Abstract
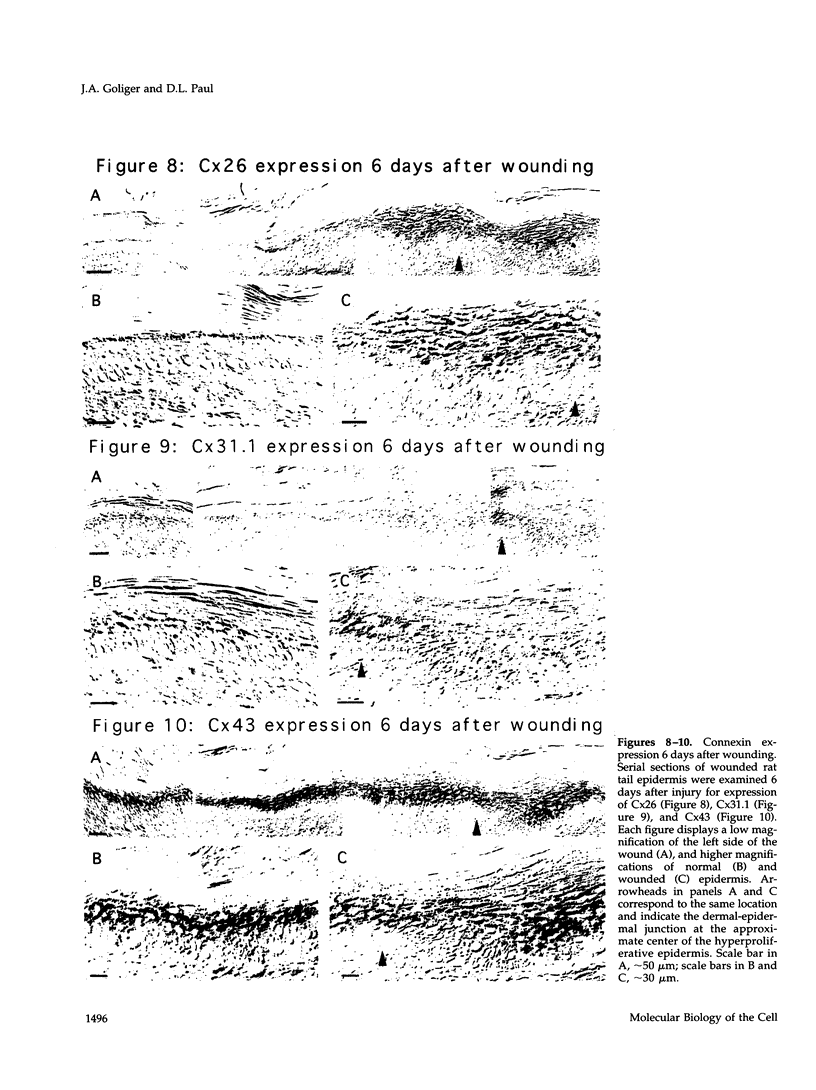
We show that connexin expression and in vivo patterns of communication were dramatically altered in response to epidermal wounding. Six hours after injury, Cx26 was up-regulated in the differentiated cells proximal to the wound, but was down-regulated in cells located at the wound edge. In contrast, Cx31.1 and Cx43 were down-regulated in cells both peripheral to and at the wounded edge. These patterns of altered connexin expression were detectable as early as 2 h after wounding and were most pronounced in 24-h old wounds. Increased expression of Cx26 was still evident in the hyperproliferative epidermis of 6-day old wounds. In vivo dye transfer experiments with Lucifer yellow and neurobiotin confirmed that junctional communication patterns were altered in ways consistent with changes in connexin expression. The data thus suggest that intercellular communication is intimately involved in regulating epidermal wound repair.
Full text
PDF

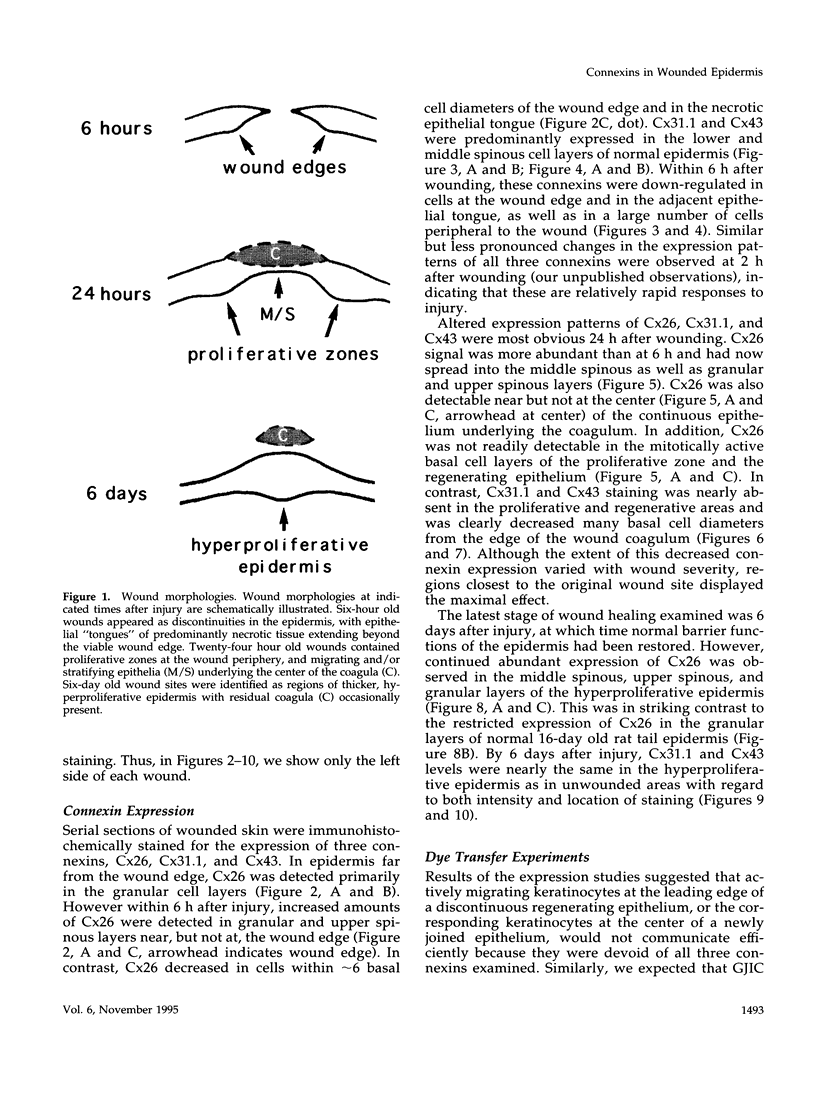







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Biotin amplification of biotin and horseradish peroxidase signals in histochemical stains. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1457–1463. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1527370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen L. Cell junctions in squamous epithelium during wound healing in palatal mucosa of guinea pigs. Scand J Dent Res. 1980 Aug;88(4):328–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1980.tb01235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Verselis V. K. Biophysics of gap junctions. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;3(1):29–47. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterweck A., Elfgang C., Willecke K., Traub O. Differential expression of the gap junction proteins connexin45, -43, -40, -31, and -26 in mouse skin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;65(1):152–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo R., Peluchetti D. The junctions of normal human epidermis. A freeze-fracture study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1977 Oct;61(1):44–61. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(77)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. Cutaneous tissue repair: basic biologic considerations. I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 Nov;13(5 Pt 1):701–725. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)70213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfgang C., Eckert R., Lichtenberg-Fraté H., Butterweck A., Traub O., Klein R. A., Hülser D. F., Willecke K. Specific permeability and selective formation of gap junction channels in connexin-transfected HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):805–817. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Hüttner I. Cytoplasmic filaments and gap junctions in epithelial cells and myofibroblasts during wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):561–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goliger J. A., Paul D. L. Expression of gap junction proteins Cx26, Cx31.1, Cx37, and Cx43 in developing and mature rat epidermis. Dev Dyn. 1994 May;200(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002000102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELL E. A., CRUICKSHANK C. N. THE EFFECT OF INJURY UPON THE UPTAKE OF 3-H-THYMIDINE BY GUINEA PIG EPIDERMIS. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Jun;31:128–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertle M. D., Kubler M. D., Leigh I. M., Watt F. M. Aberrant integrin expression during epidermal wound healing and in psoriatic epidermis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1892–1901. doi: 10.1172/JCI115794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam E., Melville L., Pitts J. D. Patterns of junctional communication in skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Dec;87(6):748–753. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamibayashi Y., Oyamada M., Oyamada Y., Mori M. Expression of gap junction proteins connexin 26 and 43 is modulated during differentiation of keratinocytes in newborn mouse epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Dec;101(6):773–778. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansbridge J. N., Knapp A. M. Penetration of lucifer yellow into human skin: a lateral diffusion channel in the stratum corneum. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jun;41(6):909–914. doi: 10.1177/41.6.8315281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Elias P. M., Lee S. H., Feingold K. R. Localization of calcium in murine epidermis following disruption and repair of the permeability barrier. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Dec;270(3):503–512. doi: 10.1007/BF00645052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Laird D. W., Revel J. P., Johnson R. G. Inhibition of gap junction and adherens junction assembly by connexin and A-CAM antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L., Yu K., Bruzzone R., Gimlich R. L., Goodenough D. A. Expression of a dominant negative inhibitor of intercellular communication in the early Xenopus embryo causes delamination and extrusion of cells. Development. 1995 Feb;121(2):371–381. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risek B., Klier F. G., Gilula N. B. Developmental regulation and structural organization of connexins in epidermal gap junctions. Dev Biol. 1994 Jul;164(1):183–196. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risek B., Klier F. G., Gilula N. B. Multiple gap junction genes are utilized during rat skin and hair development. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):639–651. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D., Masgrau E., Vischer S., Ullrich S., Dupont E., Sappino P., Saurat J. H., Meda P. Topography of mammalian connexins in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Aug;103(2):240–247. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12393218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D., Saurat J. H., Meda P. Cell-to-cell communication within intact human skin. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):248–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI113578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. W., Bruzzone R., Goodenough D. A., Paul D. L. Mouse Cx50, a functional member of the connexin family of gap junction proteins, is the lens fiber protein MP70. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):711–720. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]