Abstract
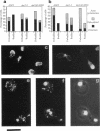
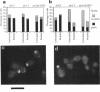
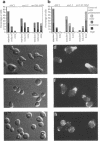
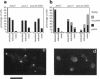
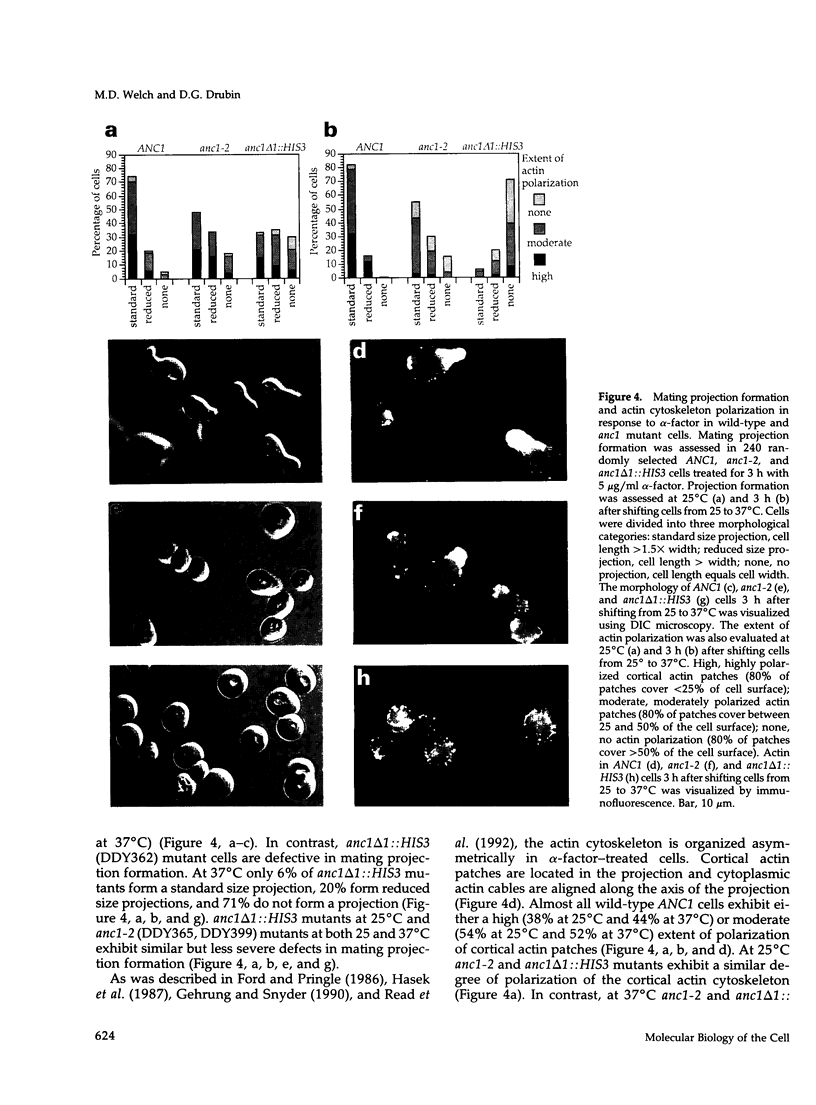
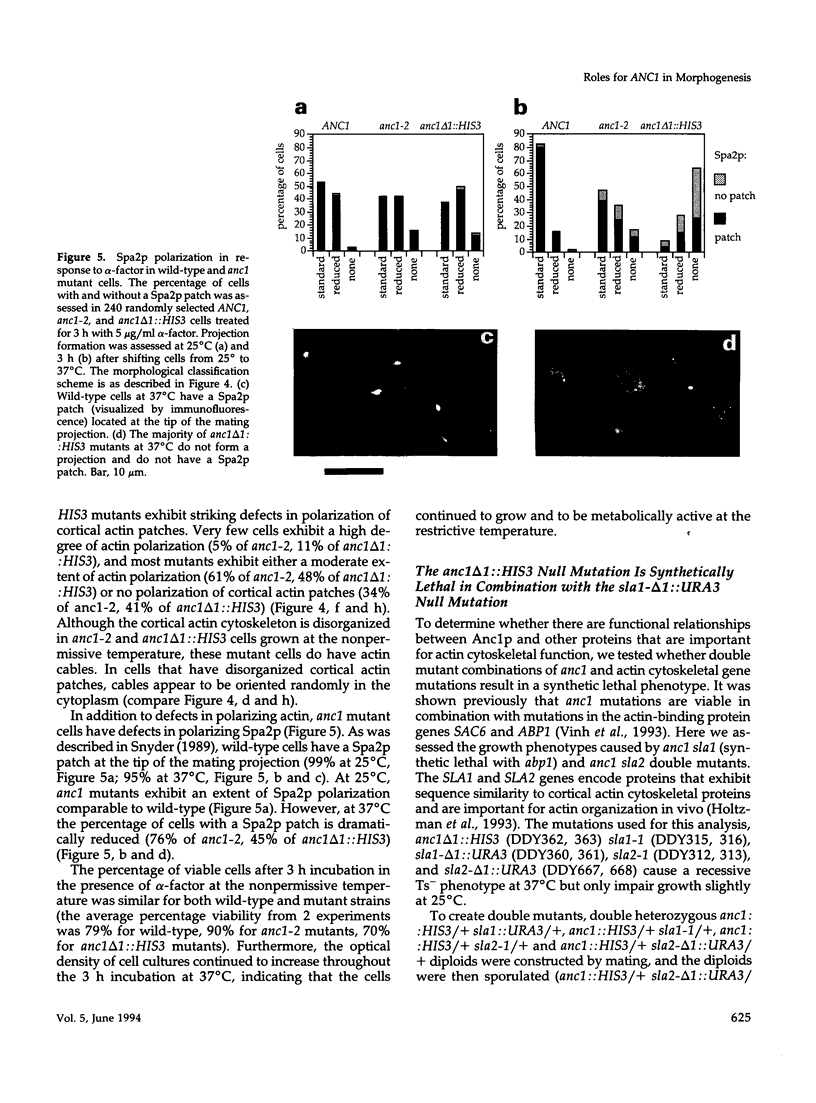
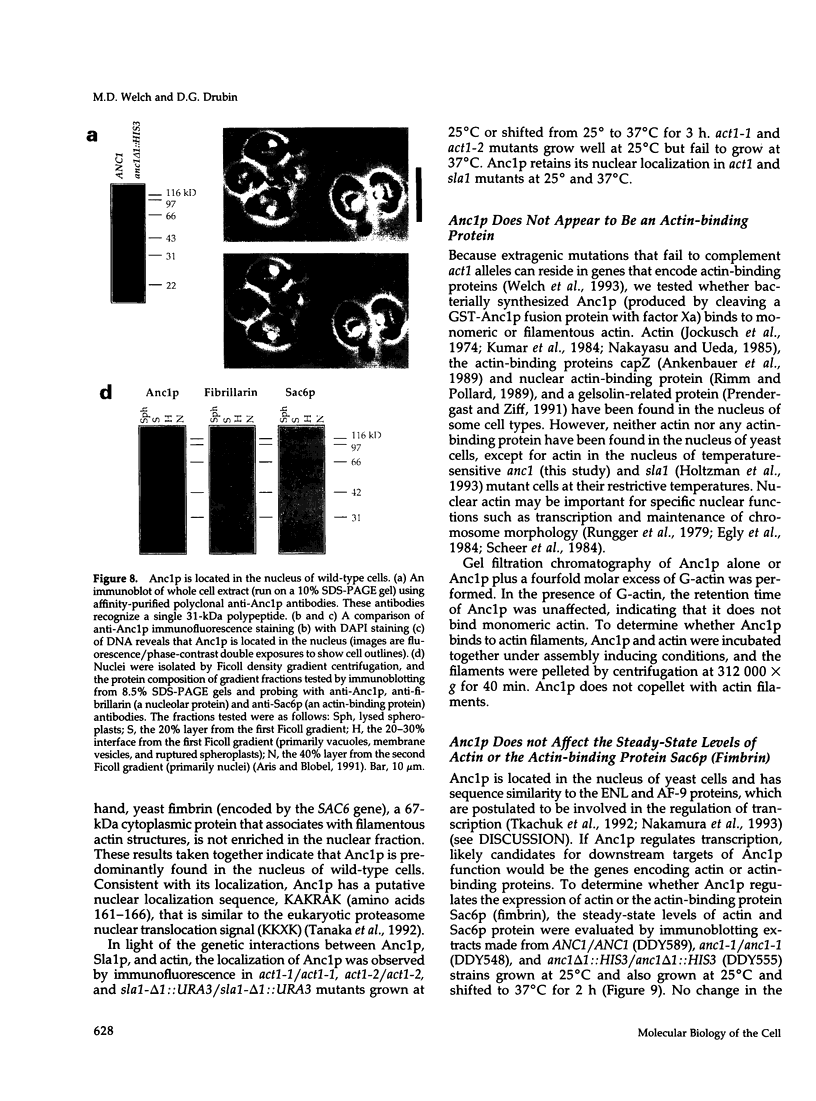
The cellular functions of the product of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ANC1 (actin non-complementing) gene were investigated. ANC1 was previously identified in a screen for mutations that enhance the defect caused by a mutation in the actin gene. Here, we show that anc1-1 and anc1 delta 1::HIS3 (gene deletion) mutants exhibit a novel combination of defects in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton and the localization of Spa2p, a protein implicated in polarity development and cytokinesis. Morphological abnormalities exhibited by anc1 mutants include failure to form a mating projection in response to alpha-factor and development of swollen or elongated cell shapes during proliferation. These morphological aberrations correlate with cytoskeletal defects that were also observed. These phenotypes demonstrate that Anc1p is important for actin function and for the functions of other proteins involved in morphogenesis. In further support of these roles for Anc1p, the anc1 delta 1::HIS3 mutation was found to be synthetically lethal in combination with a null mutation in SLA1, a gene that is important for membrane cytoskeleton function. Surprisingly, Anc1p was found to be a nuclear protein and to have sequence similarity to the human proteins ENL and AF-9. These human proteins are implicated in the development of a subset of acute lymphoblastic leukemias, acute myeloid leukemias, and lymphomas. Our findings suggest that changes in the functions or organization of actin filaments might contribute to the establishment of the neoplastic state for these leukemias and lymphomas.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Botstein D., Drubin D. G. Requirement of yeast fimbrin for actin organization and morphogenesis in vivo. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):404–408. doi: 10.1038/354404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
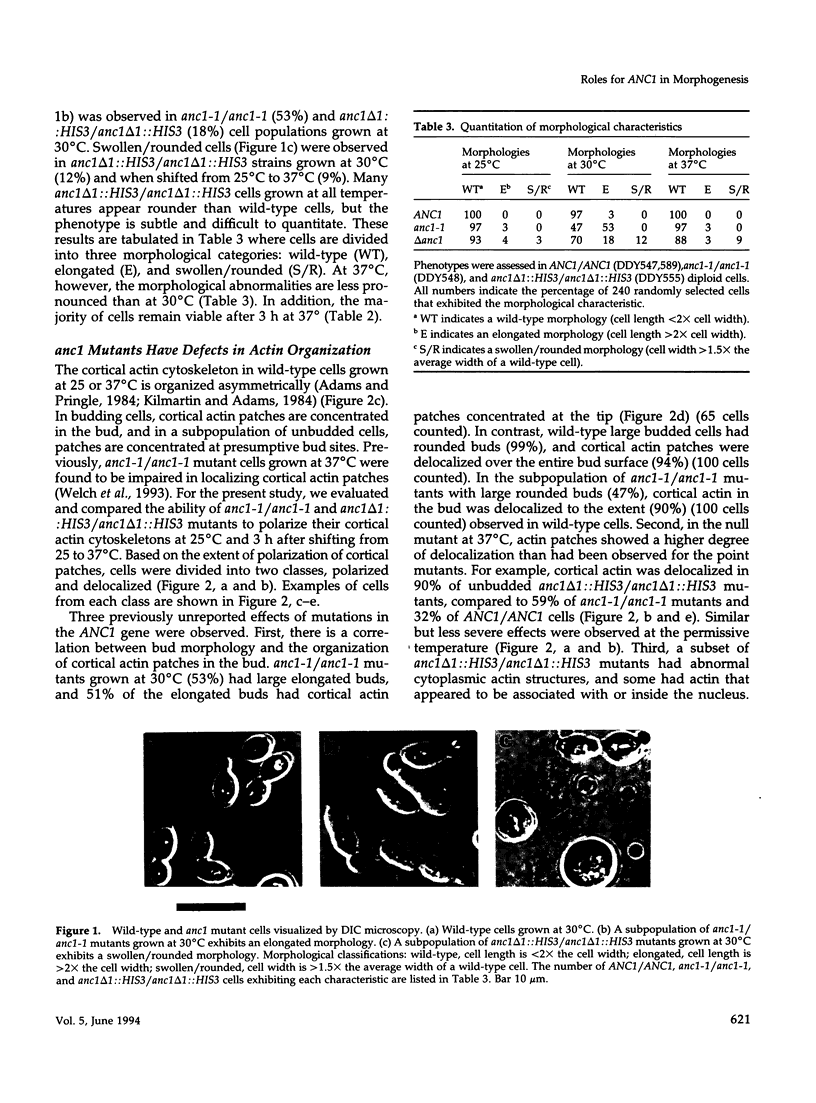
- Adams A. E., Pringle J. R. Relationship of actin and tubulin distribution to bud growth in wild-type and morphogenetic-mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):934–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ankenbauer T., Kleinschmidt J. A., Walsh M. J., Weiner O. H., Franke W. W. Identification of a widespread nuclear actin binding protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):822–825. doi: 10.1038/342822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a yeast nucleolar protein that is similar to a rat liver nucleolar protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):17–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Isolation of yeast nuclei. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:735–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94056-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes G., Drubin D. G., Stearns T. The cytoskeleton of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;2(1):109–115. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigati C., Kurtz S., Balderes D., Vidali G., Shore D. An essential yeast gene encoding a TTAGGG repeat-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1306–1314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djabali M., Selleri L., Parry P., Bower M., Young B. D., Evans G. A. A trithorax-like gene is interrupted by chromosome 11q23 translocations in acute leukaemias. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):113–118. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G. Development of cell polarity in budding yeast. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1093–1096. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90001-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Jones H. D., Wertman K. F. Actin structure and function: roles in mitochondrial organization and morphogenesis in budding yeast and identification of the phalloidin-binding site. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1277–1294. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Miller K. G., Botstein D. Yeast actin-binding proteins: evidence for a role in morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2551–2561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egly J. M., Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Chambon P. Is actin a transcription initiation factor for RNA polymerase B? EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2363–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrung S., Snyder M. The SPA2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for pheromone-induced morphogenesis and efficient mating. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1451–1464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasek J., Rupes I., Svobodová J., Streiblová E. Tubulin and actin topology during zygote formation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3355–3363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman D. A., Yang S., Drubin D. G. Synthetic-lethal interactions identify two novel genes, SLA1 and SLA2, that control membrane cytoskeleton assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):635–644. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Becker M., Hindennach I., Jockusch H. Slime mould actin: homology to vertebrate actin and presence in the nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Dec;89(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90787-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Adams A. E. Structural rearrangements of tubulin and actin during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):922–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Raziuddin, Finlay T. H., Thomas J. O., Szer W. Isolation of a minor species of actin from the nuclei of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6753–6757. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Reed S. I. Morphogenesis in the yeast cell cycle: regulation by Cdc28 and cyclins. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1305–1320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter J. R., Wang J. Y. Activation of tyrosinase kinase and microfilament-binding functions of c-abl by bcr sequences in bcr/abl fusion proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1553–1565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon A. L., Janmey P. A., Louie K. A., Drubin D. G. Cofilin is an essential component of the yeast cortical cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):421–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Alder H., Gu Y., Prasad R., Canaani O., Kamada N., Gale R. P., Lange B., Crist W. M., Nowell P. C. Genes on chromosomes 4, 9, and 19 involved in 11q23 abnormalities in acute leukemia share sequence homology and/or common motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu H., Ueda K. Ultrastructural localization of actin in nuclear matrices from mouse leukemia L5178Y cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1985 Sep;10(3):305–309. doi: 10.1247/csf.10.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Botstein D. Phenotypic analysis of temperature-sensitive yeast actin mutants. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Drubin D. G., Kelly R. B. Identification of three coated vesicle components as alpha- and beta-tubulin linked to a phosphorylated 50,000-dalton polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):40–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Mbh 1: a novel gelsolin/severin-related protein which binds actin in vitro and exhibits nuclear localization in vivo. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):757–766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08007.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read E. B., Okamura H. H., Drubin D. G. Actin- and tubulin-dependent functions during Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating projection formation. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):429–444. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Pollard T. D. Purification and characterization of an Acanthamoeba nuclear actin-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):585–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Rungger-Brändle E., Chaponnier C., Gabbiani G. Intranuclear injection of anti-actin antibodies into Xenopus oocytes blocks chromosome condensation. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):320–321. doi: 10.1038/282320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Hinssen H., Franke W. W., Jockusch B. M. Microinjection of actin-binding proteins and actin antibodies demonstrates involvement of nuclear actin in transcription of lampbrush chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Gräff A., Chaponnier C., Gabbiani G. Cytoskeletal organization of peripheral blood normal and leukemic lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1987 Apr;19(2):329–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze E., Kirschner M. Microtubule dynamics in interphase cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1020–1031. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Gehrung S., Page B. D. Studies concerning the temporal and genetic control of cell polarity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):515–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. The SPA2 protein of yeast localizes to sites of cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1419–1429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Tamura T., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A. Proteasomes: protein and gene structures. New Biol. 1992 Mar;4(3):173–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk D. C., Kohler S., Cleary M. L. Involvement of a homolog of Drosophila trithorax by 11q23 chromosomal translocations in acute leukemias. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):691–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90602-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinh D. B., Welch M. D., Corsi A. K., Wertman K. F., Drubin D. G. Genetic evidence for functional interactions between actin noncomplementing (Anc) gene products and actin cytoskeletal proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):275–286. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. D., Holtzman D. A., Drubin D. G. The yeast actin cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):110–119. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. D., Vinh D. B., Okamura H. H., Drubin D. G. Screens for extragenic mutations that fail to complement act1 alleles identify genes that are important for actin function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):265–274. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr Nuclear pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Yeast. 1989 Nov-Dec;5(6):439–457. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]