Abstract
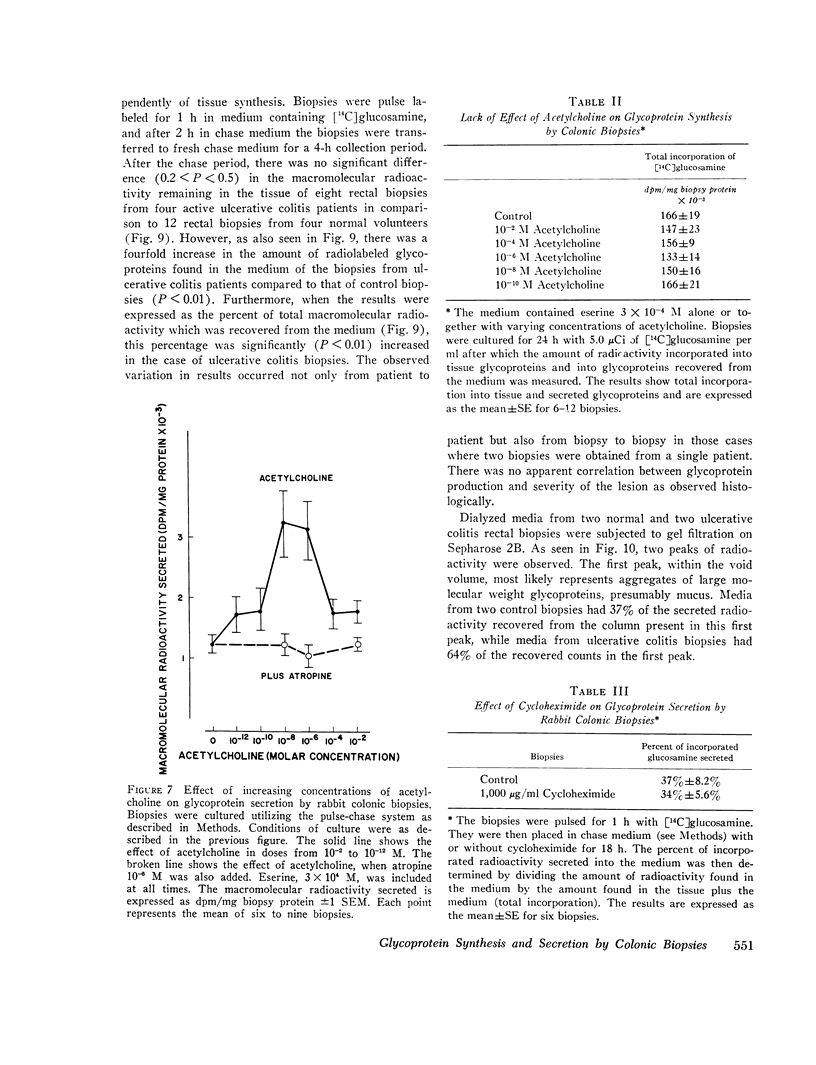
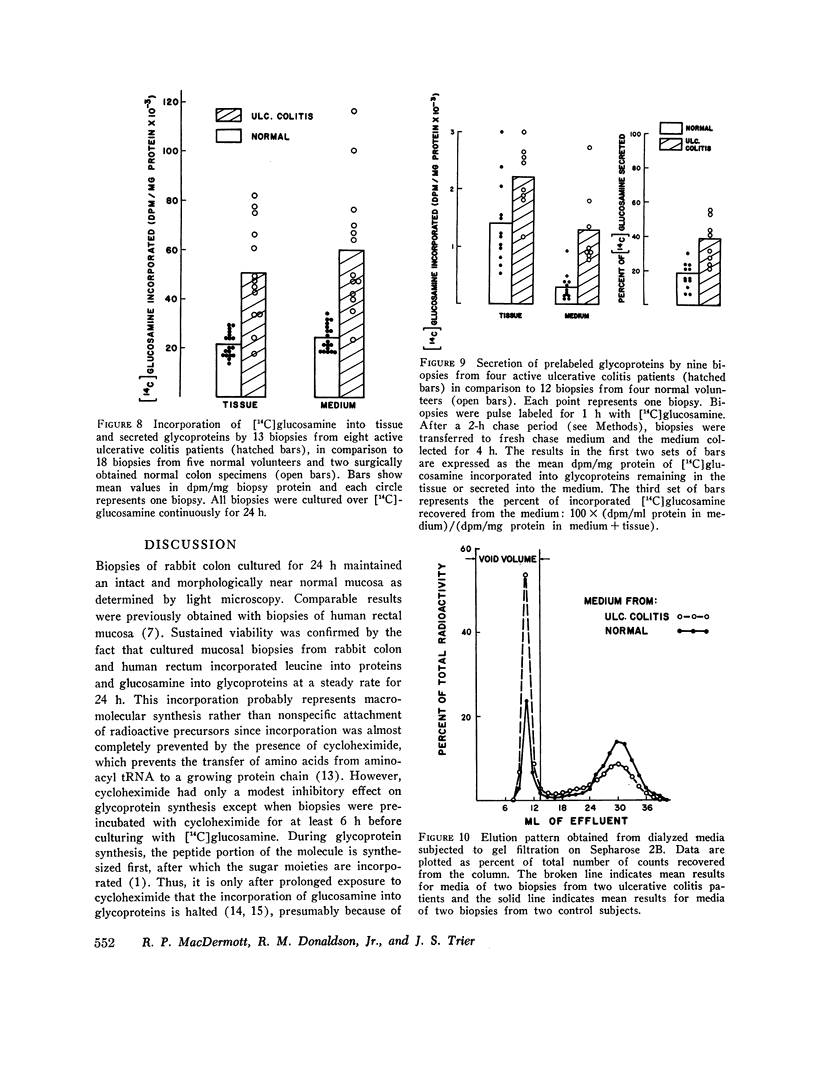
Elucidation of mechanisms involved in the control of colonic production of mucus requires direct examination of glycoprotein synthesis and secretion by colonic mucosa. In the past, the limited viability of intestinal mucosa in vitro has hampered such investigations. When maintained in an organ culture system, mucosal biopsies of rabbit colon and human rectum remained viable for 24 h as documented by morphologic appearance and a steady rate of protein synthesis and secretion. These biopsies also incorporated 14C-labeled glucosamine into tissue glycoproteins and secreted labeled glycoproteins at a steady rate for 24 h. Glucosamine was predominantly incorporated into macromolecules that were ultimately secreted, in contrast to leucine, which was predominantly incorporated into tissue macromolecules. When studied by autoradiography, cultured rabbit colonic biopsies synthesized and secreted glycoproteins in vitro at cellular sites and over a time-course similar to those previously described for the intestine of intact animals. Acetylcholine consistently stimulated secretion of labeled glycoproteins but did not alter glycoprotein synthesis. In contrast, cycloheximide inhibited glycoprotein synthesis but had no effect on the secretion of newly synthesized glycoproteins. Rectal biopsies from patients with active ulcerative colitis incorporated increased amounts of [14C]glucosamine into glycoproteins during organ culture and secreted labeled glycoproteins more rapidly into the incubation medium when compared to biopsies obtained from healthy volunteers These findings indicate that organ culture provides a useful means of directly examining the synthesis and secretion of glycoproteins by healthy and diseased colonic mucosa.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANDBORG L. L., RUBIN G. E., QUINTON W. E. A multipurpose instrument for suction biopsy of the esophagus, stomach, small bowel, and colon. Gastroenterology. 1959 Jul;37(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning T. H., Trier J. S. Organ culture of mucosal biopsies of human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1423–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI106108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P., Kent P. W. Biosynthesis of intestinal mucins. 4. Utilization of [1-C]glucose by sheep colonic mucosa in vitro. Biochem J. 1963 Feb;86(2):248–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0860248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood G. L., Trier J. S. Epithelial cell renewal in cultured rectal biopsies in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1973 Mar;64(3):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood G. L., Trier J. S. Organ culture of human rectal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1973 Mar;64(3):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. (1-14C)glucosamine incorporation by subcellular fractions of small intestinal mucosa. Identification by precursor labeling of three functionally distinct glycoprotein classes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3584–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H. Mode of action of antibiotics. II. Drugs affecting nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Am J Med. 1965 Nov;39(5):722–752. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara Y., Molnar J., Chao H. Inhibition of glycoprotein synthesis by cycloheximide in liver and Ehrlich tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;247(3):486–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Donaldson R. M., Jr, Trier J. S. Organ culture of rabbit small intestine: prolonged in vitro steady state protein synthesis and secretion and secretory IgA secretion. Gastroenterology. 1972 Oct;63(4):541–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Perdomo J., Nordberg J. Glycoprortein biosynthesis in small intestinal mucosa. I. A study of glycosyltransferases in microsomal subfractions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5466–5476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neutra M., Leblond C. P. Synthesis of the carbohydrate of mucus in the golgi complex as shown by electron microscope radioautography of goblet cells from rats injected with glucose-H3. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):119–136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID P., SCHMID C., BRODIE D. C. The determination of the total deoxyribose of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:1068–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOERGEL K. H., INGELFINGER F. J. COMPOSITION OF RECTAL MUCUS IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH ULCERATIVE COLITIS. Gastroenterology. 1964 Dec;47:610–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Spiro M. J. Glycoprotein biosynthesis: studies on thyroglobulin. Characterization of a particulate precursor and radioisotope incorporation by thyroid slices and particle systems. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1271–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]