Abstract
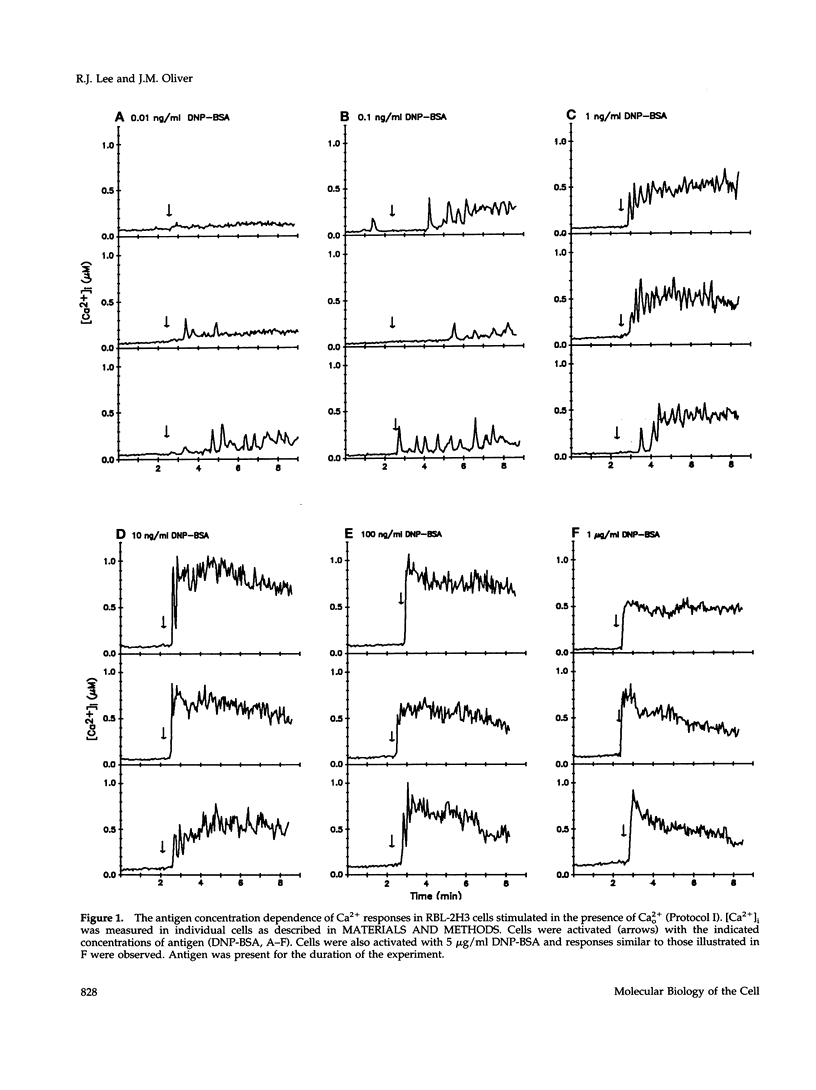
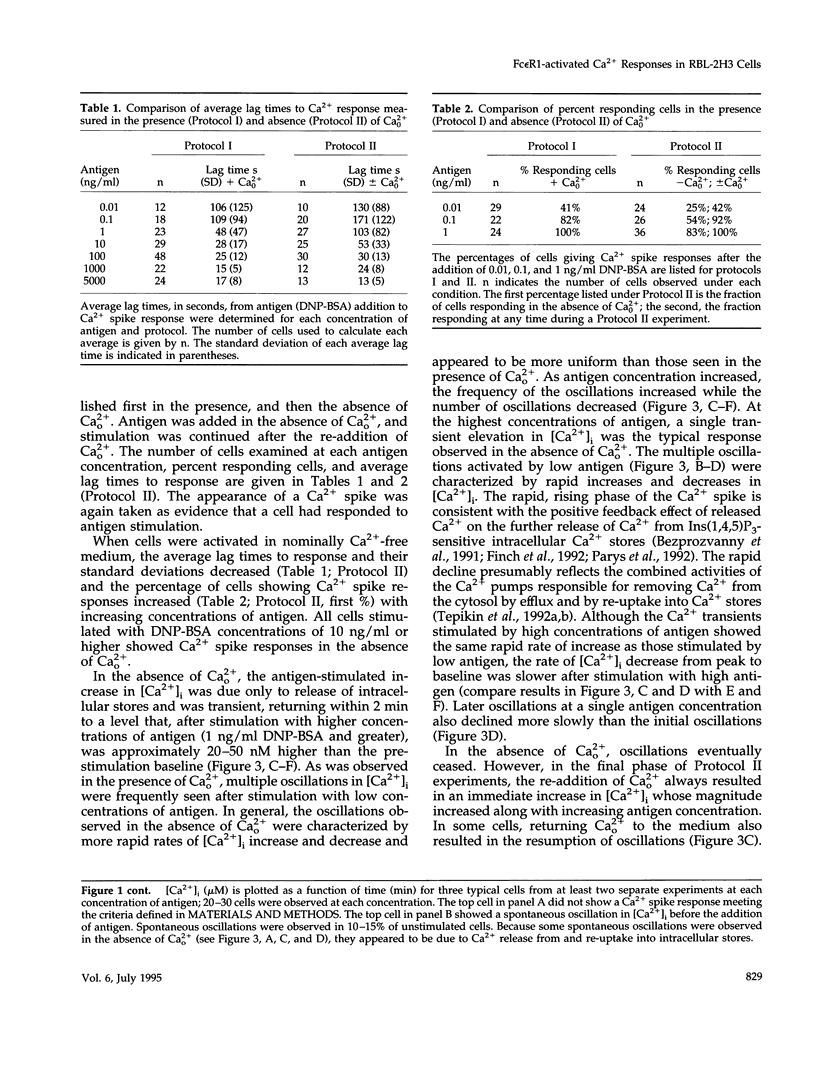
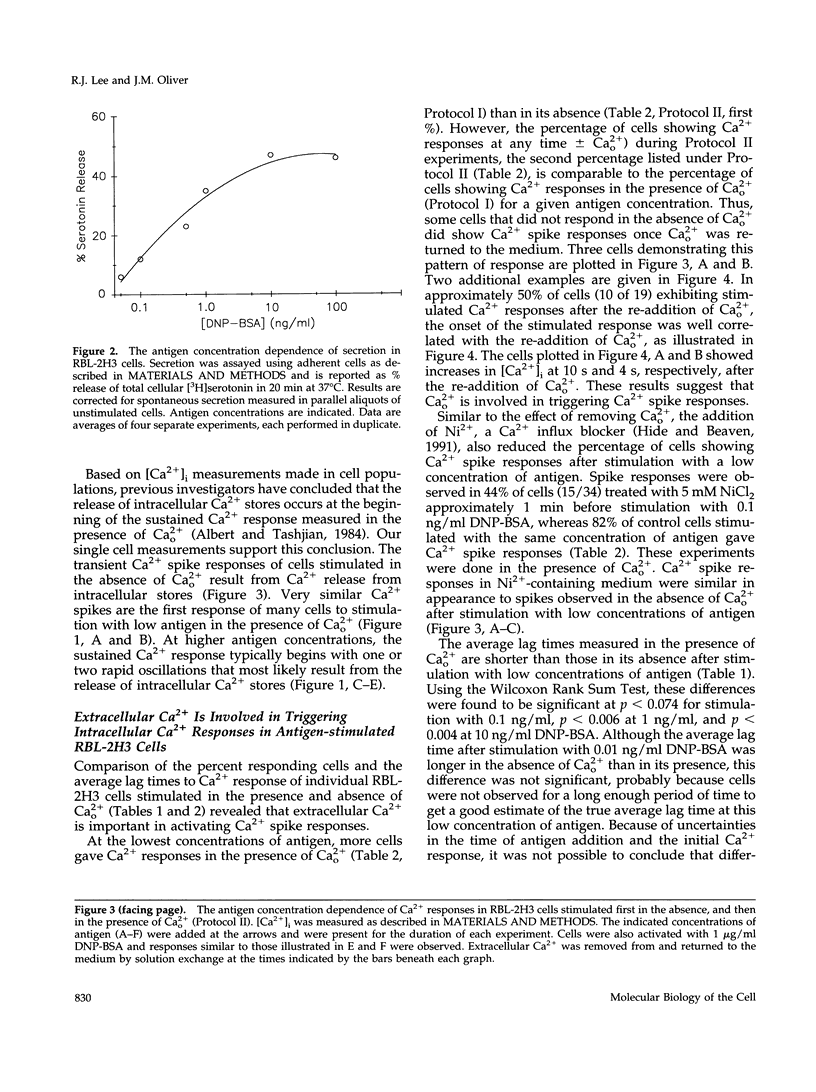
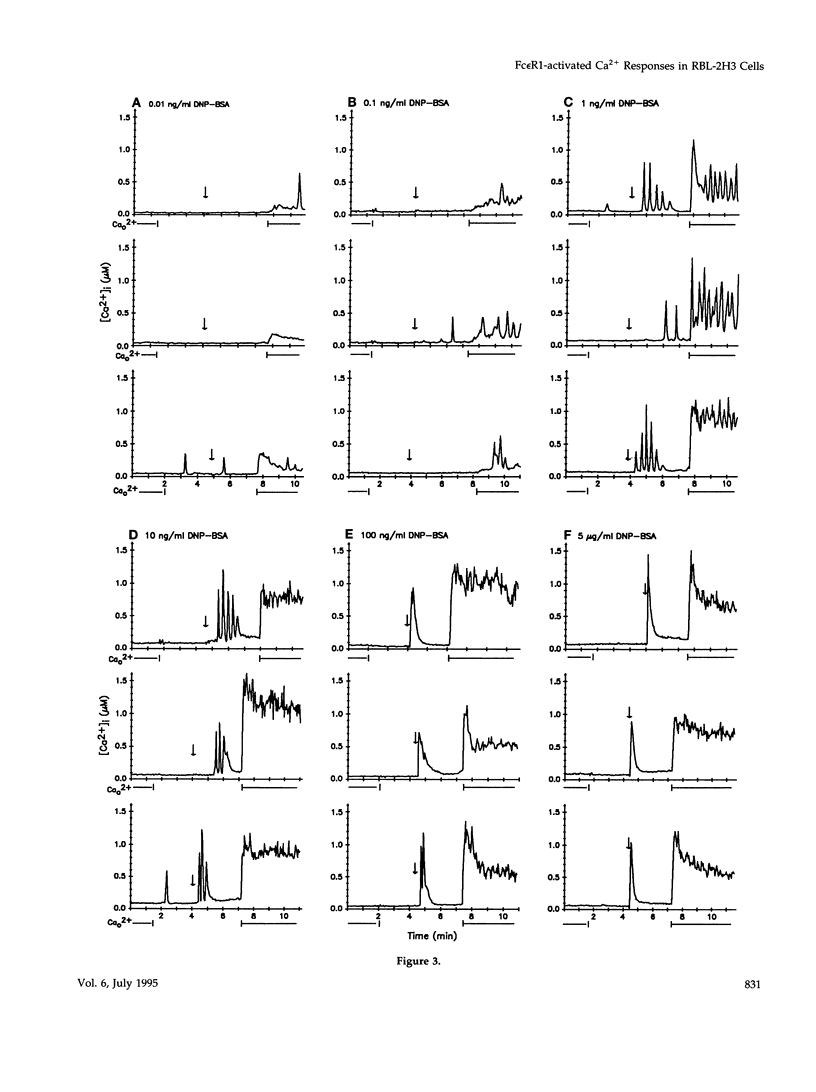
Cross-linking the high affinity IgE receptor, Fc epsilon R1, with multivalent antigen induces inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [Ins(1,4,5)P3]-dependent release of intracellular Ca2+ stores, Ca2+ influx, and secretion of inflammatory mediators from RBL-2H3 mast cells. Here, fluorescence ratio imaging microscopy was used to characterize the antigen-induced Ca2+ responses of single fura-2-loaded RBL-2H3 cells in the presence and absence of extracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+o). As antigen concentration increases toward the optimum for secretion, more cells show a Ca2+ spike or an abrupt increase in [Ca2+]i and the lag time to onset of the response decreases both in the presence and the absence of Ca2+o. When Ca2+o is absent, fewer cells respond to low antigen and the lag times to response are longer than those measured in the presence of Ca2+o, indicating that Ca2+o contributes to Ca2+ stores release. Ins(1,4,5)P3 production is not impaired by the removal of Ca2+o, suggesting that extracellular Ca2+ influences Ca2+ stores release via an effect on the Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptor. Stimulation with low concentrations of antigen can lead, only in the presence of Ca2+o, to a small, gradual increase in [Ca2+]i before the abrupt spike response that indicates store release. We propose that this small, initial [Ca2+]i increase is due to receptor-activated Ca2+ influx that precedes and may facilitate Ca2+ stores release. A mechanism for capacitative Ca2+ entry also exists in RBL-2H3 cells. Our data suggest that a previously undescribed response to Fc epsilon R1 cross-linking, inhibition of Ca2+ stores refilling, may be involved in activating capacitative Ca2+ entry in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells, thus providing the elevated [Ca2+]i required for optimal secretion. The existence of both capacitative entry and Ca2+ influx that can precede Ca2+ release from intracellular stores suggests that at least two mechanisms of stimulated Ca2+ influx are present in RBL-2H3 cells.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Relationship of thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced spike and plateau phases in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations to hormone secretion. Selective blockade using ionomycin and nifedipine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15350–15363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Metzger H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the Fc epsilon RI case. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90167-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. The relationship of the chemotactic behavior of the complement-derived factors, C3a, C5a, and C567, and a bacterial chemotactic factor to their ability to activate the proesterase 1 of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):376–387. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Bennett D. L., Berridge M. J. Smoothly graded Ca2+ release from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24783–24791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byron K. L., Babnigg G., Villereal M. L. Bradykinin-induced Ca2+ entry, release, and refilling of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Relationships revealed by image analysis of individual human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):108–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland P. L., Millard P. J., Showell H. J., Fewtrell C. M. Tenidap: a novel inhibitor of calcium influx in a mast cell line. Cell Calcium. 1993 Jan;14(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90013-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Melo J. R., Dean N. M., Moyer J. D., Maeyama K., Beaven M. A. The kinetics of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells varies with the type of IgE receptor cross-linking agent used. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11455–11463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Melo J. R., Gonzaga H. M., Ali H., Huang F. L., Huang K. P., Beaven M. A. Studies of protein kinase C in the rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cell reveal that antigen-induced signals are not mimicked by the actions of phorbol myristate acetate and Ca2+ ionophore. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2617–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deanin G. G., Cutts J. L., Pfeiffer J. R., Oliver J. M. Role of isoprenoid metabolism in IgE receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3528–3535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deanin G. G., Martinez A. M., Pfeiffer J. R., Gardner M. E., Oliver J. M. Tyrosine kinase-dependent phosphatidylinostiol turnover and functional responses in the Fc epsilon R1 signalling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):551–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Hoth M., Penner R. A GTP-dependent step in the activation mechanism of capacitative calcium influx. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20737–20740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell C., Lagunoff D., Metzger H. Secretion from rat basophilic leukaemia cells induced by calcium ionophores. Effect of pH and metabolic inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Tsien R. W. Phase-dependent contributions from Ca2+ entry and Ca2+ release to caffeine-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1109–1125. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90132-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grohovaz F., Zacchetti D., Clementi E., Lorenzon P., Meldolesi J., Fumagalli G. [Ca2+]i imaging in PC12 cells: multiple response patterns to receptor activation reveal new aspects of transmembrane signaling. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1341–1350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnóczky G., Thomas A. P. The inositol trisphosphate calcium channel is inactivated by inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):474–477. doi: 10.1038/370474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Agonist-induced calcium oscillations in depolarized fibroblasts and their manipulation by photoreleased Ins(1,4,5)P3, Ca++, and Ca++ buffer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):935–943. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide M., Beaven M. A. Calcium influx in a rat mast cell (RBL-2H3) line. Use of multivalent metal ions to define its characteristics and role in exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15221–15229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Sagara Y. Thapsigargin, a high affinity and global inhibitor of intracellular Ca2+ transport ATPases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90416-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Repetitive spikes in cytoplasmic calcium evoked by histamine in human endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):40–45. doi: 10.1038/335040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouneaux C., Audigier Y., Goldsmith P., Pecker F., Lotersztajn S. Gs mediates hormonal inhibition of the calcium pump in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2368–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Metzger H. Initial characterization of the calcium channel activated by the cross-linking of the receptors for immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10188–10193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. M., Toscas K., Villereal M. L. Inhibition of bradykinin- and thapsigargin-induced Ca2+ entry by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):9945–9948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Deanin G. G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Oliver J. M. Fc epsilon R1-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple proteins, including phospholipase C gamma 1 and the receptor beta gamma 2 complex, in RBL-2H3 rat basophilic leukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3176–3182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotersztajn S., Pavoine C., Brechler V., Roche B., Dufour M., Le-Nguyen D., Bataille D., Pecker F. Glucagon-(19-29) exerts a biphasic action on the liver plasma membrane Ca2+ pump which is mediated by G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9876–9880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Gross D., Webb W. W., Fewtrell C. Imaging asynchronous changes in intracellular Ca2+ in individual stimulated tumor mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1854–1858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Ryan T. A., Webb W. W., Fewtrell C. Immunoglobulin E receptor cross-linking induces oscillations in intracellular free ionized calcium in individual tumor mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19730–19739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Parys J. B., Casteels R. Co-activation of inositol trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release by cytosolic Ca2+ is loading-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7238–7242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr F. C., Fewtrell C. Depolarization of rat basophilic leukemia cells inhibits calcium uptake and exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakade S., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Involvement of the C-terminus of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in Ca2+ release analysed using region-specific monoclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2770125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan V., Holowka D., Fewtrell C., Baird B. Cholera toxin increases the rate of antigen-stimulated calcium influx in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19626–19632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Seagrave J., Stump R. F., Pfeiffer J. R., Deanin G. G. Signal transduction and cellular response in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Prog Allergy. 1988;42:185–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Min H. K., Rhee S. G. IgE-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24237–24240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parys J. B., Sernett S. W., DeLisle S., Snyder P. M., Welsh M. J., Campbell K. P. Isolation, characterization, and localization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor protein in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18776–18782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. C., Petersen O. H., Berridge M. J. The role of endoplasmic reticulum calcium pumps during cytosolic calcium spiking in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22262–22264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer J. R., Seagrave J. C., Davis B. H., Deanin G. G., Oliver J. M. Membrane and cytoskeletal changes associated with IgE-mediated serotonin release from rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribluda V. S., Metzger H. Calcium-independent phosphoinositide breakdown in rat basophilic leukemia cells. Evidence for an early rise in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate which precedes the rise in other inositol phosphates and in cytoplasmic calcium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11449–11454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Reast R., Rink T. J. ADP evokes biphasic Ca2+ influx in fura-2-loaded human platelets. Evidence for Ca2+ entry regulated by the intracellular Ca2+ store. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):675–680. doi: 10.1042/bj2650675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagi-Eisenberg R., Lieman H., Pecht I. Protein kinase C regulation of the receptor-coupled calcium signal in histamine-secreting rat basophilic leukaemia cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):59–60. doi: 10.1038/313059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seagrave J., Oliver J. M. Antigen-dependent transition of IgE to a detergent-insoluble form is associated with reduced IgE receptor-dependent secretion from RBL-2H3 mast cells. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):128–136. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stump R. F., Oliver J. M., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Deanin G. G. The control of mediator release from RBL-2H3 cells: roles for Ca2+, Na+, and protein kinase C1. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):881–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepikin A. V., Voronina S. G., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Acetylcholine-evoked increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration and Ca2+ extrusion measured simultaneously in single mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3569–3572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepikin A. V., Voronina S. G., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Pulsatile Ca2+ extrusion from single pancreatic acinar cells during receptor-activated cytosolic Ca2+ spiking. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14073–14076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Deanin G. G., Standefer J. C., Vanderjagt D., Oliver J. M. Depletion of guanine nucleotides with mycophenolic acid suppresses IgE receptor-mediated degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A., Cook M. N., Foley J. J., Sarau H. M., Marshall P., Hwang S. M. Influx of extracellular calcium is required for the membrane translocation of 5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene synthesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9346–9354. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Papp B., Verboomen H., Raeymaekers L., Dode L., Bobe R., Enouf J., Bokkala S., Authi K. S., Casteels R. A sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase 3-type Ca2+ pump is expressed in platelets, in lymphoid cells, and in mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1410–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


