Abstract
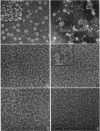
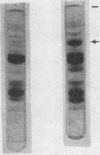
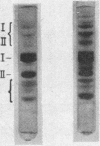
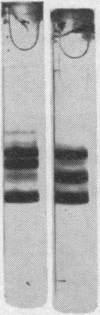
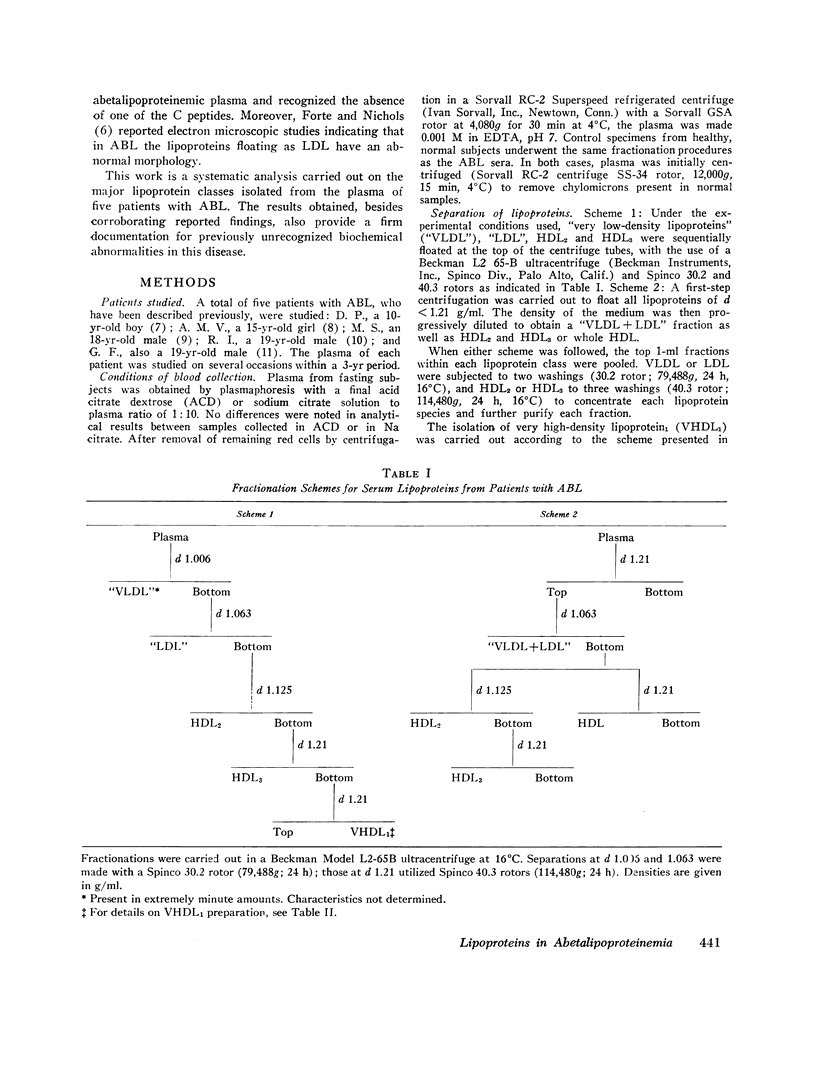
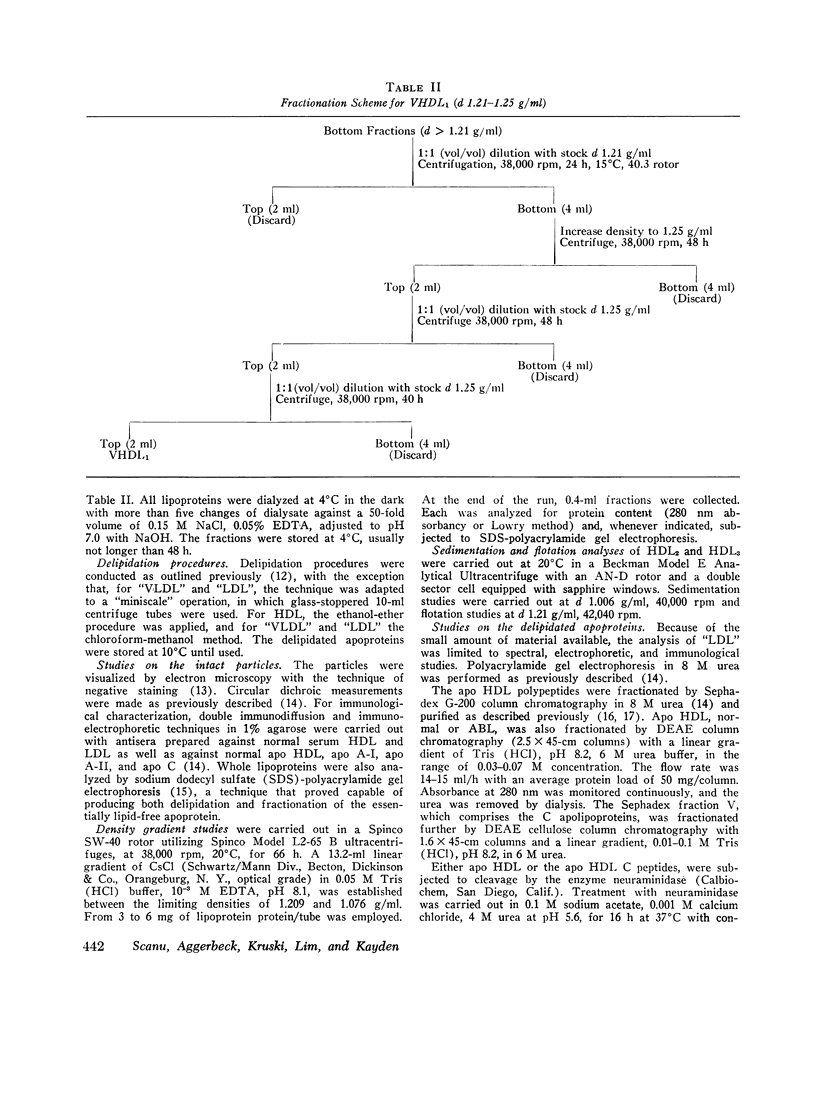
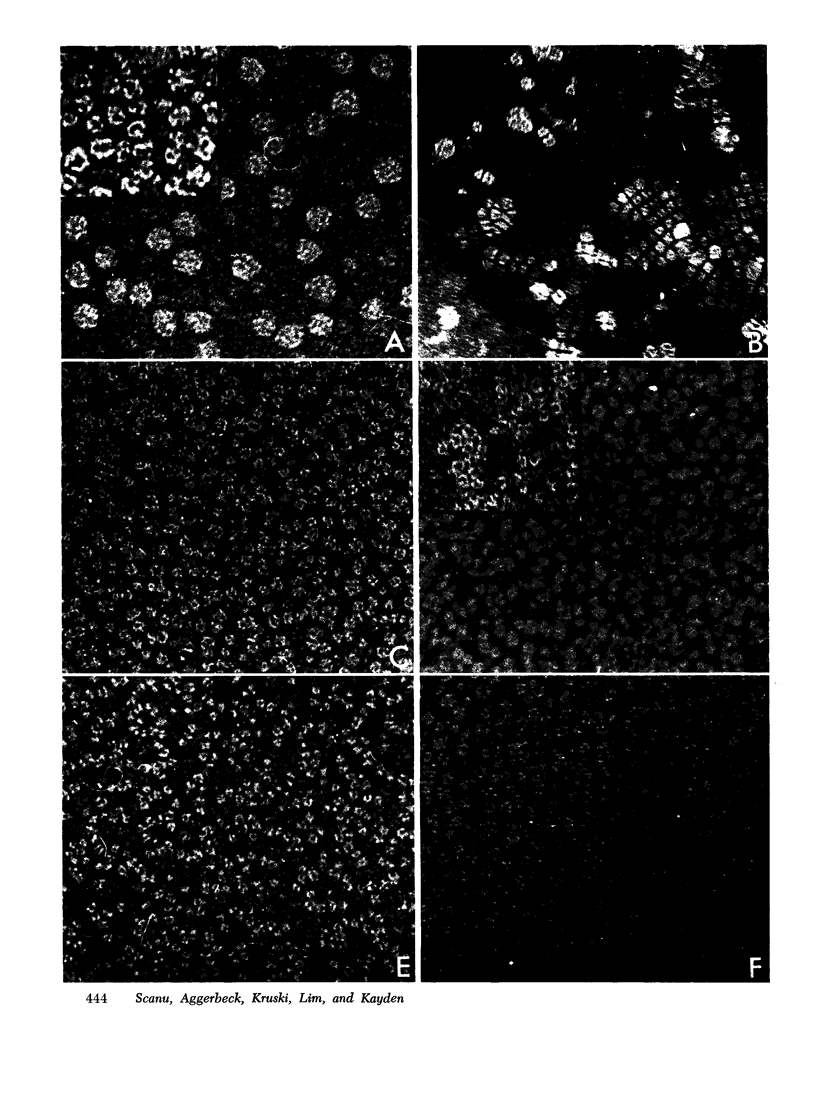
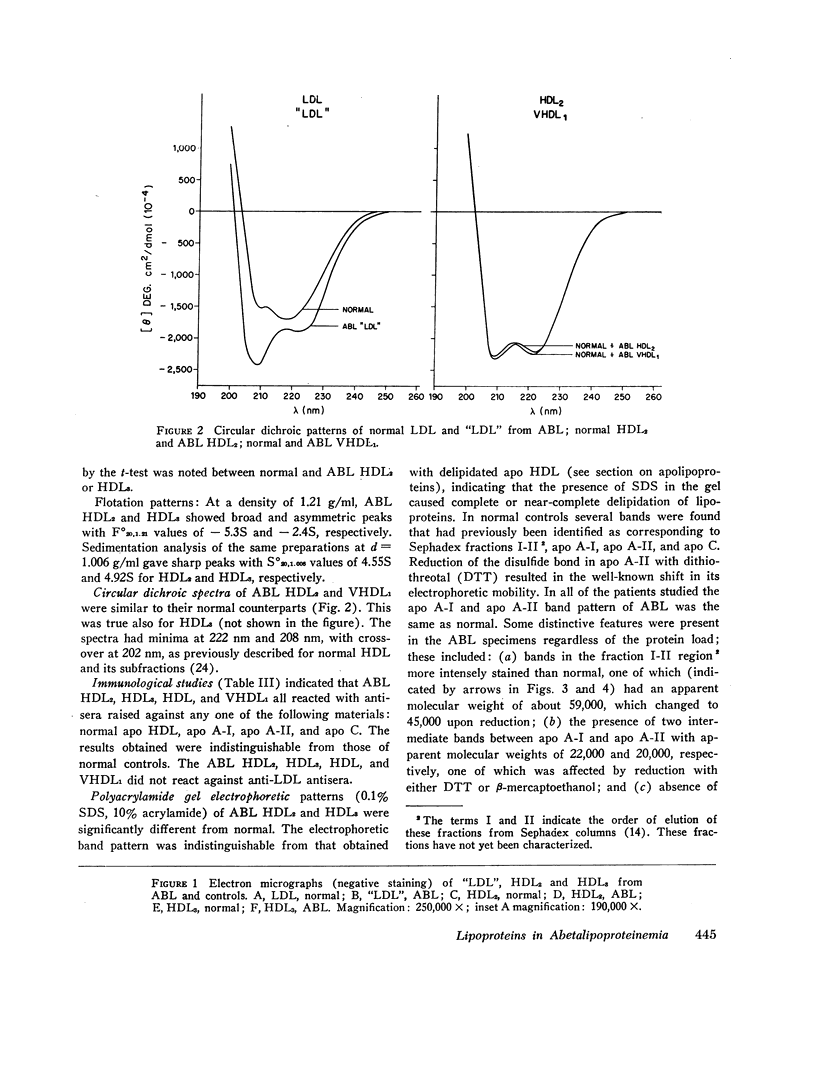
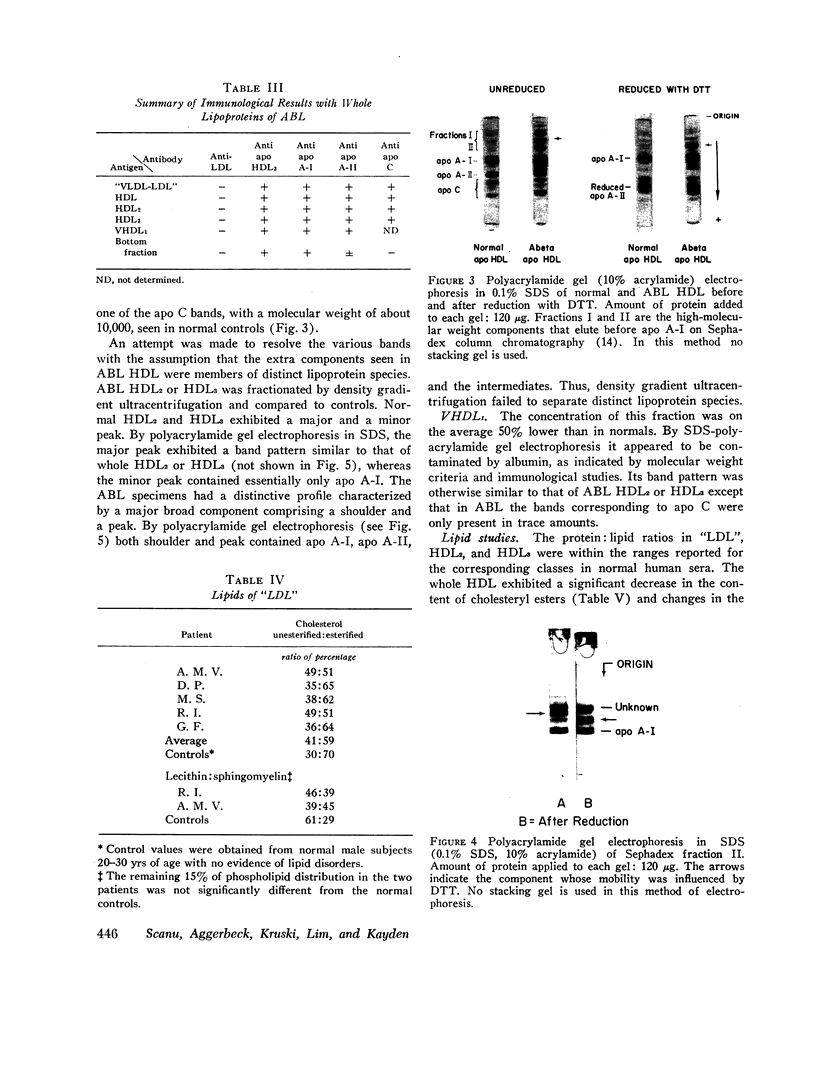
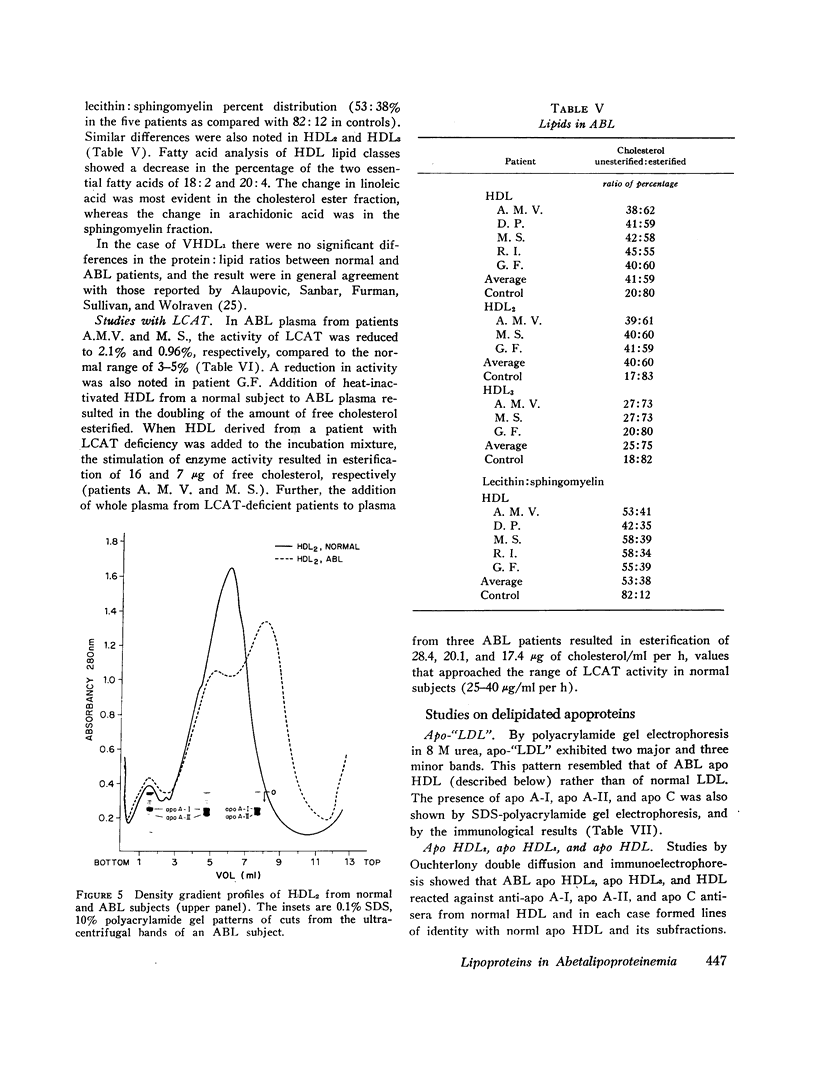
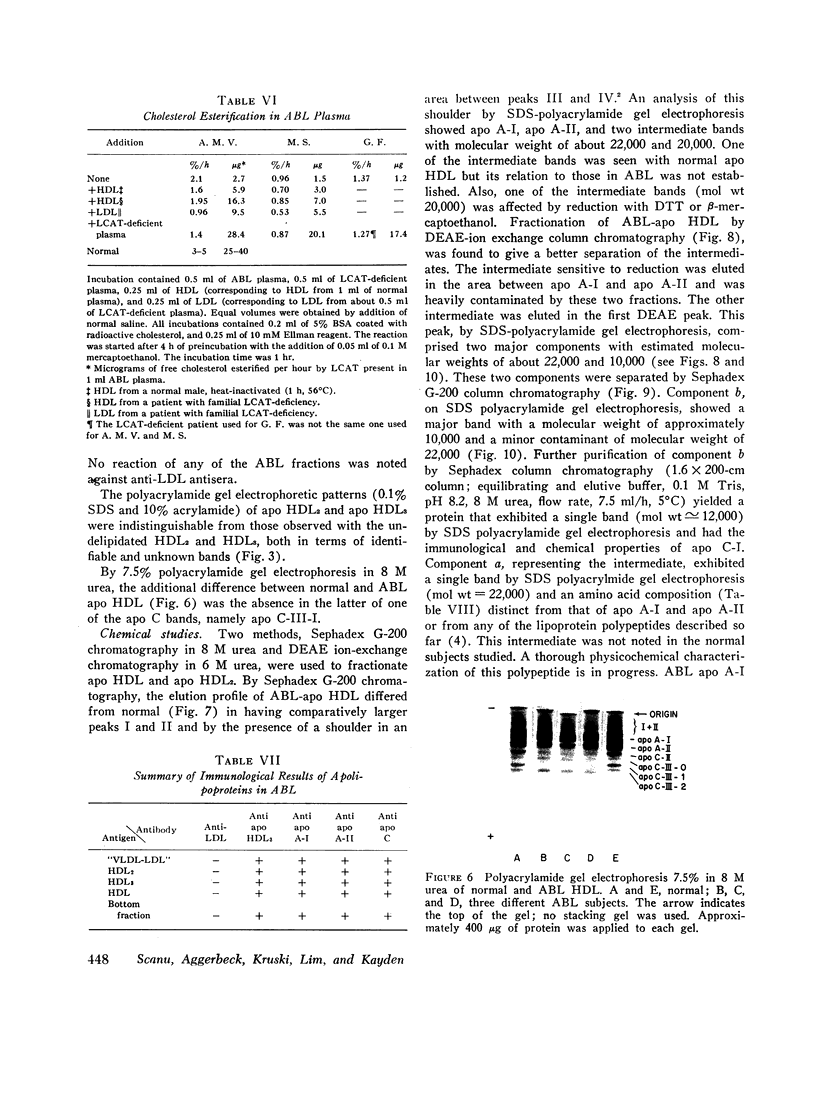
The serum lipoproteins of five patients with abetalipoproteinemia (ABL) were separated by ultracentrifugation and then analyzed either intact or after delipidation. In accord with previous findings, all of the patients lacked serum particles with the characteristics of normal low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and of the LDL apoprotein as assessed by immunochemical methods. Each patient exhibited on every examination an abnormal particle, "LDL", which had the flotational properties of LDL, the polypeptide makeup of high-density lipoproteins HDL, the spectral and morphological characteristics of neither LDL nor HDL, and a relatively low content of cholesteryl esters. The HDL were abnormal in having a marked decrease in their total plasma content, an altered proportion of the subclasses HDL2 and HDL3, and a peculiar polypeptide distribution, comprising both normal and additional components, usually not seen in normal controls. The patients also exhibited a decrease of plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT) activity which probably accounted for the low content of cholesteryl esters in both "LDL" and HDL, and in turn for the unusual appearance of "LDL" on electron microscopy. It is concluded that ABL is a disorder affecting all serum lipoprotein classes. Whether the abetalipoproteinemia previously described and noted in the current studies is related to or independent of the abnormalities observed in the other lipoproteins was not established. How the deficiency of LCAT activity, observed in all patients studied, contributed to some of the observed structural lipoprotein abnormalities also remained undetermined.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Scanu A. M. Isoelectric fractionation and characterization of polypeptides from human serum very low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach C., Polonovski J., Polonovski C., Leluc R., Jolly G., Moszer M. L'absence congénitale de beta-lipoprotéines. Une nouvelle observation. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1967 Dec;24(10):1093–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Gulbrandsen C. L. The relationship between serum lipoproteins and red cell membranes in abetalipoproteinemia: deficiency of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):323–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Nichols A. V. Application of electron microscopy to the study of plasma lipoprotein structure. Adv Lipid Res. 1972;10:1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: structure of low and high density lipoproteins as revealed by elctron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI106586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franey R. J., Amador E. Serum cholesterol measurement based on ethanol extraction and ferric chloride-sulfuric acid. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Levy R. I., John K., Fredrickson D. S. On the protein defect in abetalipoproteinemia. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):813–818. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. W., Ways P. Abnormalities of high density lipoproteins in abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1151–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI105608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A., WHYTE M., GOODMAN D. S. FATTY ACID ESTERIFICATION AND CHYLOMICRON FORMATION DURING FAT ABSORPTION. 1. TRIGLYCERIDES AND CHOLESTEROL ESTERS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jul;4:312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayden H. J. Abetalipoproteinemia. Annu Rev Med. 1972;23:285–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMY M., FREZAL J., POLONOVSKI J., DRUEZ G., REY J. Congenital absence of beta-lipoproteins. Pediatrics. 1963 Feb;31:277–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees R. S. Immunological evidence for the presence of B protein (apoprotein of beta-lipoprotein) in normal and abetalipoproteinemic plasma. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):396–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S., Laster L. The lipoproteins and lipid transport in abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):531–541. doi: 10.1172/JCI105367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., Scanu A. M., Taylor E. W. On the geometrical arrangement of the protein subunits of human serum low-density lipoprotein: evidence for a dodecahedral model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):304–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Edelstein C. Solubility in aqueous solutions of ethanol of the small molecular weight peptides of the serum very low density and high density lipoproteins: relevance to the recovery problem during delipidation of serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):576–588. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Lim C. T., Edelstein C. On the subunit structure of the protein of human serum high density lipoprotein. II. A study of Sephadex fraction IV. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5850–5855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Toth J., Edelstein C., Koga S., Stiller E. Fractionation of human serum high density lipoprotein in urea solutions. Evidence for polypeptide heterogeneity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3309–3316. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel D., Agostini B., Müller P. Sturucture of an abnormal plasma lipoprotein (LP-X) characterizing obstructive jaundice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 27;260(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Micromethod for the direct determination of serum triglycerides. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAYS P., REED C. F., HANAHAN D. J. RED-CELL AND PLASMA LIPIDS IN ACANTHOCYTOSIS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1248–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI104810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]