Abstract
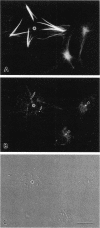
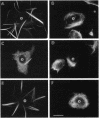
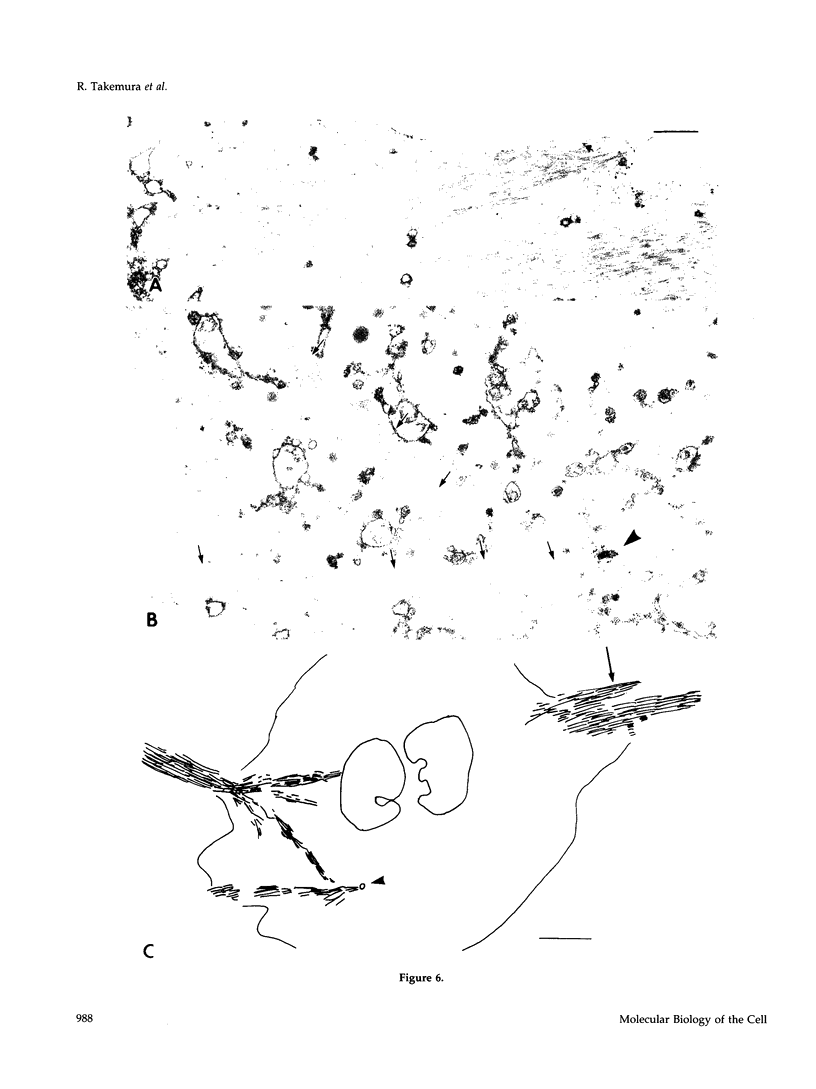
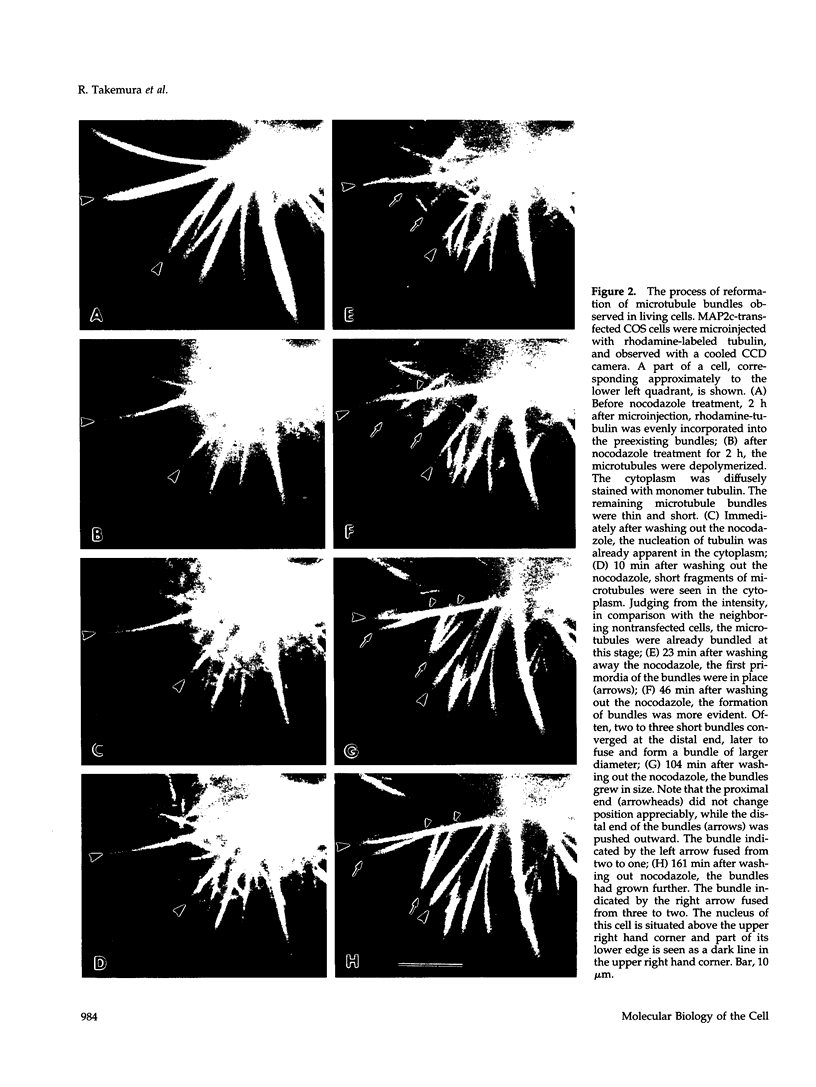
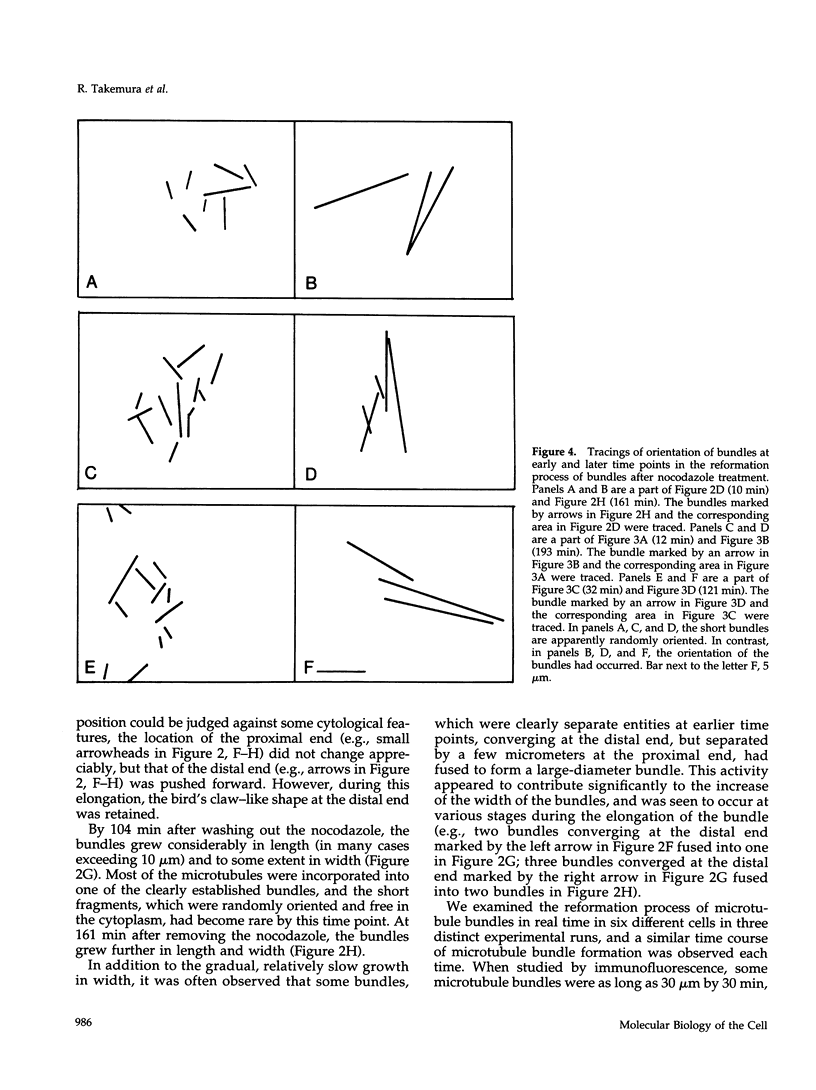
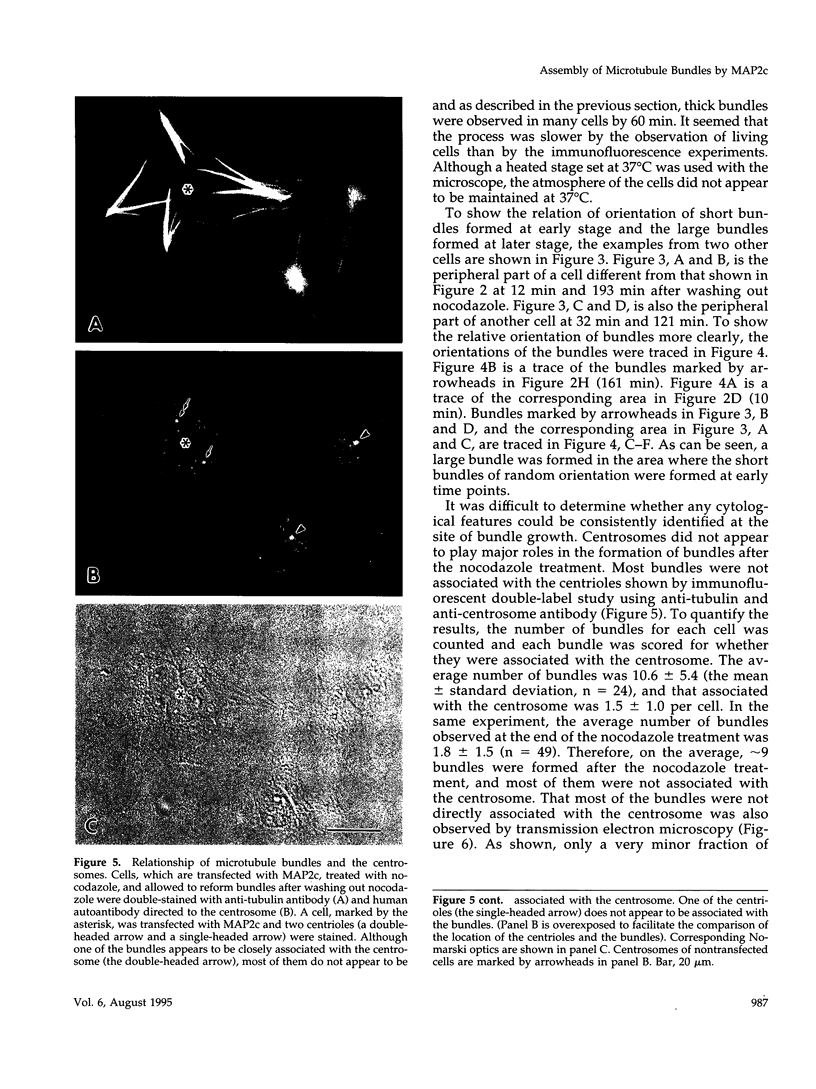
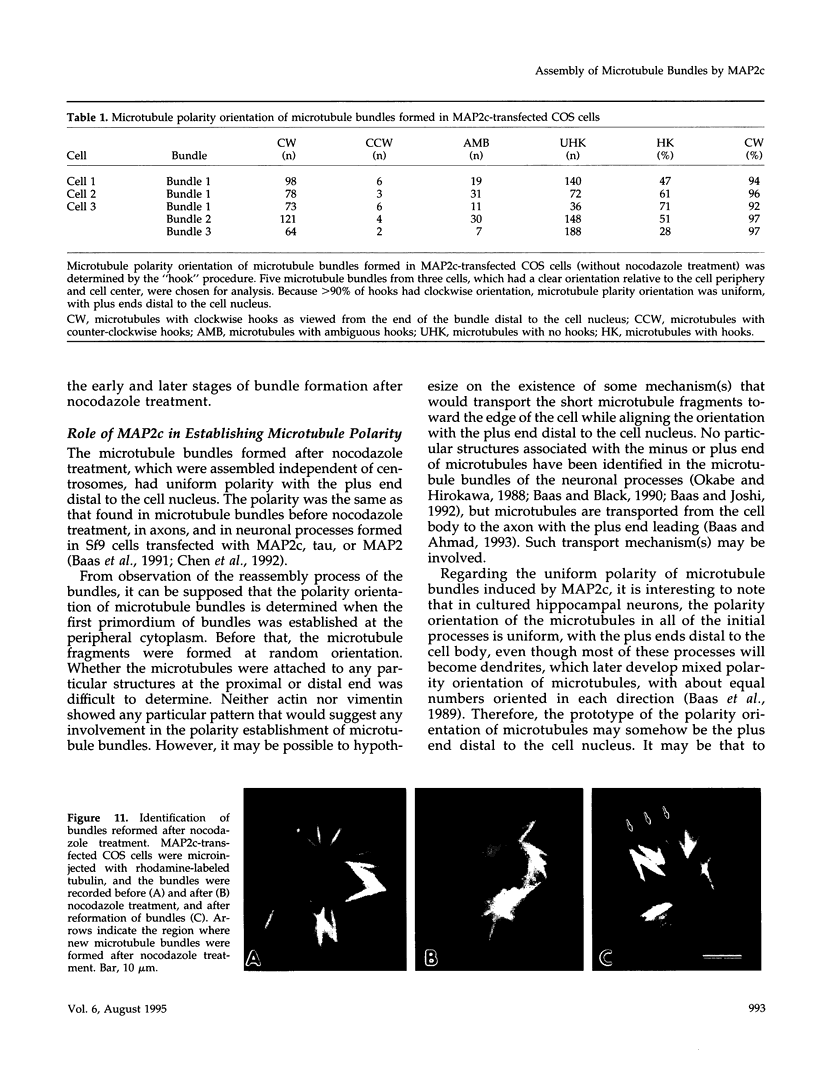
Microtubule bundles reminiscent of those found in neuronal processes are formed in fibroblasts and Sf9 cells that are transfected with the microtubule-associated proteins tau, MAP2, or MAP2c. To analyze the assembly process of these bundles and its relation to the microtubule polarity, we depolymerized the bundles formed in MAP2c-transfected COS cells using nocodazole, and observed the process of assembly of microtubule bundles after removal of the drug in cells microinjected with rhodamine-labeled tubulin. Within minutes of its removal, numerous short microtubule fragments were observed throughout the cytoplasm. These short fragments were randomly oriented and were already bundled. Somewhat longer, but still short bundles, were then found in the peripheral cytoplasm. These bundles became the primordium of the larger bundles, and gradually grew in length and width. The polarity orientation of microtubules in the reformed bundle as determined by "hook" procedure using electron microscope was uniform with the plus end distal to the cell nucleus. The results suggest that some mechanism(s) exists to orient the polarity of microtubules, which are not in direct continuity with the centrosome, during the formation of large bundles. The observed process presents a useful model system for studying the organization of microtubules that are not directly associated with the centrosomes, such as those observed in axons.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas P. W., Ahmad F. J. The transport properties of axonal microtubules establish their polarity orientation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1427–1437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Black M. M., Banker G. A. Changes in microtubule polarity orientation during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3085–3094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Black M. M. Individual microtubules in the axon consist of domains that differ in both composition and stability. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):495–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Joshi H. C. Gamma-tubulin distribution in the neuron: implications for the origins of neuritic microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):171–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Pienkowski T. P., Kosik K. S. Processes induced by tau expression in Sf9 cells have an axon-like microtubule organization. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1333–1344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Bunge M. B. Serial analysis of microtubules in cultured rat sensory axons. J Neurocytol. 1981 Aug;10(4):589–605. doi: 10.1007/BF01262592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R. Microtubule organizing centers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:145–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R. Microtubules of frog olfactory axons: their length and number/axon. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 14;409(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90742-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Paige J. L. Polarity of axoplasmic microtubules in the olfactory nerve of the frog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3269–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Kanai Y., Cowan N. J., Hirokawa N. Projection domains of MAP2 and tau determine spacings between microtubules in dendrites and axons. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):674–677. doi: 10.1038/360674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson K., Weisshaar B., Matus A. Actin depolymerisation induces process formation on MAP2-transfected non-neuronal cells. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):689–700. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen G. G., Khawaja S., Bulinski J. C. Postpolymerization detyrosination of alpha-tubulin: a mechanism for subcellular differentiation of microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):251–264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Landers J. M., Hamborg M. A. Polarity orientation of axonal microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):661–665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., McIntosh J. R. Visualization of the structural polarity of microtubules. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):517–519. doi: 10.1038/286517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R. Microtubule polarity determination based on formation of protofilament hooks. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:469–477. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi H. C., Baas P. W. A new perspective on microtubules and axon growth. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1191–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Chen J., Hirokawa N. Microtubule bundling by tau proteins in vivo: analysis of functional domains. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3953–3961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Takemura R., Oshima T., Mori H., Ihara Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Hirokawa N. Expression of multiple tau isoforms and microtubule bundle formation in fibroblasts transfected with a single tau cDNA. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1173–1184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knops J., Kosik K. S., Lee G., Pardee J. D., Cohen-Gould L., McConlogue L. Overexpression of tau in a nonneuronal cell induces long cellular processes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):725–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Cowan N. Microtubule bundling. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):674–674. doi: 10.1038/345674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Ivanov I. E., Lee G. H., Cowan N. J. Organization of microtubules in dendrites and axons is determined by a short hydrophobic zipper in microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and tau. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):498–505. doi: 10.1038/342498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Leslie R., Kuriyama R. Identification of a minus end-specific microtubule-associated protein located at the mitotic poles in cultured mammalian cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;54(2):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Murata I., Takeuchi A., Kamatani N., Tanimoto K., Yokohari R. Human anticentriole autoantibody in patients with scleroderma and Raynaud's phenomenon. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Dec;29(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe S., Hirokawa N. Microtubule dynamics in nerve cells: analysis using microinjection of biotinylated tubulin into PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):651–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Cytoplasmic microtubules in tissue culture cells appear to grow from an organizing structure towards the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):867–871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell S. W., Grasser W. A., Murphy D. B. End-to-end annealing of microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):619–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M. Action of cytochalasin D on cytoskeletal networks. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):79–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S. Cytoplasmic structure in rapid-frozen axons. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):667–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura R., Okabe S., Umeyama T., Kanai Y., Cowan N. J., Hirokawa N. Increased microtubule stability and alpha tubulin acetylation in cells transfected with microtubule-associated proteins MAP1B, MAP2 or tau. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):953–964. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeyama T., Okabe S., Kanai Y., Hirokawa N. Dynamics of microtubules bundled by microtubule associated protein 2C (MAP2C). J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):451–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisshaar B., Doll T., Matus A. Reorganisation of the microtubular cytoskeleton by embryonic microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2c). Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):1151–1161. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille H., Mandelkow E. M., Dingus J., Vallee R. B., Binder L. I., Mandelkow E. Domain structure and antiparallel dimers of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2). J Struct Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;108(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90006-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille H., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. The juvenile microtubule-associated protein MAP2c is a rod-like molecule that forms antiparallel dimers. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10737–10742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W., Centonze V. E., Ahmad F. J., Baas P. W. Microtubule nucleation and release from the neuronal centrosome. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):349–359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]