Abstract
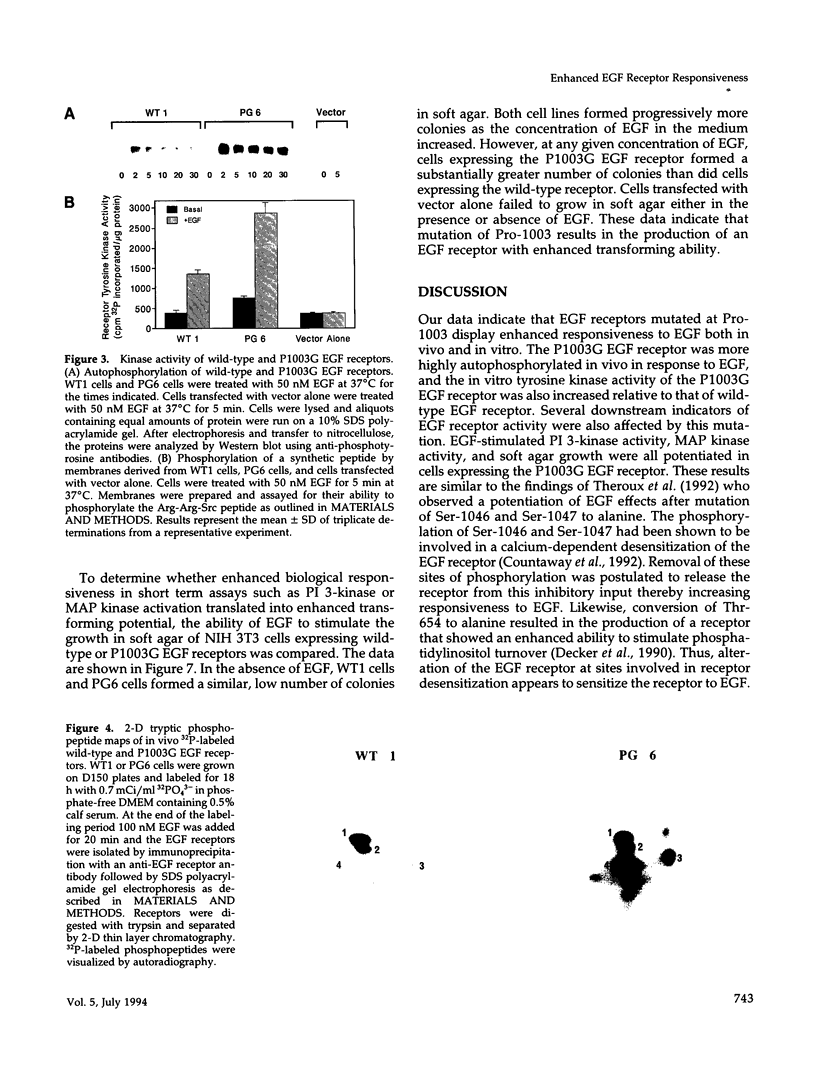
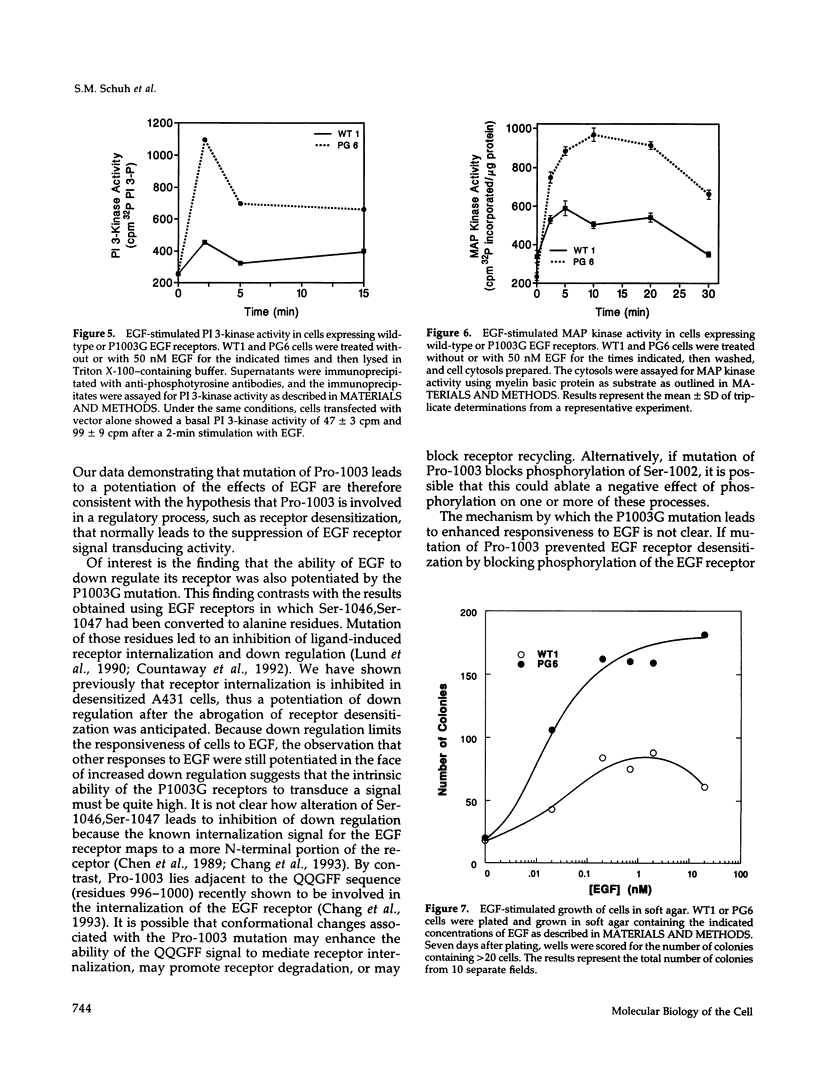
We have shown previously that the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor is phosphorylated at Ser-1002 and that this phosphorylation is associated with desensitization of the EGF receptor. Ser-1002 is followed immediately by Pro-1003, a residue that may promote the adoption of a specific conformation at this site or severe as a recognition element for the interaction of the EGF receptor with other proteins. To examine these possibilities, we have mutated Pro-1003 of the EGF receptor to a Gly residue and have analyzed the effect of this mutation on EGF-stimulated signaling. Cells expressing the P1003G EGF receptors exhibited higher EGF-stimulated autophosphorylation and synthetic peptide phosphorylation compared to cells expressing wild-type EGF receptors. In addition, the ability of EGF to stimulate PI 3-kinase activity and mitogen-activated protein kinase activity was enhanced in cells expressing the P1003G EGF receptor. Cells expressing P1003G receptors also demonstrated an increased ability to form colonies in soft agar in response to EGF. These results indicate that mutation of Pro-1003 leads to a potentiation of the biological effects of EGF. The findings are consistent with the hypothesis that Pro-1003 plays a role in a form of regulation that normally suppresses EGF receptor function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):409–410. doi: 10.1038/276409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Lazar C. S., Walsh B. J., Komuro M., Collawn J. F., Kuhn L. A., Tainer J. A., Trowbridge I. S., Farquhar M. G., Rosenfeld M. G. Ligand-induced internalization of the epidermal growth factor receptor is mediated by multiple endocytic codes analogous to the tyrosine motif found in constitutively internalized receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19312–19320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Lund K. A., Welsh J. B., Chang C. P., Walton G. M., Der C. J., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and calcium regulation. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Kashles O., Chambaz E. M., Borrello I., King C. R., Schlessinger J. Demonstration of epidermal growth factor-induced receptor dimerization in living cells using a chemical covalent cross-linking agent. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3290–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., Nairn A. C., Davis R. J. Mechanism of desensitization of the epidermal growth factor receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1129–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. W., Kuppuswamy D., Pike L. J. Treatment of A431 cells with epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces desensitization of EGF-stimulated phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15351–15356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1974–1978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Ellis C., Pawson T., Velu T. Effects of substitution of threonine 654 of the epidermal growth factor receptor on epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7009–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Connors J. M., Fujiki H., Sugimura T., Rosner M. R. Tumor promoters block tyrosine-specific phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale N. W., Kaplan S., Lowenstein E. J., Schlessinger J., Bar-Sagi D. Grb2 mediates the EGF-dependent activation of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ras. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):88–92. doi: 10.1038/363088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsuan J. J., Totty N., Waterfield M. D. Identification of a novel autophosphorylation site (P4) on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):659–663. doi: 10.1042/bj2620659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
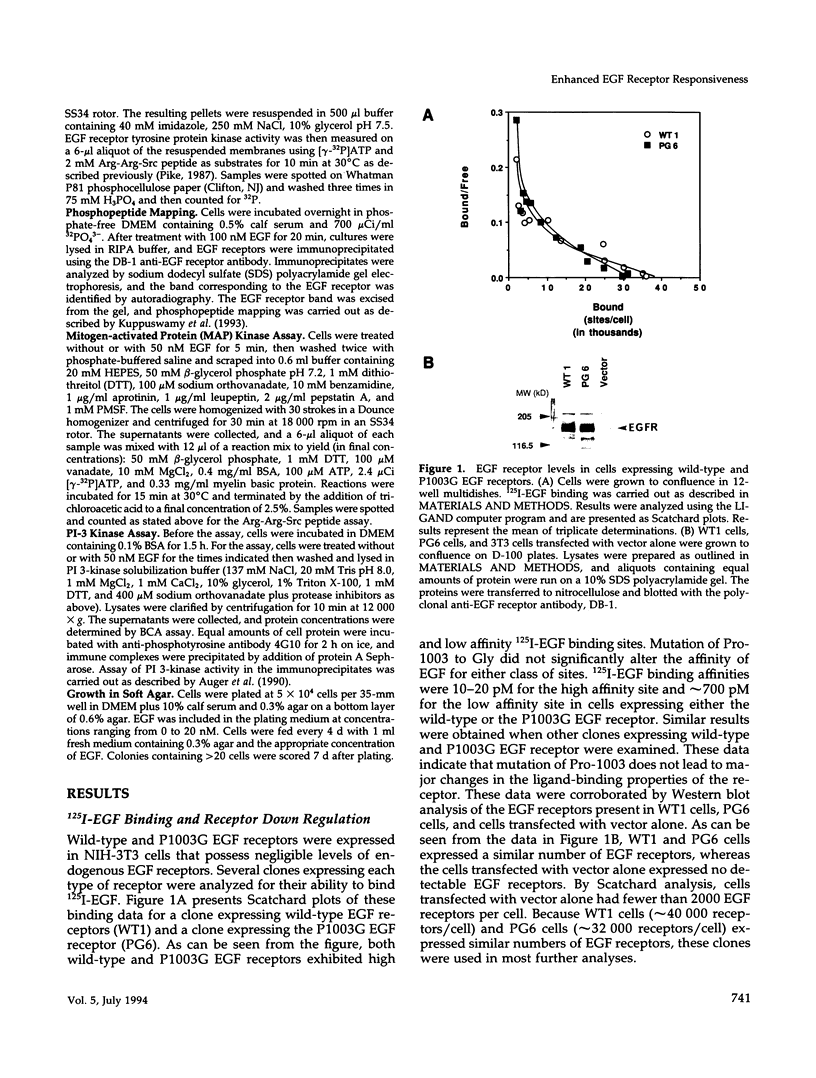
- Kuppuswamy D., Dalton M., Pike L. J. Serine 1002 is a site of in vivo and in vitro phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19134–19142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy D., Pike L. J. Desensitization of the EGF receptor alters its ability to undergo EGF-induced dimerization. Cell Signal. 1991;3(2):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90017-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy D., Pike L. J. Ligand-induced desensitization of 125I-epidermal growth factor internalization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3357–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Kruiger W., Stolarsky L. S., Weber W., Evans R. M., Verma I. M., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression cloning of human EGF receptor complementary DNA: gene amplification and three related messenger RNA products in A431 cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):843–848. doi: 10.1126/science.6326261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K. A., Lazar C. S., Chen W. S., Walsh B. J., Welsh J. B., Herbst J. J., Walton G. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N., Wiley H. S. Phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 654 inhibits ligand-induced internalization and down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20517–20523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J. Assay of growth factor-stimulated tyrosine kinases using synthetic peptide substrates. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:353–362. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
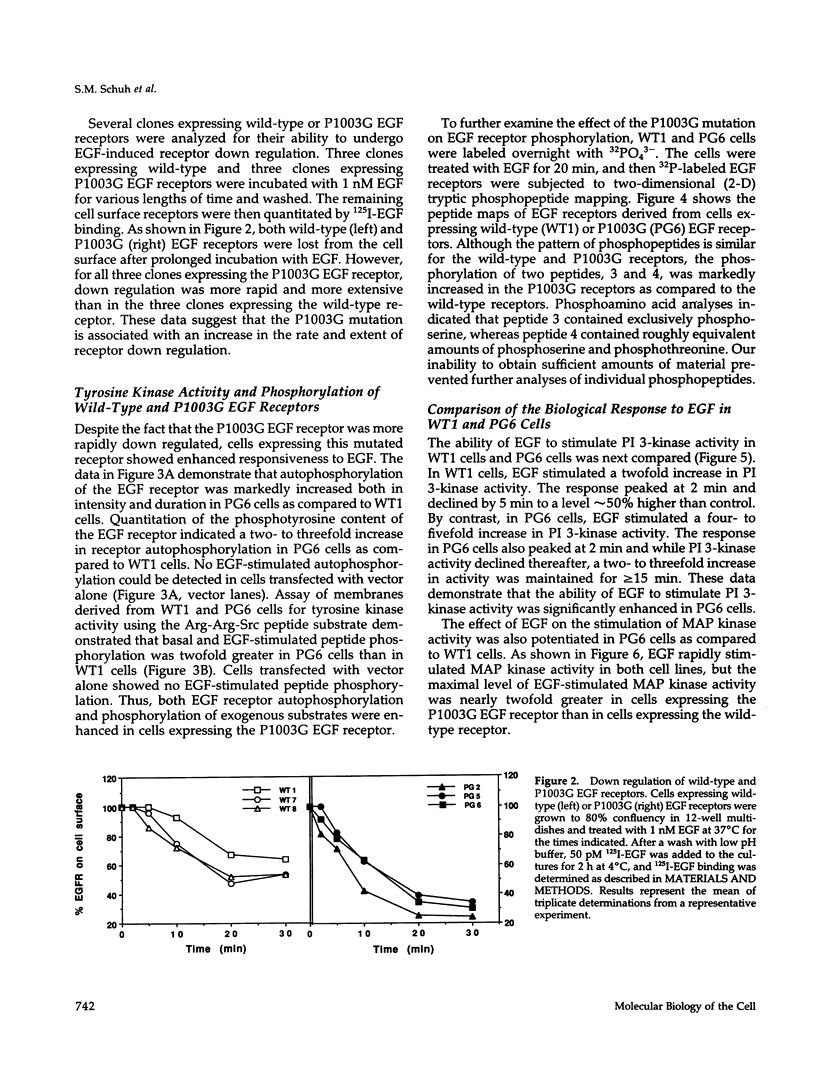
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theroux S. J., Latour D. A., Stanley K., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Signal transduction by the epidermal growth factor receptor is attenuated by a COOH-terminal domain serine phosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16620–16626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega Q. C., Cochet C., Filhol O., Chang C. P., Rhee S. G., Gill G. N. A site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the C terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor is required to activate phospholipase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Chen W. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Analysis of deletions of the carboxyl terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor reveals self-phosphorylation at tyrosine 992 and enhanced in vivo tyrosine phosphorylation of cell substrates. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1750–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Hakomori S., Kitamura K., Igarashi Y. GM3 directly inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation and de-N-acetyl-GM3 directly enhances serine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor, independently of receptor-receptor interaction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1959–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]