Abstract
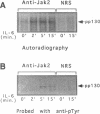
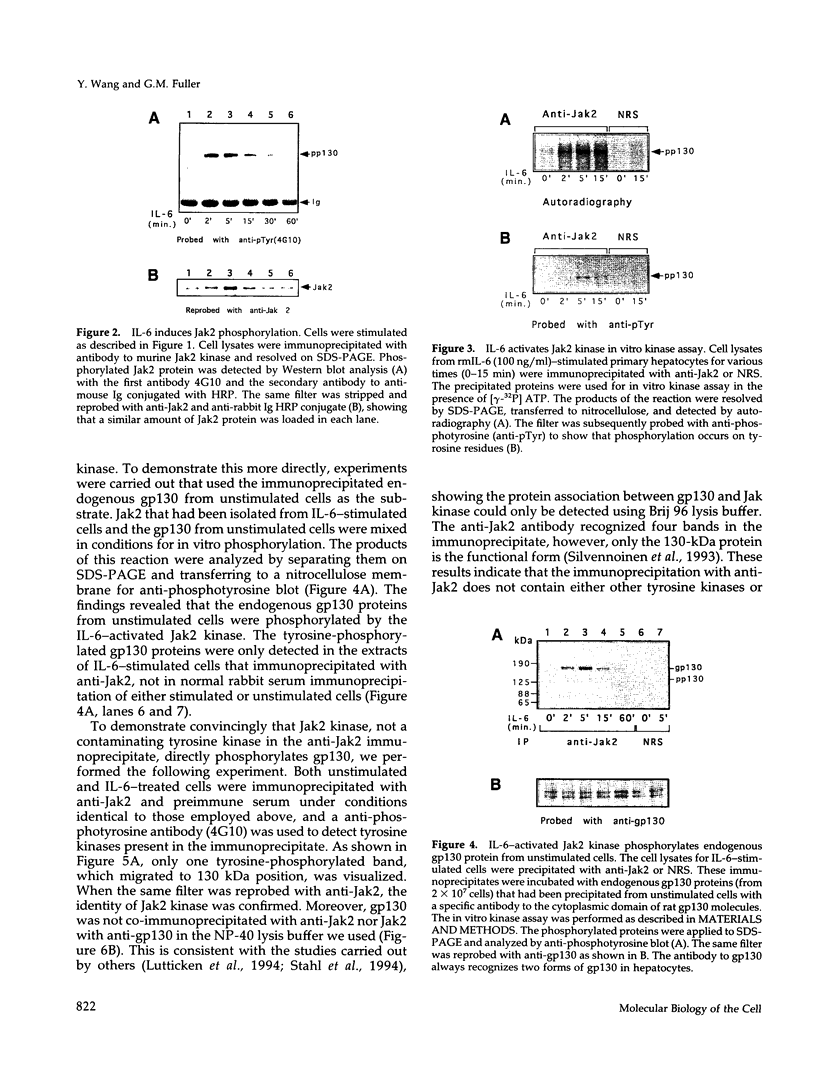
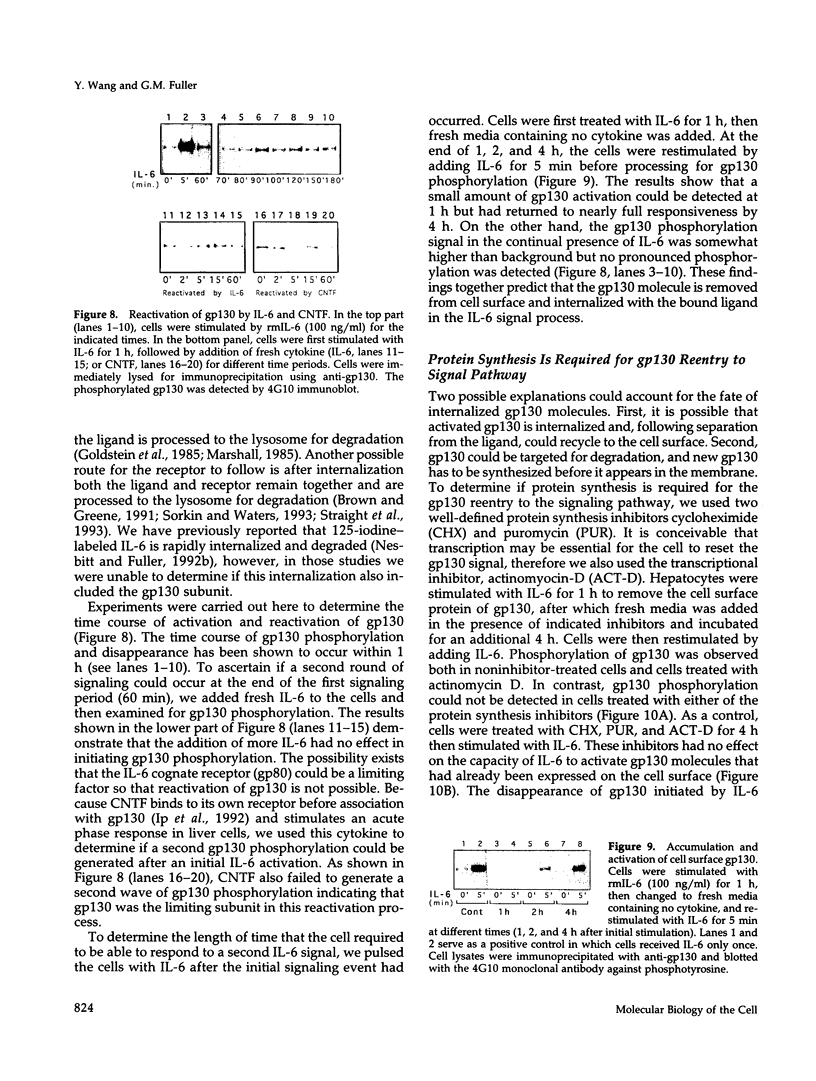
Recent evidence has shown that members of the Jak kinase family are activated after IL-6 binds to its receptor complex, leading to a tyrosine phosphorylation of gp130, the IL-6 signal-transducing subunit. The different members of the IL-6 cytokine subfamily induce distinct patterns of Jak-Tyk phosphorylation in different cell types. Using monospecific antibodies to gp130, Jak2 kinase, and phosphotyrosine, we investigated the kinetics of IL-6 stimulation of members of this pathway in primary hepatocytes. Our findings show that Jak 2 is maximally activated within 2 min of exposure to IL-6, followed by gp130 phosphorylation that reaches its peak in another 2 min then declines to basal level by 60 min. In vitro phosphorylation experiments show that activated Jak 2 is able to phosphorylate both native gp130 and a fusion peptide containing its cytoplasmic domain, demonstrating gp130 is a direct substrate of Jak 2 kinase. Experiments designed to explore the cell surface expression of gp130 show that > or = 2 h are required to get a second round of phosphorylation after the addition of more cytokines. This finding suggests that activated gp130 is internalized from the cell surface after IL-6 stimulation. Additional experiments using protein synthesis inhibitors reveal that new protein synthesis is required to get a second cycle of gp130 phosphorylation indicating gp130 must be synthesized de novo and inserted into the membrane. These findings provide strong evidence that down regulation of the IL-6 signal in hepatocytes involves the internalization and cytosol degradation of gp130.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argetsinger L. S., Campbell G. S., Yang X., Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Carter-Su C. Identification of JAK2 as a growth hormone receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90415-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Schendel P. Interleukin-11 regulates the hepatic expression of the same plasma protein genes as interleukin-6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20424–20427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Ziegler S. F., Mosley B., Morella K. K., Pajovic S., Gearing D. P. Reconstitution of the response to leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin M, and ciliary neurotrophic factor in hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8414–8417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Neuropoietic cytokines in the hematopoietic fold. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown V. I., Greene M. I. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of receptor-mediated endocytosis. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jul-Aug;10(6):399–409. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firmbach-Kraft I., Byers M., Shows T., Dalla-Favera R., Krolewski J. J. tyk2, prototype of a novel class of non-receptor tyrosine kinase genes. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1329–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sugamura K., Sano K., Nakai M., Sugita K., Hinuma Y. High-affinity receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of interleukin 2 in human T cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):550–562. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Zuber C. E., Cabrillat H., Djossou O., Banchereau J. Internalization of human interleukin 4 and transient down-regulation of its receptor in the CD23-inducible Jijoye cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6984–6989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenett H. E., Danley D. E., Strick C. A., James L. C., Otterness I. G., Fuentes N., Nesbitt J. E., Fuller G. M. Isolation and characterization of biologically active murine interleukin-6 produced in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 May 30;101(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90422-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., McClain J., Barrezueta N. X., Aldrich T. H., Pan L., Li Y., Wiegand S. J., Friedman B., Davis S., Yancopoulos G. D. The alpha component of the CNTF receptor is required for signaling and defines potential CNTF targets in the adult and during development. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90245-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Fu X. Y., Levy D. E. Interferon-alpha regulates nuclear translocation and DNA-binding affinity of ISGF3, a multimeric transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1753–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Taga T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):593–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1411569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 trigger the same immediate early response, including tyrosine phosphorylation, upon induction of myeloid leukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Wegenka U. M., Yuan J., Buschmann J., Schindler C., Ziemiecki A., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Yasukawa K., Taga T. Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8272872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S. Kinetics of insulin receptor internalization and recycling in adipocytes. Shunting of receptors to a degradative pathway by inhibitors of recycling. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4136–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Hara T., Kitamura T. Common subunits of cytokine receptors and the functional redundancy of cytokines. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90004-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Harada N., Yokota T., Arai K. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:295–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Hibi M., Nakagawa N., Nakagawa T., Yasukawa K., Yamanishi K., Taga T., Kishimoto T. IL-6-induced homodimerization of gp130 and associated activation of a tyrosine kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.8511589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Narazaki M., Hibi M., Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Hamaguchi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11349–11353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt J. E., Fuller G. M. Differential regulation of interleukin-6 receptor and gp130 gene expression in rat hepatocytes. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):103–112. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt J. E., Fuller G. M. Dynamics of interleukin-6 internalization and degradation in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5739–5742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt J. E., Fuller G. M. Transcription and translation are required for fibrinogen mRNA degradation in hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 2;1089(1):88–94. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qwarnstrom E. E., Page R. C., Gillis S., Dower S. K. Binding, internalization, and intracellular localization of interleukin-1 beta in human diploid fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8261–8269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose T. M., Bruce A. G. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8641–8645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Cleveland J. L., Yi T., Ihle J. N. Structure of the murine Jak2 protein-tyrosine kinase and its role in interleukin 3 signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8429–8433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A., Waters C. M. Endocytosis of growth factor receptors. Bioessays. 1993 Jun;15(6):375–382. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Claesson-Welsh L. Effect of receptor kinase inactivation on the rate of internalization and degradation of PDGF and the PDGF beta-receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):469–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Davis S., Wong V., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. Cross-linking identifies leukemia inhibitory factor-binding protein as a ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor component. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7628–7631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straight S. W., Hinkle P. M., Jewers R. J., McCance D. J. The E5 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus type 16 transforms fibroblasts and effects the downregulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in keratinocytes. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4521–4532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4521-4532.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Hibi M., Hirata Y., Yamasaki K., Yasukawa K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma B., Bird T. A., Friend D. J., Gearing D. P., Dower S. K. Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor trigger overlapping and different signals through partially shared receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6215–6222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D., Carpentier J. L., Sawano F., Gorden P., Orci L. Ligands internalized through coated or noncoated invaginations follow a common intracellular pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7957–7961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Nesbitt J. E., Fuentes N. L., Fuller G. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat liver IL-6 signal transducing molecule, gp130. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):666–672. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Guschin D., Müller M., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Rogers N. C., Schindler C., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N. Complementation by the protein tyrosine kinase JAK2 of a mutant cell line defective in the interferon-gamma signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):166–170. doi: 10.1038/366166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Harpur A. G., Kurban R. R., Ralph S. J., Zürcher G., Ziemiecki A. Two novel protein-tyrosine kinases, each with a second phosphotransferase-related catalytic domain, define a new class of protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2057–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F. Two putative protein-tyrosine kinases identified by application of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Yi T., Tang B., Miura O., Ihle J. N. JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90414-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]