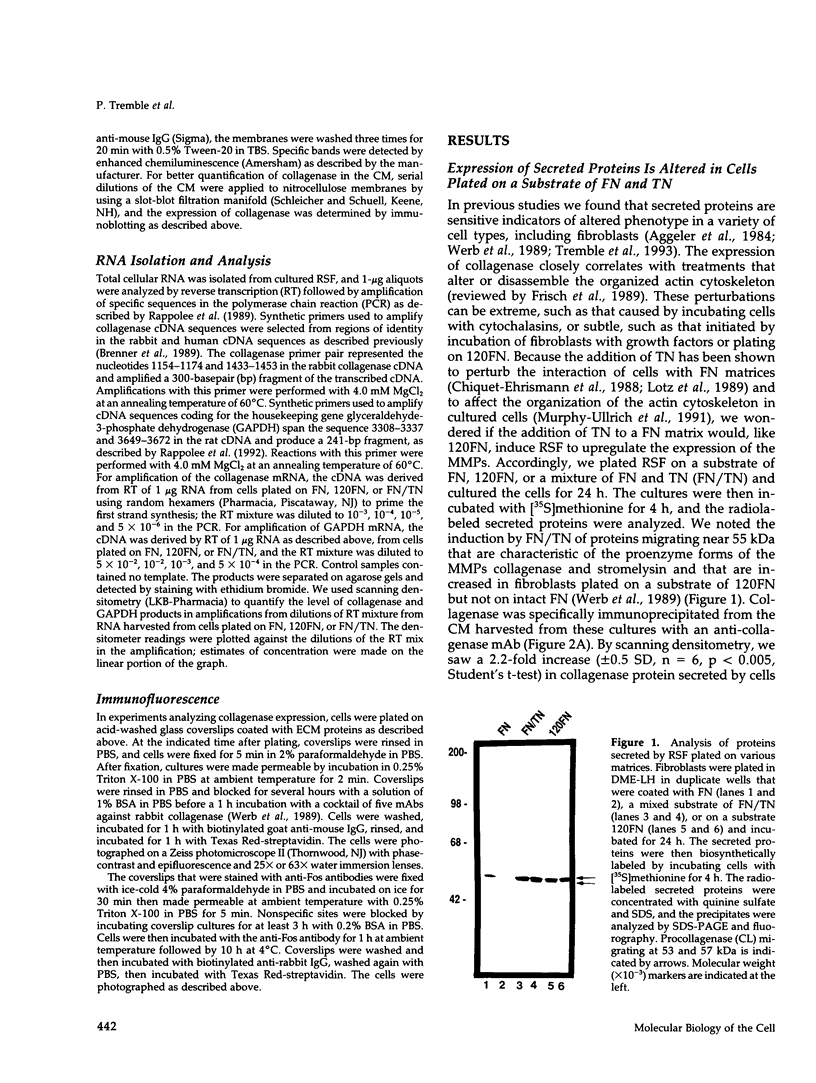
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby D. J., Ferguson M. W. The extracellular matrix of lip wounds in fetal, neonatal and adult mice. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):651–668. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby D. J., Longaker M. T., Harrison M. R., Adzick N. S., Ferguson M. W. Rapid epithelialisation of fetal wounds is associated with the early deposition of tenascin. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jul;99(Pt 3):583–586. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.3.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Wunderlich D., Maniglia C. A., Eisen A. Z., Goldberg G. I. Primary structure and function of stromelysin/transin in cartilage matrix turnover. Matrix Suppl. 1992;1:37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R. Protein kinase C involvement in focal adhesion formation. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):277–290. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisch A. H., D'Alessandri L., Ranscht B., Falchetto R., Winterhalter K. H., Vaughan L. Neuronal cell adhesion molecule contactin/F11 binds to tenascin via its immunoglobulin-like domains. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):203–213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]