Abstract
Background
Disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) would be most beneficial if applied during the ‘preclinical’ stage (pathology present with cognition intact) before significant neuronal loss occurs. Therefore, biomarkers that can detect AD pathology in its early stages and predict dementia onset and progression will be invaluable for patient care and efficient clinical trial design.
Methods
2D–difference gel electrophoresis and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry were used to measure AD-associated changes in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Concentrations of CSF YKL-40 were further evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the discovery cohort (N=47), an independent sample set (N=292) with paired plasma samples (N=237), frontotemporal lobar degeneration (N=9), and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP, N=6). Human AD brain was studied immunohistochemically to identify potential source(s) of YKL-40.
Results
In the discovery and validation cohorts, mean CSF YKL-40 was higher in very mild and mild AD-type dementia (Clinical Dementia Rating [CDR] 0.5 and 1) vs. controls (CDR 0) and PSP. Importantly, CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 ratio predicted risk of developing cognitive impairment (CDR 0 to CDR>0 conversion) as well as the best CSF biomarkers identified to date, tau/Aβ42 and p-tau181/Aβ42. Mean plasma YKL-40 was higher in CDR 0.5 and 1 vs. CDR 0 groups, and correlated with CSF levels. YKL-40 immunoreactivity was observed within astrocytes near a subset of amyloid plaques, implicating YKL-40 in the neuroinflammatory response to Aβ deposition.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate that YKL-40, a putative indicator of neuroinflammation, is elevated in AD, and that, together with Aβ42, has potential prognostic utility as a biomarker for preclinical AD.
Keywords: YKL-40, Alzheimer’s disease, biomarkers, cerebrospinal fluid, chitinase-3 like-1, inflammation
Introduction
Clinicopathological studies suggest that the pathological hallmarks of AD, amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, begin to appear ~10–20 years before the synaptic and neuronal loss that accompany dementia onset (1–3). Identifying and treating individuals during this preclinical stage will maximize benefit from disease-modifying therapies. By definition, this preclinical phase of AD will elude detection by conventional clinical examination, and will therefore require the use of biomarkers for diagnosis. Beyond diagnosis, biomarkers may also provide prognostic information and facilitate the monitoring of disease progression and response to treatment. In addition, novel biomarkers may advance our understanding of AD pathophysiology, and thereby inform future treatment strategies.
Because many proteins expressed in the brain are present in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the CSF proteome is a logical source for potential AD biomarkers. Indeed, CSF amyloid-β42 (Aβ42), tau, and phosphorylated forms of tau (p-tau) have already shown great promise for use in AD diagnosis and prognosis (4–7). Nevertheless, there remains a need for supplemental biomarkers that represent different aspects of AD pathophysiology and can improve diagnosis and prognosis at early disease stages.
To discover additional CSF biomarkers for early AD, we have used two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis in conjunction with tandem mass spectrometry (2-D DIGE LC-MS/MS) to identify proteins that increase or decrease in the setting of early AD relative to age-matched cognitively normal controls. One protein found to be significantly more abundant in AD CSF, YKL-40 (chitinase-3 like-1 [CHI3L1], human cartilage glycoprotein-39 [HC-gp39], and chondrex) is a secreted 40-kDa glycoprotein with sequence homology to bacterial and fungal chitinases and chitin binding ability, but no chitinase activity (8). Reports suggest a role in inflammation and tissue remodeling, and an upregulation in AD brain (9), but its physiological function remains unclear (10, 11). Nevertheless, plasma/serum and/or CSF levels of YKL-40 have been proposed as a candidate biomarker for arthritis, asthma, multiple sclerosis, and myriad cancers (10–12).
In this study, we evaluate the potential of CSF and plasma YKL-40 to serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for AD; additionally, using immunohistochemistry, we investigate the source(s) of YKL-40 in the brain in the setting of AD. Our data suggest that CSF YKL-40 is produced by astrocytes, is significantly elevated in very mild and mild AD, and predicts conversion from cognitive normalcy to very mild cognitive impairment.
Methods and Materials
Subjects
Discovery cohort
Subjects (N=48), community-dwelling volunteers from University of Washington [N=18], Oregon Health and Science University [N=11], University of Pennsylvania [N=11], and University of California San Diego [N=8], were 51–87 years of age and in good general health, having no other neurological, psychiatric, or major medical diagnoses that could contribute importantly to dementia, nor use of exclusionary medications within 1–3 months of lumbar puncture (LP) (e.g. neuroleptics, anticonvulsants, anticoagulants). Study protocols at each institution were approved by their respective Institutional Review Boards and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. Cognitive status was evaluated based on criteria from the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Diseases and Stroke-Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders Association (13). CSF was collected in the morning by LP after overnight fasting and immediately frozen at −80°C. Subjects with a clinical dementia rating (CDR) of 0 (N=24), indicating no dementia, and CDR 1 (N=24), indicating mild dementia, were selected from a larger group of 120 samples on the basis of CSF Aβ42 (relatively high and low values, respectively), and, when possible, CSF tau (relatively low and high values, respectively) to increase the likelihood of CDR 1 subjects having and CDR 0 subjects not having AD pathology. CSF Aβ42 and tau levels were measured in a single laboratory using well-established ELISAs ((14) and Innotest, Innogenetics, respectively). Quantitative thresholds were not defined prior to sample selection; the lowest CDR 0 and highest CDR 1 CSF Aβ42 value were 572 and 399 pg/mL, respectively; CSF tau ranges were CDR 0: 141–448 pg/mL, CDR 1: 216–1965 pg/mL
Validation cohort
Subjects (N=292), community-dwelling volunteers enrolled in longitudinal studies of healthy aging and dementia at the Washington University Alzheimer Disease Research Center (WU-ADRC), were ≥60 years of age and met the same exclusion criteria as the discovery cohort. The study protocol was approved by the Human Studies Committee at WU, and we obtained written and verbal informed consent from participants at enrollment. CDR status was determined as with the discovery cohort, with an additional category of CDR 0.5, indicating very mild dementia; some of these met criteria for MCI and some were more mildly impaired, or “pre-MCI” (15). A subset of subjects (N=159) underwent positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with Pittsburgh Compound-B (PIB) for assessment of in vivo amyloid burden (16–18). Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotypes were determined by the WU-ADRC Genetics Core. Fasted CSF was collected, mixed, centrifuged, and frozen at −80°C in polypropylene tubes; blood was collected at the time of LP, and plasma prepared by centrifugation and stored at −80°C (19).
FTLD/PSP Cohort
Volunteer subjects were diagnosed with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) (N=9) or progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) (N=6) at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) Memory and Aging Center using published criteria (20, 21). Subjects in the FTLD group met criteria for one of the three clinical syndromes that comprise FTLD: frontotemporal dementia (FTD) (N=6), semantic dementia (SD) (N=1), and progressive non-fluent aphasia (PNFA) (N=2) (20). The study protocol was approved by the UCSF Committee on Human Research, and informed consent was obtained from all participants. CSF was collected by LP and immediately frozen at −80°C.
2-D DIGE LC-MS/MS Proteomic Analysis
Samples were processed and analyzed as described previously (22, 23) (see Supplement).
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISAs)
CSF and plasma samples were analyzed by ELISA for Aβ42, total tau, and phospho-tau181 (Innotest, Innogenetics) after one freeze-thaw, and for YKL-40 (Quidel) after two freeze-thaw cycles. Intra- and inter-assay coefficient of variation for CSF YKL-40 were 5.27% and 6.03%, respectively; for plasma, 5.73% and 11.26%.
Statistical Analyses
Correlations were evaluated using the Pearson rho correlation coefficient (α=0.05). Survival analyses assessed the ability of baseline biomarkers and biomarker ratios to predict time to conversion from cognitive normalcy (CDR 0) to very mild or mild dementia (CDR 0.5, 1) and time to progression from very mild dementia (CDR 0.5) to more severe dementia (CDR>0.5). Data from subjects who did not convert/progress were statistically censored at the date of last assessment. Biomarker measurements were converted to standard Z-scores to allow comparison of hazard ratios between different biomarkers. Cox proportional hazard models adjusted for age and gender were conducted treating the CSF biomarkers as continuous and categorical variables. Categorical analyses compared subjects within the highest tertile of baseline values to those within the lowest two tertiles; this tertile-based assessment was applied because Kaplan-Meier curves illustrating the unadjusted time to CDR>0 for each tertile of each biomarker suggested similar outcomes for the lower two tertiles. The difference between the survival curves reflecting the upper tertile versus the lower tertiles of each biomarker was tested using the log-rank test. Survival analyses were conducted using baseline CDR scores determined at clinical assessment prior to LP; analyses using scores determined at clinical assessment closest to LP yielded almost identical results. Similar survival analyses were carried out for plasma YKL-40.
Immunohistochemistry
Six-µm-thick sections of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human postmortem brain tissue (middle frontal gyrus, post mortem interval <6 hrs) from the WU-ADRC Neuropathology Core were double-labeled using rabbit anti-human YKL-40 antibody (Quidel) in series with either goat anti-human GFAP (Santa Cruz), mouse anti-human HLA Class II antigen, LN-3 (Novocastra), RCA-1 (Vector), or mouse anti-human PHF-1 (gift of Dr. Peter Davies), followed by staining with the ImmPress kit (Vector). In control experiments, the primary antibody was omitted and replaced with 1% bovine serum albumin-PBS. Thioflavin S stain (1% aqueous) was applied for 20 minutes and destained with 50% ethanol.
Results
Proteomic Analysis Identifies YKL-40 as Increased in AD CSF
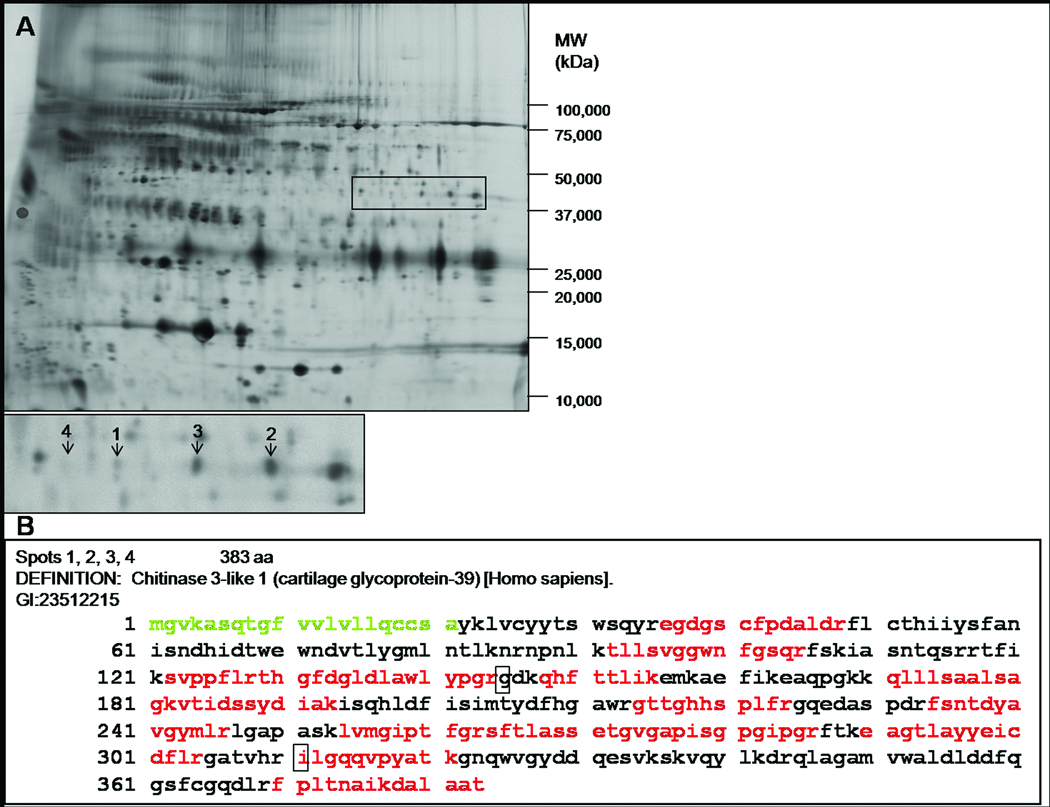
To identify new candidate biomarkers for AD, we utilized an unbiased proteomics approach, 2-D DIGE LC-MS/MS (22, 23), to compare the concentrations of CSF proteins in individuals with mild dementia (CDR 1, N=24) of the Alzheimer's type to those in individuals without dementia (CDR 0, N=24). The two groups differed with respect to age at LP and gender (CDR 0: 64.8 yrs, 38% female; CDR 1: 72.8 yrs, 54% female). From this proteomic analysis, we identified 47 proteins that differed in abundance between the CDR 0 and CDR 1 groups (unpublished data); one of the most promising, in terms of fold-change and novelty, was YKL-40. Interestingly, in a smaller, previous study, we identified YKL-40 as being significantly more abundant in CSF from CDR 0.5 relative to CDR 0 subjects (23). YKL-40 appeared in four gel features that were more abundant in the CDR 1 group (Figure 1A). Tryptic peptides from these spots collectively provide amino acid sequence coverage of 52% and span virtually the full length of the protein (Figure 1B), suggesting that these spots represent full-length secreted YKL-40. We hypothesize that this pattern of four spots may be due to allelic differences, post-translational modifications, or both.
Figure 1.
(A) A representative 2-D DIGE image of CSF from the discovery cohort. Samples were depleted of six highly abundant proteins, fluorescently labeled, and subjected to isoelectric focusing followed by SDS-PAGE. YKL-40 is more abundant in four spots in the CDR 1 group (labeled 1–4 in the inset, with mean fold changes of 1.41, 1.50, 1.46, 1.32, respectively). The near invisibility of spot 4 in this printed representation illustrates the great sensitivity of 2-D DIGE to detect proteins of low abundance. (B) Sequence coverage of human YKL-40 by mass spectrometry. Indicated in red is the compilation of peptides identified in the four spots. The signal sequence is shown in green, and polymorphisms are indicated by boxes.
ELISA Confirms Increased CSF YKL-40 in AD in Original and Independent Cohorts
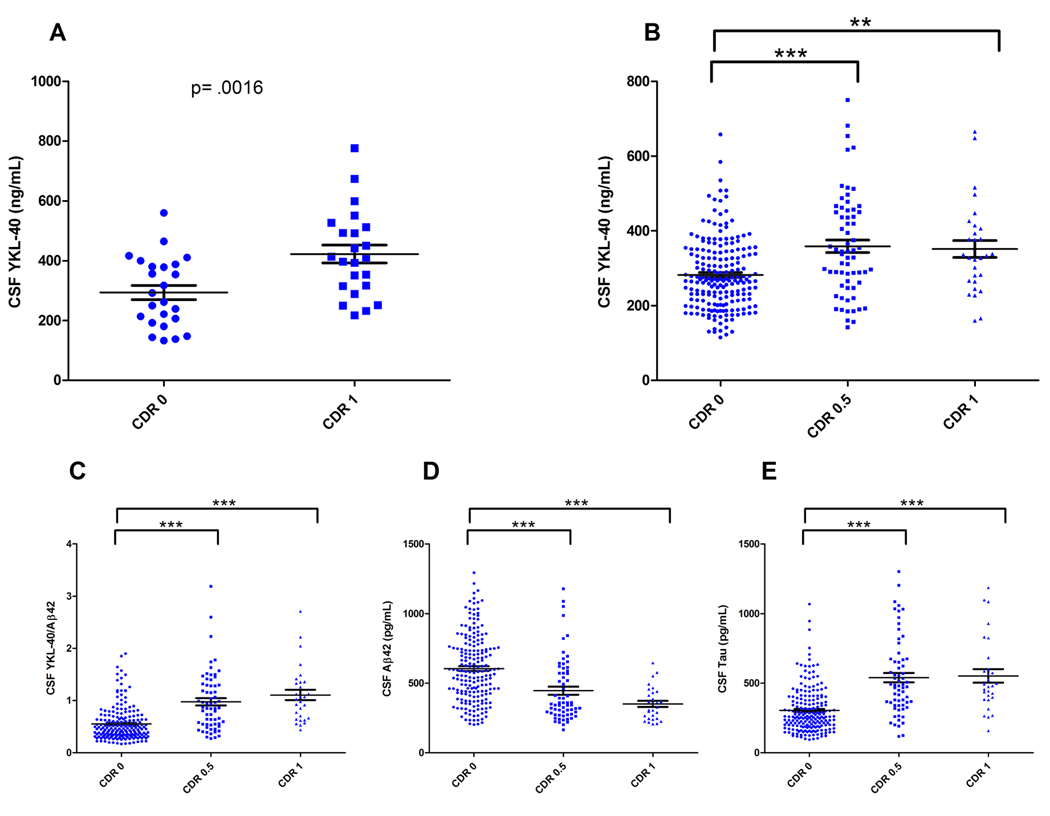
To validate our 2-D DIGE findings, we applied a YKL-40 ELISA to the original ‘discovery’ cohort samples (one sample was unavailable for re-evaluation, N=47). Mean CSF YKL-40 was increased 43% in the CDR 1 vs CDR 0 group (p=.0016) (Figure 2A), consistent with the fold-changes measured by 2-D DIGE. We next assayed a larger, independent set of CDR 0, 0.5, and 1 CSF samples collected at the WU-ADRC (N=292) that was not preselected on the basis of CSF Aβ42 and tau values (characteristics at baseline assessment in Table 1). In this validation cohort, mean CSF YKL-40 was significantly (27%) higher in the CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups vs. CDR 0 (p<.0001 and p=.004, respectively) (Figure 2B). An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) revealed that this increase remained significant after adjusting for age, F(2, 288) = 9.075, p<.0001.
Figure 2.
Mean YKL-40 is increased in the CSF of CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 subjects. (A) CSF from the discovery cohort (CDR 0, N= 24; CDR 1, N=23) was analyzed for YKL-40 by ELISA (CDR 0= 293.6 +/− 23.9; CDR 1= 422.2 +/− 30.0, ng/mL, mean +/− SEM). CSF YKL-40 was significantly higher in the CDR 1 group as compared to the CDR 0 group (p=.0016, unpaired student’s t-test). (B) CSF from a larger, independent sample set (N=292) was analyzed for YKL-40 by ELISA. Mean CSF YKL-40 was significantly higher in the CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups as compared to the CDR 0 group (** p=.004, *** p<.0001; One-way ANOVA with Welch’s correction for unequal variances, Tukey post-hoc Test) (CDR 0= 282.1 +/- 6.7; CDR 0.5= 358.9 +/− 16.9; CDR 1= 351.7 +/− 22.6, ng/mL, mean +/− SEM). (C) Mean CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 was significantly higher in the CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups as compared to the CDR 0 group (***p<.0001; One-way ANOVA with Welch’s correction for unequal variances, Tukey post-hoc Test). (D & E) Mean CSF Aβ42 was significantly higher while mean CSF tau was significantly lower in the CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups as compared to the CDR 0 group (*** p<.0001; Oneway ANOVA with Welch’s correction for unequal variances, Tukey post-hoc Test). The degree of overlap between clinical groups is comparable for all biomarkers evaluated.
Table 1.
Demographic, Clinical, and Genotypic Characteristics of Validation Cohort
| Characteristic | CDR 0 | CDR 0.5 | CDR 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 198 | 65 | 29 |
| Gender (% Female) | 63% | 54% | 52% |
| APOE genotype, % ε4+ | 35% | 51% | 59% |
| Mean MMSE score (SD) | 28.9 (1.3) | 26.3 (2.8) | 22.3 (3.9) |
| Mean age at LP (SD), yrs | 71.0 (7.3) | 73.8 (6.8) | 76.5 (6.2) |
| Mean CSF Aβ42 (SD), pg/mL | 605 (240) | 446 (230) | 351 (118) |
| Mean CSF tau (SD), pg/mL | 304 (161) | 539 (276) | 552 (263) |
| Mean CSF ptau181 (SD), pg/mL | 55 (25) | 85 (44) | 77 (38) |
Abbreviations: CDR, Clinical Dementia Rating; APOE, apolipoprotein E; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; LP, lumbar puncture; SD, standard deviation; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; Aβ-42, amyloid-beta peptide 1–42; ptau181, tau phosphorylated at threonine 181.
CSF YKL-40 is Increased in FTLD and Decreased in PSP
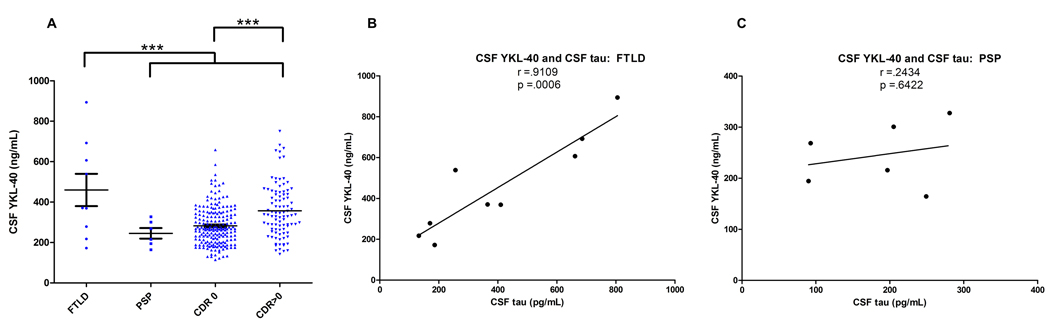
In an effort to determine whether CSF YKL-40 might have potential to distinguish AD from other dementing illnesses, we evaluated levels in two other neurodegenerative diseases: frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD, N=9) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP, N=6). Mean CSF YKL-40 was increased in FTLD relative to AD, although a wide range of values was observed, possibly reflecting the pathological heterogeneity of FTLD; in contrast, PSP cases showed relatively low levels and range of CSF YKL-40 (Figure 3A). Although this study does not evaluate the complete differential diagnosis for mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia, these data suggest that CSF YKL-40 may be useful to distinguish AD from some other forms of neurodegenerative disease.
Figure 3.
(A) CSF samples from subjects with FTLD (N=9) and PSP (N=6) were analyzed for YKL-40 by ELISA, and levels were compared to those of the validation cohort (CDR 0 and CDR>0 [CDR 0.5&1 combined], N=292). Because the groups differed with respect to mean age at LP (FTLD: 59 yrs, PSP: 66 yrs, CDR 0: 71 yrs, CDR 0.5&1: 75 yrs), analyses were adjusted for age. CSF YKL-40 was significantly higher in the FTLD group as compared to the PSP, CDR 0, and CDR>0 groups (*** p<.0001; ANCOVA, LSD post-hoc Test). While not reaching statistical significance (defined here as α=0.05), CSF YKL-40 levels trended lower in the PSP group as compared to the CDR>0 group. (B–C) CSF YKL-40 and CSF tau values correlated strongly in the FTLD group, but did not correlate in the PSP group.
Correlation of CSF YKL-40 With Demographic Features and Other Biomarker Values
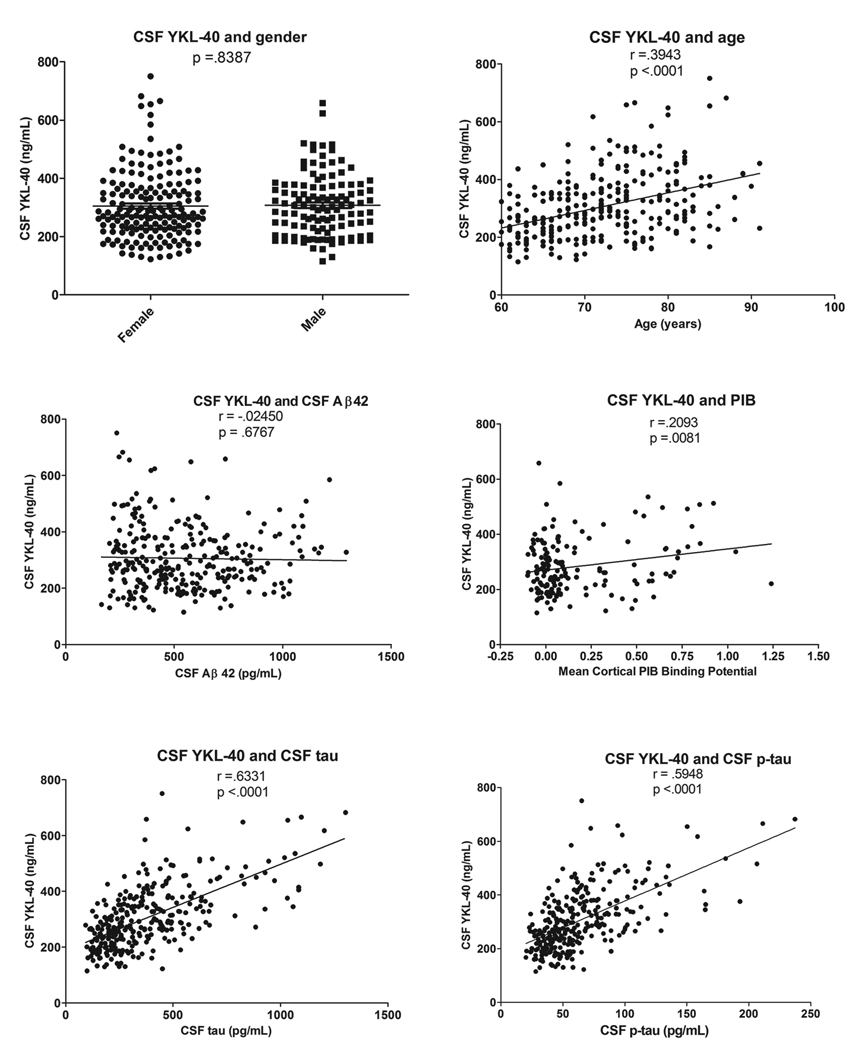
Because the CDR 0, 0.5, and 1 groups show somewhat different distributions with regard to age at LP, gender, and APOE genotype, levels of CSF YKL-40 were evaluated for potential correlation with these variables. CSF YKL-40 levels did not vary based on gender (p=.8355) or APOE genotype (not shown) but did correlate with increasing age (r=.3943, p<.0001) (Figure 4). Next, seeking insight into the role of YKL-40 in AD pathology, we evaluated its associations with CSF Aβ42, CSF tau, and cortical amyloid burden measured by PIB-PET imaging. In this validation cohort, CSF YKL-40 did not correlate with CSF Aβ42 (r=−.02463, p=6745), but did correlate with CSF tau (r=.6331, p<.0001), and p-tau181 (r=.5947, p<.0001), and modestly with cortical amyloid burden (r=.2093, p=.0081) (Figure 4). Interestingly, a similar correlation of CSF YKL-40 with tau was observed in FTLD (r=.9109, p=.0006), but not in PSP (r=.2434, p=6422) (Figure 3B,C), suggesting that these two biomarkers are not inextricably linked, and that they may reflect separate but interrelated pathophysiological processes.
Figure 4.
In the validation cohort, CSF YKL-40 levels do not vary based on gender and are not correlated with CSF Aβ42. However, CSF YKL-40 levels are correlated with age, CSF tau, CSF p-tau181, and mean cortical PIB binding potential.
Ability of CSF YKL-40 To Predict Onset and Progression of Dementia
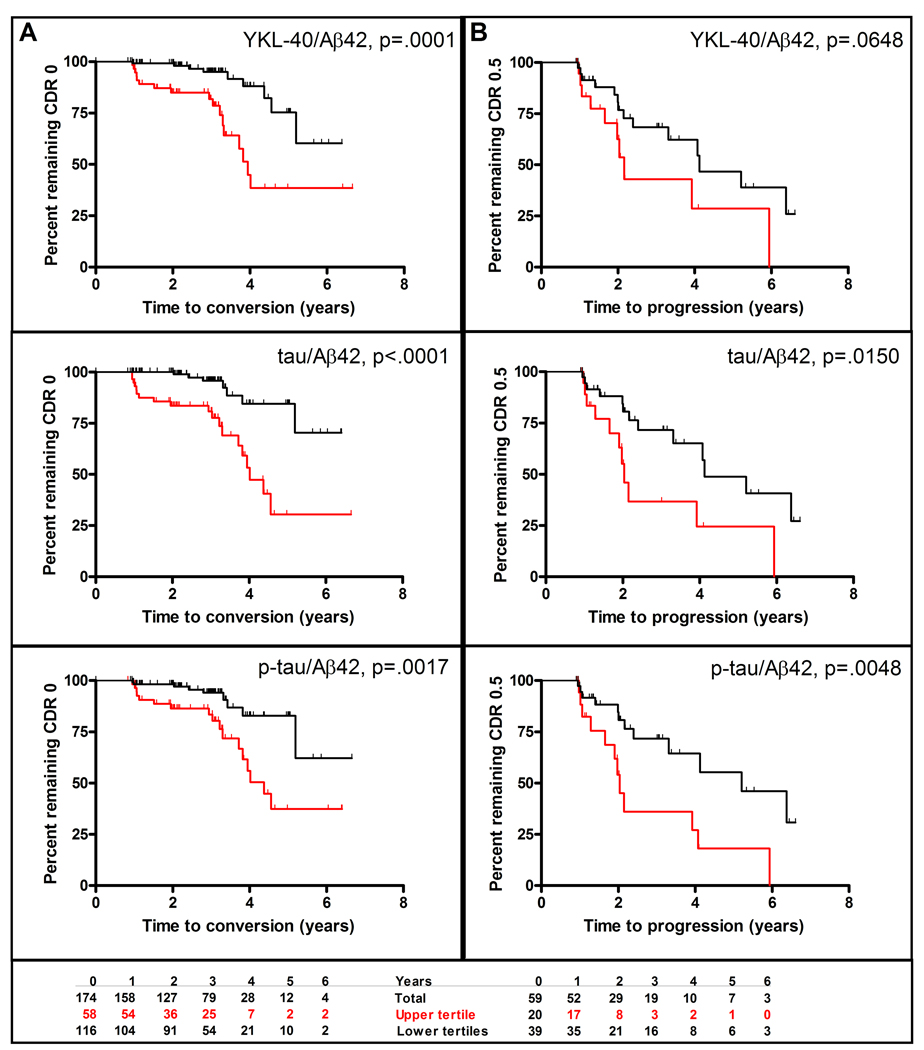
Recognizing the need for preclinical diagnosis and prognosis, we applied survival analyses to evaluate whether CSF YKL-40 can predict risk of developing cognitive impairment (conversion from CDR 0 to CDR>0) and of dementia progression (CDR 0.5 to CDR>0.5). Of the 174 CDR 0 subjects with at least one follow-up clinical assessment, 26 received a CDR>0 at follow-up, and thus were classified as “converters.” Since CSF tau/Aβ42 and p-tau181/Aβ42 ratios have been shown to predict cognitive decline in cognitively normal (19, 24) and MCI (25, 26) cohorts, survival analyses were also conducted for these biomarkers. Treated as categorical variables, subjects with high ratios (upper tertile) of CSF YKL-40/Aβ42, tau/Aβ42, and p-tau181/Aβ42 were faster to convert to CDR>0 than were subjects with lower ratios (lower tertiles) (Figure 5A), even after adjusting for age and gender (Figure 6; see also Table S1 in the Supplement). Likewise, when treated as continuous variables, CSF YKL-40/Aβ42, tau/Aβ42, and p-tau181/Aβ42 ratios again predicted conversion from CDR 0 to CDR>0 (p=0.0003, p=0.0001, p<.0001, respectively) after adjustment for age and gender (Figure 6; see also Table S1 in the Supplement). Importantly, when evaluated individually, CSF YKL-40, Aβ42, tau, and p-tau181 did not perform as well as the YKL-40/Aβ42, tau/Aβ42, and p-tau181/Aβ42 ratios at predicting conversion from CDR 0 to CDR>0 (see Figure S1 and Table S2 in the Supplement). Thus, the CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 ratio, as a prognostic biomarker of future cognitive impairment in normal individuals, is comparable to the best CSF biomarkers of this type to date, tau/Aβ42 and p-tau181/Aβ42.
Figure 5.
CSF YKL-40/Aβ42, tau/Aβ42, and p-tau/Aβ42 as predictors of (A) conversion from CDR 0 to CDR>0 and (B) progression from CDR 0.5 to CDR>0.5. Kaplan-Meier estimates of rates of conversion and progression are shown with red curves representing the upper tertile and black curves representing the lower two tertiles. The bottom panel shows for the CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 analyses the number of subjects in the upper and lower tertiles at baseline and at each year of follow-up.
Figure 6.
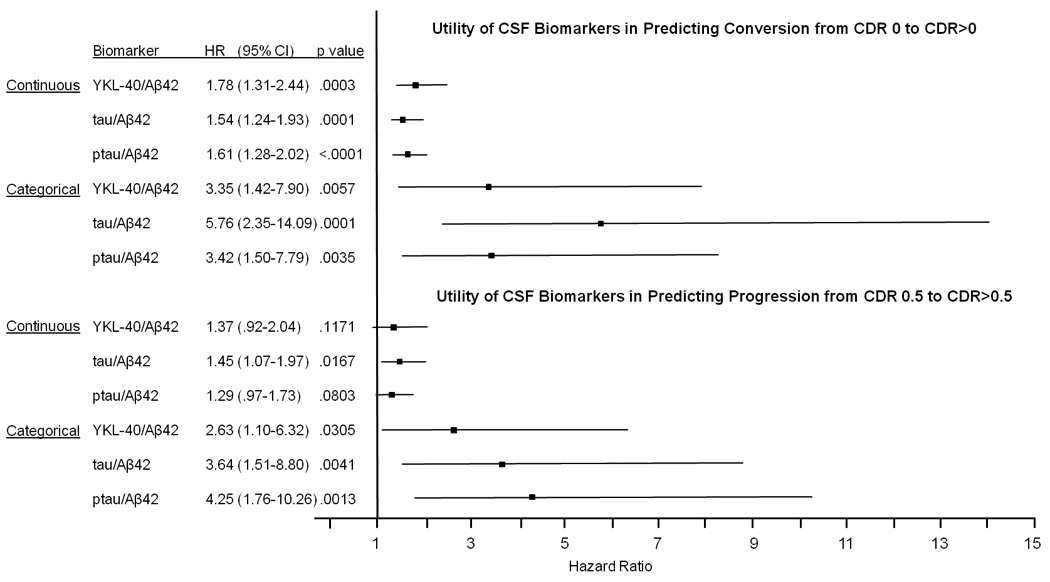
Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the ability of CSF YKL-40/Aβ42, tau/Aβ42, and ptau/Aβ42 to predict (top) conversion from cognitive normalcy (CDR 0) to cognitive impairment (CDR>0) and (bottom) progression from very mild dementia (CDR 0.5) to mild or moderate dementia (CDR>0.5). Biomarker measures were analyzed as both continuous and categorical variables, and were converted to standard Z-scores to allow comparison of hazard ratios between different biomarkers. In evaluating risk, analyses were adjusted for age and gender. Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Of the 59 CDR 0.5 subjects with at least one follow-up clinical assessment, 24 received a CDR>0.5 at follow-up, and thus were classified as “progressors.” Kaplan-Meier estimates of the rate of progression suggest that those with high CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 ratios (upper tertile) were faster to progress to CDR>0.5 than those with lower CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 ratios (lower two tertiles) (p=.0648) (Figure 5B). The tau/Aβ42 and p-tau181/Aβ42 ratios showed similar patterns (Figure 5B). After adjustment for age and gender, similar results were found for all three categorical biomarker variables (Figure 6, see also Table S1 in the Supplement). Treated as a continuous variable and adjusted for age and gender, p-tau181/Aβ42 and YKL-40/Aβ42 ratios showed trends associated with time to progression that did not reach statistical significance (Figure 6, see also Table S1 in the Supplement).
Plasma YKL-40 Demonstrates Limited Utility as AD Biomarker
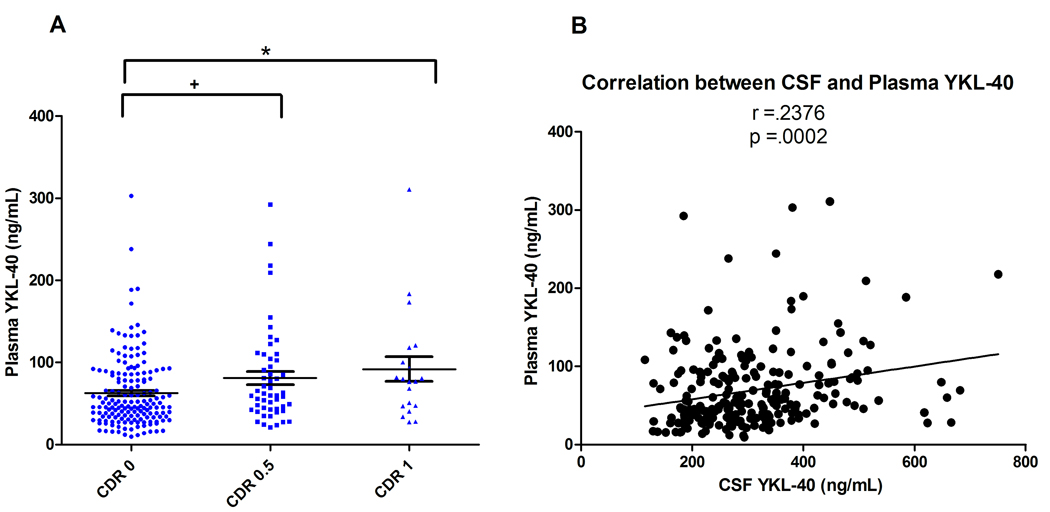
To evaluate plasma YKL-40 as a potential AD biomarker, we applied the ELISA to 237 plasma samples from the validation cohort. Mean plasma YKL-40 was significantly higher in the CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 vs CDR 0 group (p=.046, p=.031, respectively, One-way ANOVA, Tukey post-hoc), with percent increases similar to those observed in CSF (Figure 7A). Plasma and CSF YKL-40 levels correlated modestly (r=.2376, p=.0002) (Figure 7B), with levels roughly 5-fold higher in CSF. Plasma YKL-40 also correlated with increasing age (r=2284, p=.0004), but not with gender (p=.6558), CSF Aβ42 (r= -.07902, p=.2255), CSF tau (r=.03769, p=.5637), CSF p-tau181 (r=−.02738, p=.6749), or cortical amyloid load (r=.01789, p=.8576) (see Figure S2 in the Supplement). Plasma YKL-40 did not demonstrate utility for predicting cognitive decline (not shown).
Figure 7.
Plasma samples of the validation cohort (N=237) were evaluated for YKL-40 by ELISA. (A) Mean plasma YKL-40 was significantly higher in the CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups as compared to the CDR 0 group (+ p=.046, * p=.031; One-way ANOVA, Tukey post-hoc Test) (CDR 0= 62.5 +/− 3.4; CDR 0.5= 81.1 +/− 8.0; CDR 1= 91.9 +/− 15.0, ng/mL, mean +/− SEM). (B) CSF and plasma YKL-40 levels are significantly correlated (r =.2376, p=.0002).
In AD Brain, YKL-40 is Expressed in Astrocytes in Vicinity of Plaques and in Rare White Matter Neurons
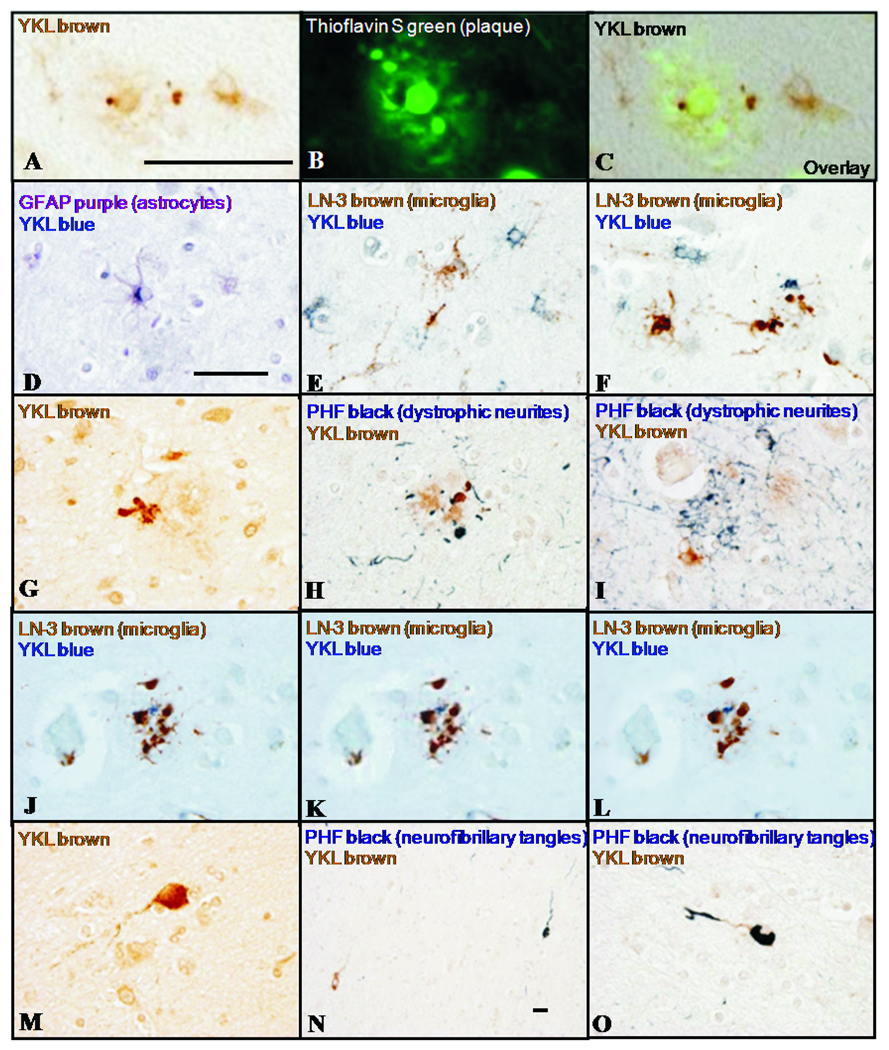
To investigate potential source(s) of YKL-40 in AD, we performed single and double-label immunohistochemistry on human frontal cortex. YKL-40 immunoreactivity was observed in the vicinity of a subset of thioflavin S-positive amyloid plaques (Figure 8A,B,C) within GFAP-positive astrocytes (Figure 8D), and not within microglia stained with LN-3 (Figure 8E,F) or lectin RCA-1 (not shown). YKL-40 immunoreactivity was also present in plaque-associated cell processes (Figure 8G) that lacked reactivity for dystrophic neurite marker PHF-1 (Figure 8H) and microglial marker LN-3 (Figure 8J,K,L representing adjacent focal planes), and that may represent astrocytic processes (suggested in Figure 8I by the plaque-associated YKL-40-positive astrocyte in lower left quadrant). YKL-40 immunoreactivity was also observed within the superficial cortical white matter in rare neurons (Figure 8M,N,O) with occasional PHF-1-positive neurofibrillary tangles (Figure 8N,O). These neurons may represent cells of multiform layer VI and/or ‘interstitial neurons’ of the white matter (27).
Figure 8.
In AD neocortex, YKL-40 immunoreactivity is observed in the vicinity of thioflavin S-positive fibrillar amyloid plaques (A,B,C). YKL-40 immunoreactivity is present within a subset of GFAP-positive astrocytes (D) and not in LN-3-positive microglia (E,F). YKL-40 is also observed in cell processes associated with plaques (G); these processes lack reactivity for dystrophic neurite marker PHF-1 (H,I) and microglial marker LN-3 (J,K,L representing adjacent focal planes), and may represent astrocytic processes. YKL-40 immunoreactivity is also observed in occasional neurons in the superficial white matter (M,N,O), some of which contain neurofibrillary tangles (evidenced by PHF-1 staining, N,O). These neurons may represent cells of multiform layer VI or ‘interstitial neurons’ of the white matter. Scale bars = 50 µm; scale bar in A applies to A–C; scale bar in D applies to D–O, with the exception of N.
Discussion
This study suggests that CSF YKL-40, a novel inflammatory biomarker for AD, is increased in AD, and, together with Aβ42, will assist in prognosis of patients and clinical trial participants who are under examination for the preclinical and early clinical stages of AD.
Having identified CSF YKL-40 as a potential AD biomarker through non-biased proteomics, we verified this finding using a commercially available ELISA, and more importantly, validated the results in a much larger, independent cohort. By including very mildly impaired (CDR 0.5) individuals who may be classified at some other institutions as having MCI, or even “pre-MCI,” as some were insufficiently impaired to meet MCI criteria, this validation cohort revealed the promise of CSF YKL-40 as a biomarker for very early stage AD. By including individuals with FTLD and PSP, albeit in small numbers, we also demonstrated that CSF YKL-40 shows promise for distinguishing AD from PSP.
By including individuals who were cognitively normal at the time of CSF collection, but subsequently developed cognitive impairment, this validation cohort also revealed the potential utility of YKL-40, coupled with Aβ42, to predict cognitive decline. It has previously been shown that ratios of CSF tau/Aβ42 and p-tau181/Aβ42 can predict conversion from cognitively normal to cognitively impaired over a 2–4 year period (19, 24). Here we confirm those findings in a cohort of twice the size, and show that CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 has predictive value comparable to that of these best current CSF measures. This finding is particularly notable because, whereas CSF tau is derived principally from neurons, YKL-40 appears to be secreted predominantly from astrocytes. To our knowledge, YKL-40 is the first astrocyte-derived marker shown to be useful in such a way. CSF YKL-40/Aβ42 also showed promise in predicting progression of dementia from CDR 0.5 to CDR>0.5. However, tau/Aβ42 and p-tau181/Aβ42 appear to show greater utility for predicting progression.
We also evaluated plasma YKL-40 as a potential AD biomarker. While plasma YKL-40 levels displayed a pattern of elevation in the CDR 0.5 and 1 groups similar to that observed for CSF, and plasma and CSF levels were modestly correlated, plasma YKL-40 did not show similar prognostic utility. Whether this increase in plasma YKL-40 reflects passive or active export of central nervous system (CNS)-derived YKL-40 or coincident peripheral production in response to a systemic inflammatory signal is unclear. Similar coincident elevations of CSF and serum YKL-40 levels have been reported with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (28) and multiple sclerosis (12). However, in the setting of CNS infection, CSF levels of YKL-40 appear to rise without a concomitant increase in serum levels (29, 30), suggesting that YKL-40 produced in the brain does not influence serum/plasma levels. Data to address the converse- whether YKL-40 produced in the periphery can influence CSF levels- have not yet been reported. This issue is important to assess in future studies because peripheral inflammatory and neoplastic conditions are not uncommon within populations most likely to be screened for AD.
To examine its role in AD and to identify potential sources of CSF YKL-40, we immunohistochemically double-labeled human AD brain tissue for YKL-40 and other cell-specific markers, and observed YKL-40 in a subset of plaque-associated astrocytes and in rare white matter neurons. These results should help to clarify the origins of CSF YKL-40, which have been controversial among the small number of relevant studies (29, 31, 32). Additionally, the pattern of expression within a subset of plaque-associated astrocytes may account for the positive correlation we observe between CSF YKL-40 and cortical amyloid load (Figure 4); as amyloid plaque burden increases, so does the amount of plaque associated-astrocyte activation, and likely, the amount of CSF YKL-40. It may also account for the lack of correlation we observe between CSF YKL-40 and CSF Aβ42, and for the relatively equal levels of CSF YKL-40 between CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups; once plaque formation commences, which is estimated to occur ~15 years prior to cognitive decline (4, 5, 7), CSF Aβ42 remains at a low steady state (17, 33–35), so no correlation with YKL-40 would be expected. Likewise, amyloid burden appears close to its maximal extent once cognitive decline begins (17, 19, 35), so plaque burden and CSF YKL-40 levels might be expected to be similar in CDR 0.5 and CDR 1 groups. More importantly, these results implicate YKL-40 in the astrocytic neuroinflammatory response to fibrillar Aβ deposition that appears to play a role in AD pathogenesis (36–38).
What induces YKL-40 expression in the presence of AD pathology, and how increased YKL-40 expression may influence the disease process are unknown. In models of peripheral inflammation such as asthma and arthritis, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) appear to stimulate YKL-40 synthesis in macrophages and chondrocytes (39, 40). Since TNF-α and IL-1β are implicated in AD neuroinflammation, it is reasonable to hypothesize that astrocytic expression of YKL-40 may be similarly induced. Given that TNF-α and IL-1β can cross the blood brain barrier, it is also reasonable to hypothesize that YKL-40 levels in plasma and CSF might be modulated by systemic or central inflammation. Defining the factors required to induce YKL-40 expression in astrocytes will be an important first step in understanding the role of YKL-40 in AD and, more generally, in the CNS.
Defining the targets of YKL-40 in the brain is also critically important for understanding its role in AD. In the periphery, YKL-40 can reportedly stimulate connective tissue cell growth (41, 42); modulate the effects of inflammatory cytokines in fibroblasts (43); bind collagen and influence its fibrillogenesis (44); stimulate endothelial cell migration (45); modulate vascular smooth muscle cell adhesion and migration (46); support antigen-induced Th2 inflammatory responses (47); and stimulate alveolar macrophages to release metalloproteinases and proinflammatory and fibrogenic chemokines (40). In the brain, YKL-40 is reported to release extracellular matrix-bound bFGF (29). Clearly, further study of YKL-40 in AD and, more generally, within the CNS and periphery, is warranted to define its pathophysiological role(s).
This study identifies YKL-40 as a novel astrocyte-derived CSF biomarker that can distinguish groups of AD and control subjects and predict risk of developing dementia among cognitively normal subjects. Nevertheless, like all AD biomarker candidates to date, YKL-40 is likely to have less value when applied in isolation, and, alone, will be insufficient to provide definitive information for an individual patient. While significant differences in mean CSF and plasma YKL-40 levels exist between CDR 0 and CDR 0.5, and CDR 0 and CDR 1 groups, the ranges of YKL-40 values among the groups show considerable overlap. This overlap may stem from several sources. The greatest contribution is likely due to the inclusion of individuals with asymptomatic (preclinical) AD pathology in the CDR 0 group; AD neuropathology is present in ~25% of non-demented individuals age ≥75 years (48, 49). It is also possible that different alleles of the CHI3L1 gene may influence baseline or reactive levels of YKL-40 protein expression, or that members of this cohort may be afflicted by other diseases that affect CSF YKL-40 levels. For example, elevated CSF YKL-40 has been reported in the setting of other CNS pathologies (12, 28–30); however, most of these conditions would be easily distinguishable from early AD on the basis of clinical assessment. It is important to note that the overlap observed for CSF YKL-40 is comparable to that seen for the best biomarkers identified to date, CSF Aβ42 and CSF tau (Figure 2 D & E) (50). The best use of YKL-40 may be in a panel of biomarkers that provide complementary information to guide diagnosis, prognosis, clinical trial design, and treatment decisions. Indeed, in other work stemming from this 2-D DIGE study, stepwise logistic regression analyses indicate that YKL-40, as part of a panel with other CSF biomarkers, contributes additional sensitivity and specificity for discriminating mildly demented individuals from cognitively normal individuals (Perrin RJ, Craig-Schapiro R, Holtzman DM et al. 2010, in preparation). Additionally, YKL-40 may confer specificity to a panel by distinguishing PSP or other illnesses from AD, as our early results suggest. It will be of interest in future studies to confirm these results and to evaluate CSF YKL-40 levels in the setting of additional dementing conditions. Perhaps more importantly, YKL-40, for its own part, might contribute diagnostic sensitivity for early cognitive impairment, prognostic information for risk of cognitive decline in normal and very mildly impaired individuals, and, more fundamentally, a direct estimate of neuroinflammation, which tau and Aβ42 do not provide.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of Ms. Aarti Shah, our lumbar puncture physicians, and the Clinical, Psychometrics, Biomarker, Imaging and Biostatistics Cores of the Washington University Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health [P50 AG05681, P01 AG03991, P01 AG026276, P50 AG005136, U01 AG16976, P30 NS057105, T32 NS007205, P41 RR000954]; the Charles and Joanne Knight Alzheimer Research Initiative; the Department of Veterans Affairs; and the W.M. Keck Foundation. FTLD/PSP CSF was generously provided by the UCSF Memory and Aging Center (work supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging [R01AG031278, K23-AG031861, P01 AG019724, P50 AG023501]; UCSF Alzheimer’s Disease Research Centers [P50 AG023501]; the CurePSP; and the Association for Frontotemporal Dementias. This publication was made possible by Grant Number UL1 RR024992 from the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and NIH Roadmap for Medical Research. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NCRR or NIH.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Financial Disclosures: Dr. Holtzman co-founded the company C2N Diagnostics, is on the scientific advisory board of C2N Diagnostics, En Vivo, and Satori, consulted for Pfizer, receives grants that did not support this work from Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Astra-Zeneca, and in conjunction with Dr. Fagan, has filed a patent related to some of the data in this manuscript. Dr. Morris has consulted for Astra Zeneca, Genentech, and Merck, has received honoraria from Ohio Wesleyan, ANA Soriano lecture, payment for manuscript preparation from Journal Watch, royalties from Blackwell Publishers and Taylor and Francis, and travel funding for ANA meeting Baltimore, Praque. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Davies L, Wolska B, Hilbich C, Multhaup G, Martins R, Simms G, et al. A4 amyloid protein deposition and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: prevalence in aged brains determined by immunocytochemistry compared with conventional neuropathologic techniques. Neurology. 1988;38:1688–1693. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Morris J, Price J. Pathologic correlates of nondemented aging, mild cognitive impairment, and early stage Alzheimer's disease. J Mol Neurosci. 2001;17:101–118. doi: 10.1385/jmn:17:2:101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hulette CM, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Murray MG, Saunders AM, Mash DC, McIntyre LM. Neuropathological and neuropsychological changes in "normal" aging: Evidence for preclinical Alzheimer disease in cognitively normal individuals. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998;57:1168–1174. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199812000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Craig-Schapiro R, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM. Biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;35:128–140. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Perrin RJ, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM. Multimodal techniques for diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2009;461:916–922. doi: 10.1038/nature08538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hampel H, Burger K, Teipel SJ, Bokde AL, Zetterberg H, Blennow K. Core candidate neurochemical and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2008;4:38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jack CR, Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Shaw LM, Aisen PS, Weiner MW, et al. Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer's pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:119–128. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70299-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hakala BE, White C, Recklies AD. Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:25803–25810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Colton CA, Mott RT, Sharpe H, Xu Q, Van Nostrand WE, Vitek MP. Expression profiles for macrophage alternative activation genes in AD and in mouse models of AD. J Neuroinflammation. 2006;3:27. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-3-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johansen JS. Studies on serum YKL-40 as a biomarker in diseases with inflammation, tissue remodelling, fibroses and cancer. Dan Med Bull. 2006;53:172–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johansen JS, Schultz NA, Jensen BV. Plasma YKL-40: a potential new cancer biomarker? Future Oncol. 2009;5:1065–1082. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Comabella M, Fernandez M, Martin R, Rivera-Vallve S, Borras E, Chiva C, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid chitinase 3-like 1 levels are associated with conversion to multiple sclerosis. Brain. 133:1082–1093. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan E. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Suzuki N, Cheung TT, Cai XD, Odaka A, Otvos L, Jr, Eckman C, et al. An increased percentage of long amyloid beta protein secreted by familial amyloid beta protein precursor (beta APP717) mutants. Science. 1994;264:1336–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.8191290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Storandt M, Grant E, Miller J, Morris J. Longitudinal course and neuropathologic outcomes in original vs revised MCI and in pre-MCI. Neurology. 2006;67:467–473. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000228231.26111.6e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Klunk W, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt D, et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer's disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:306–319. doi: 10.1002/ana.20009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fagan A, Mintun M, Mach R, Lee S-Y, Dence C, Shah A, et al. Inverse relation between in vivo amyloid imaging load and CSF Ab42 in humans. Ann Neurol. 2006;59:512–519. doi: 10.1002/ana.20730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mintun M, LaRossa G, Sheline Y, Dence C, Lee S-Y, Mach R, et al. [11C]PIB in a nondemented population: Potential antecedent marker of Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2006;67:446–452. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000228230.26044.a4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fagan A, Roe C, Xiong C, Mintun M, Morris J, Holtzman D. Cerebrospinal fluid tau/Ab42 ratio as a prediction of cognitive decline in nondemented older adults. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:343–349. doi: 10.1001/archneur.64.3.noc60123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 1998;51:1546–1554. doi: 10.1212/wnl.51.6.1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D, Campbell G, Dubois B, Duvoisin RC, et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology. 1996;47:1–9. doi: 10.1212/wnl.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hu Y, Hosseini A, Kauwe J, Gross J, Cairns N, Goate A, et al. Identification and validation of novel CSF biomarkers for early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Proteomics - Clin Appl. 2007;1:1373–1384. doi: 10.1002/prca.200600999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hu Y, Malone J, Fagan A, Townsend R, Holtzman D. Comparative proteomic analysis of intra- and interindividual variation in human cerebrospinal fluid. Mol & Cell Proteom. 2005;4:2000–2009. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M500207-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li G, Sokal I, Quinn J, Leverenz J, Brodey M, Schellenberg G, et al. CSF tau/Ab42 ratio for increased risk of mild cognitive impairment: A follow-up study. Neurology. 2007;69:631–639. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000267428.62582.aa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hansson O, Zetterberg H, Buchhave P, Londos E, Blennow K, Minthon L. Association Between CSF Biomarkers and Incipient Alzheimer's Disease in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Follow-Up Study. Lancent Neurology. 2006;5:228–234. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Snider BJ, Fagan AM, Roe C, Shah AR, Grant EA, Xiong C, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and rate of cognitive decline in very mild dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:638–645. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2009.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Suarez-Sola ML, Gonzalez-Delgado FJ, Pueyo-Morlans M, Medina-Bolivar OC, Hernandez-Acosta NC, Gonzalez-Gomez M, et al. Neurons in the white matter of the adult human neocortex. Front Neuroanat. 2009;3:7. doi: 10.3389/neuro.05.007.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kacira T, Hanimoglu H, Kucur M, Sanus GZ, Kafadar AM, Tanriverdi T, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid and serum YKL-40 levels are not associated with symptomatic vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15:1011–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2006.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bonneh-Barkay D, Bissel SJ, Wang G, Fish KN, Nicholl GC, Darko SW, et al. YKL-40, a marker of simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis, modulates the biological activity of basic fibroblast growth factor. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:130–143. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.080045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ostergaard C, Johansen JS, Benfield T, Price PA, Lundgren JD. YKL-40 is elevated in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with purulent meningitis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:598–604. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.9.3.598-604.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Roberts ES, Zandonatti MA, Watry DD, Madden LJ, Henriksen SJ, Taffe MA, et al. Induction of pathogenic sets of genes in macrophages and neurons in NeuroAIDS. Am J Pathol. 2003;162:2041–2057. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64336-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bonneh-Barkay D, Wang G, Starkey A, Hamilton RL, Wiley CA. In vivo CHI3L1 (YKL-40) expression in astrocytes in acute and chronic neurological diseases. J Neuroinflammation. 7:34. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Andreasen N, Hess C, Davidsson P, Minthon L, Wallin A, Winblad B, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid b-amyloid(1–42) in Alzheimer's disease: Differences between early- and late-onset Alzheimer's disease and stability during the course of disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56:673–680. doi: 10.1001/archneur.56.6.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zetterberg H, Pedersen M, Lind K, Svensson M, Rolstad S, Eckerstrom C, et al. Intra-individual stability of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease over two years. J Alzheimers Dis. 2007;12:255–260. doi: 10.3233/jad-2007-12307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fagan AM, Mintun MA, Shah AR, Aldea P, Roe CM, Mach RH, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid tau and ptau(181) increase with cortical amyloid deposition in cognitively normal individuals: implications for future clinical trials of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO Mol Med. 2009;1:371–380. doi: 10.1002/emmm.200900048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wyss-Coray T, Mucke L. Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease--a double-edged sword. Neuron. 2002;35:419–432. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00794-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(00)00124-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Heneka MT, O'Banion MK. Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;184:69–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Recklies AD, Ling H, White C, Bernier SM. Inflammatory cytokines induce production of CHI3L1 by articular chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:41213–41221. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510146200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Letuve S, Kozhich A, Arouche N, Grandsaigne M, Reed J, Dombret MC, et al. YKL-40 is elevated in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and activates alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 2008;181:5167–5173. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.5167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.De Ceuninck F, Gaufillier S, Bonnaud A, Sabatini M, Lesur C, Pastoureau P. YKL-40 (cartilage gp-39) induces proliferative events in cultured chondrocytes and synoviocytes and increases glycosaminoglycan synthesis in chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285:926–931. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Recklies AD, White C, Ling H. The chitinase 3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC-gp39) stimulates proliferation of human connective-tissue cells and activates both extracellular signal-regulated kinase- and protein kinase B-mediated signalling pathways. Biochem J. 2002;365:119–126. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ling H, Recklies AD. The chitinase 3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 inhibits cellular responses to the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem J. 2004;380:651–659. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bigg HF, Wait R, Rowan AD, Cawston TE. The mammalian chitinase-like lectin, YKL-40, binds specifically to type I collagen and modulates the rate of type I collagen fibril formation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:21082–21095. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601153200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Malinda KM, Ponce L, Kleinman HK, Shackelton LM, Millis AJ. Gp38k, a protein synthesized by vascular smooth muscle cells, stimulates directional migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1999;250:168–173. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nishikawa KC, Millis AJ. gp38k (CHI3L1) is a novel adhesion and migration factor for vascular cells. Exp Cell Res. 2003;287:79–87. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lee CG, Hartl D, Lee GR, Koller B, Matsuura H, Da Silva CA, et al. Role of breast regression protein 39 (BRP-39)/chitinase 3-like-1 in Th2 and IL-13-induced tissue responses and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1149–1166. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Morris JC, Roe CM, Xiong C, Fagan AM, Goate AM, Holtzman DM, et al. APOE Predicts Abeta but not Tau Alzheimer's Pathology in Cognitively Normal Aging. Ann Neurol. 2010 doi: 10.1002/ana.21843. In Press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Price JL, Morris JC. Tangles and plaques in nondemented aging and "preclinical" Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1999;45:358–368. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199903)45:3<358::aid-ana12>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sunderland T, Linker G, Mirza N, Putnam K, Friedman D, Kimmel L, et al. Decreased b-amyloid1–42 and increased tau levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. JAMA. 2003;289:2094–2103. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.16.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.