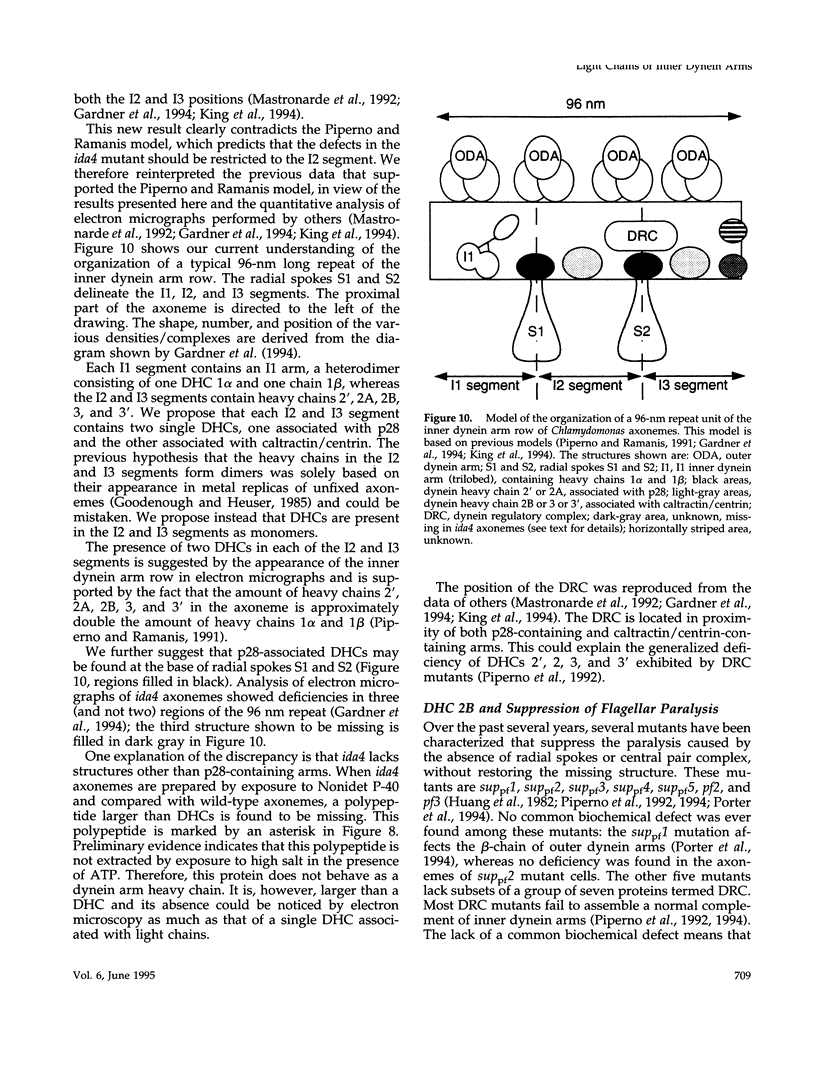
Abstract
We show here that I2 and I3 inner dynein arm heavy chains of Chlamydomonas axonemes are resolved into two classes: one class associated with the protein p28 and the other associated with the protein caltractin/centrin. We have determined the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding p28, a light chain that, together with actin and caltractin/centrin, is associated with inner dynein arms I2 and I3 of Chlamydomonas axonemes. p28 is a novel protein with affinity for a subset of the inner dynein arm heavy chains, but with no apparent significant homologies to tubulin- or actin-binding proteins. An antiserum specific for p28 showed that p28 is present along the entire axoneme. The same antiserum coimmunoprecipitated p28, actin, and dynein heavy chains 2' and 2. In contrast, an anti-caltractin/centrin antiserum coimmunoprecipitated caltractin/centrin, actin, and the heavy chains 2, 3, and 3'. It is likely that the dynein heavy chain 2 associated with p28, referred to as 2A, is a different polypeptide from dynein heavy chain 2 bound to caltractin/centrin, referred to as 2B. The complex formed by heavy chain 2B, actin, and caltractin/centrin is preferentially extracted by exposure to Nonidet P-40 and is missing in mutants lacking components 1 and 2 of the dynein regulatory complex.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya D., Steinkötter J., Melkonian M. Molecular cloning and evolutionary analysis of the calcium-modulated contractile protein, centrin, in green algae and land plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Dec;23(6):1243–1254. doi: 10.1007/BF00042357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokaw C. J., Kamiya R. Bending patterns of Chlamydomonas flagella: IV. Mutants with defects in inner and outer dynein arms indicate differences in dynein arm function. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer M. The selection-mutation-drift theory of synonymous codon usage. Genetics. 1991 Nov;129(3):897–907. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.3.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox L. A., Sale W. S. Direction of force generated by the inner row of dynein arms on flagellar microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1781–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner L. C., O'Toole E., Perrone C. A., Giddings T., Porter M. E. Components of a "dynein regulatory complex" are located at the junction between the radial spokes and the dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1311–1325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Heuser J. E. Substructure of inner dynein arms, radial spokes, and the central pair/projection complex of cilia and flagella. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):2008–2018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Mengersen A., Lee V. D. Molecular cloning of cDNA for caltractin, a basal body-associated Ca2+-binding protein: homology in its protein sequence with calmodulin and the yeast CDC31 gene product. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):133–140. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Ramanis Z., Luck D. J. Suppressor mutations in Chlamydomonas reveal a regulatory mechanism for Flagellar function. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Watterson D. M., Lee V. D., Schibler M. J. Purification and characterization of a basal body-associated Ca2+-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):121–131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagami O., Takada S., Kamiya R. Microtubule translocation caused by three subspecies of inner-arm dynein from Chlamydomonas flagella. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80243-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Kurimoto E., Muto E. Two types of Chlamydomonas flagellar mutants missing different components of inner-arm dynein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):441–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Kagami O., Yagi T., Kamiya R. Isolation of two species of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagellar mutants, ida5 and ida6, that lack a newly identified heavy chain of the inner dynein arm. Cell Struct Funct. 1993 Dec;18(6):371–377. doi: 10.1247/csf.18.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. J., Inwood W. B., O'Toole E. T., Power J., Dutcher S. K. The bop2-1 mutation reveals radial asymmetry in the inner dynein arm region of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1255–1266. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDizet M., Piperno G. Cytoplasmic microtubules containing acetylated alpha-tubulin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: spatial arrangement and properties. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):13–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. D., Huang B. Molecular cloning and centrosomal localization of human caltractin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11039–11043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long M., Gillespie J. H. Codon usage divergence of homologous vertebrate genes and codon usage clock. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jan;32(1):6–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02099923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck D., Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Huang B. Flagellar mutants of Chlamydomonas: studies of radial spoke-defective strains by dikaryon and revertant analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3456–3460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastronarde D. N., O'Toole E. T., McDonald K. L., McIntosh J. R., Porter M. E. Arrangement of inner dynein arms in wild-type and mutant flagella of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1145–1162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Fuller M. T. Monoclonal antibodies specific for an acetylated form of alpha-tubulin recognize the antigen in cilia and flagella from a variety of organisms. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2085–2094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Huang B., Ramanis Z., Luck D. J. Radial spokes of Chlamydomonas flagella: polypeptide composition and phosphorylation of stalk components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):73–79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G. Isolation of a sixth dynein subunit adenosine triphosphatase of Chlamydomonas axonemes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):133–140. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Mead K., LeDizet M., Moscatelli A. Mutations in the "dynein regulatory complex" alter the ATP-insensitive binding sites for inner arm dyneins in Chlamydomonas axonemes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1109–1117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Mead K., Shestak W. The inner dynein arms I2 interact with a "dynein regulatory complex" in Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1455–1463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):379–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z. The proximal portion of Chlamydomonas flagella contains a distinct set of inner dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):701–709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Knott J. A., Gardner L. C., Mitchell D. R., Dutcher S. K. Mutations in the SUP-PF-1 locus of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identify a regulatory domain in the beta-dynein heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1495–1507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Power J., Dutcher S. K. Extragenic suppressors of paralyzed flagellar mutations in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identify loci that alter the inner dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1163–1176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale W. S., Satir P. Direction of active sliding of microtubules in Tetrahymena cilia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2045–2049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D. C., Sharp P. M., Higgins D. G., Wright F. "Silent" sites in Drosophila genes are not neutral: evidence of selection among synonymous codons. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Nov;5(6):704–716. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Regulation of dynein-driven microtubule sliding by the radial spokes in flagella. Science. 1992 Sep 11;257(5076):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1387971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z., Vashishtha M., Hall J. L. The Chlamydomonas FLA10 gene encodes a novel kinesin-homologous protein. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):175–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson C. G., King S. M., Witman G. B. Molecular analysis of the gamma heavy chain of Chlamydomonas flagellar outer-arm dynein. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):497–506. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]