Abstract
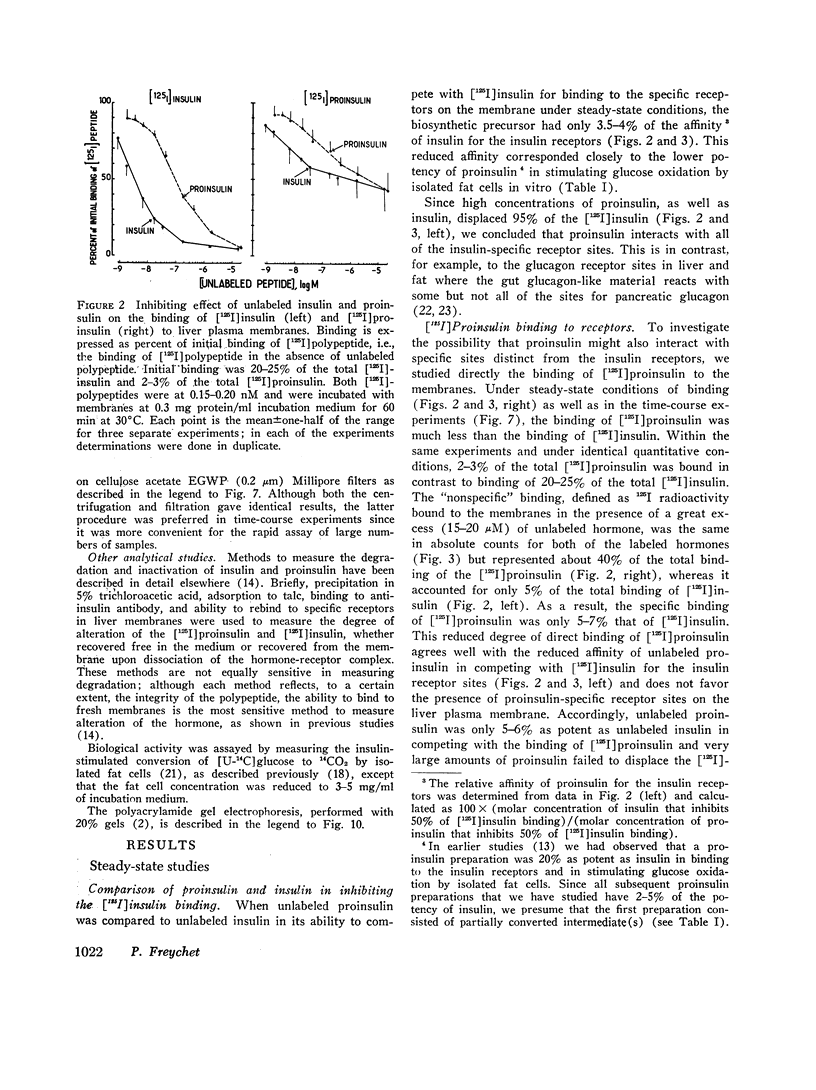
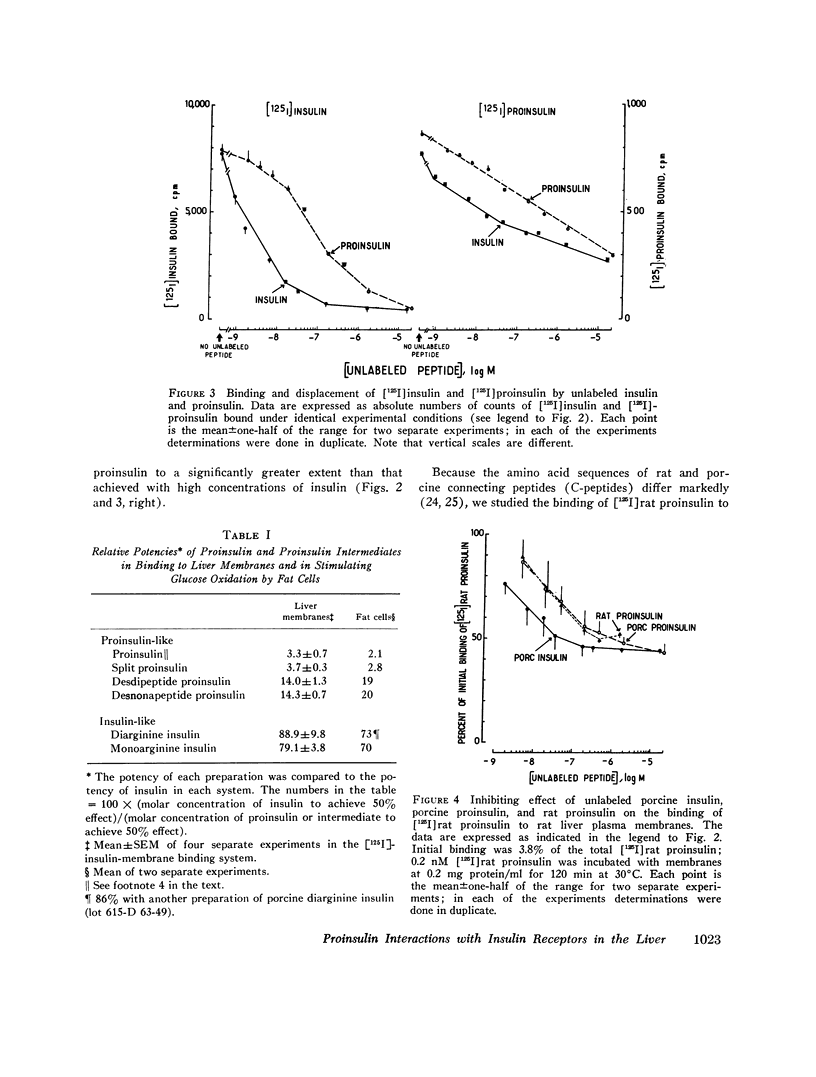
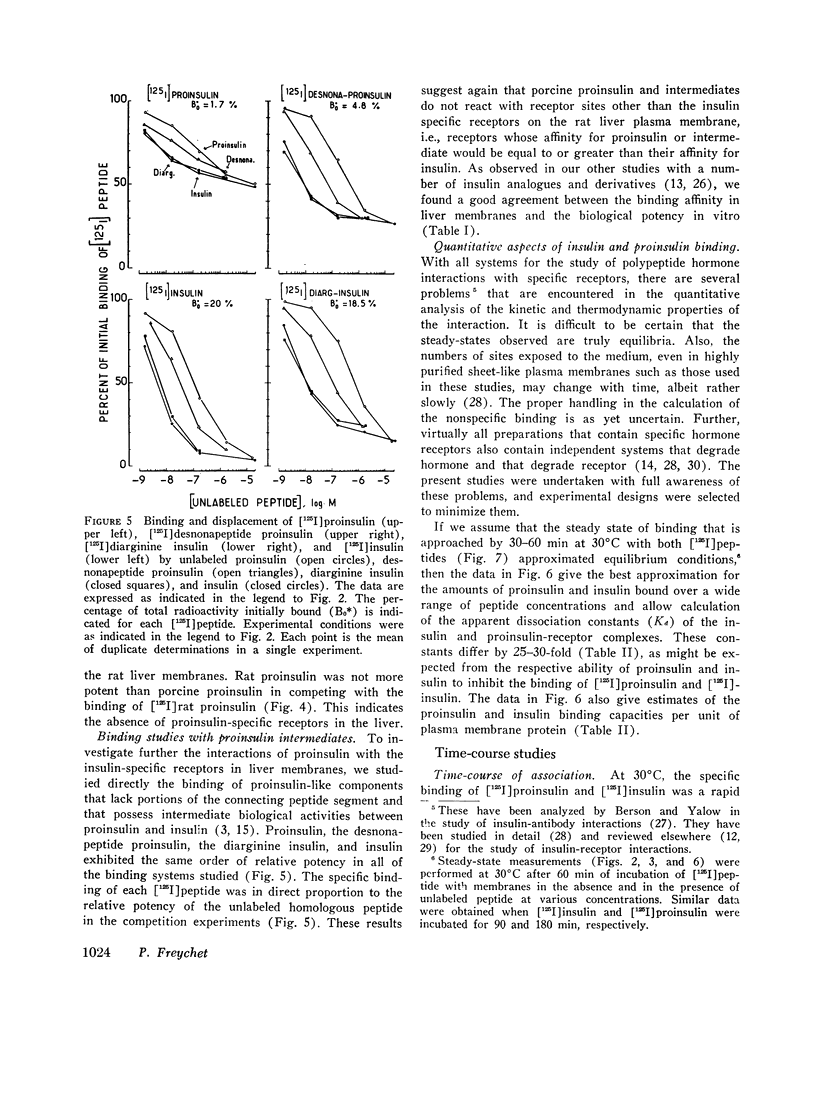
The interactions of proinsulin with the insulin-specific receptors were investigated in purified rat liver plasma membranes. These studies were designed to characterize the binding of proinsulin to the insulin receptors, to search for proinsulin-specific receptor sites, and to examine the possibility of proinsulin conversion at the insulin receptor site. Proinsulin was only 3-5% as potent as insulin in binding to insulin receptors. Proinsulin reacted with all of the insulin-specific receptors, and direct binding studies of [125I]porcine proinsulin and [125I]rat proinsulin did not reveal proinsulin-specific receptor sites other than the insulin receptors in rat liver membranes.
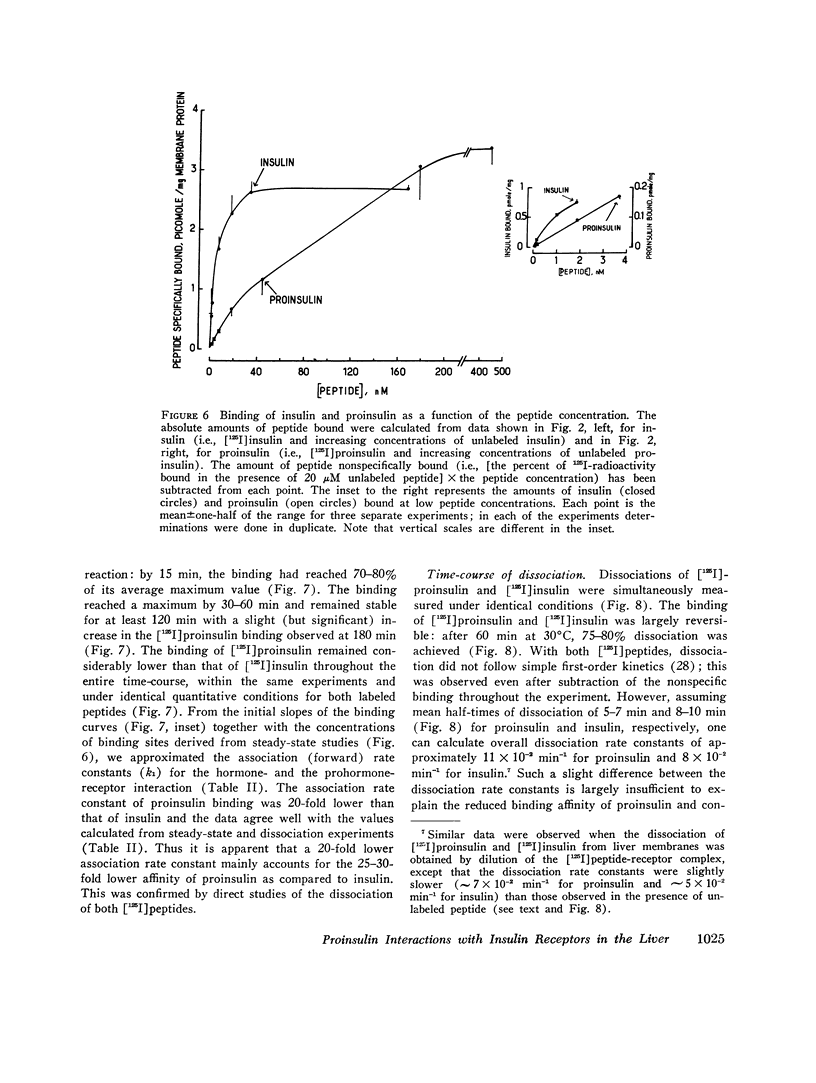
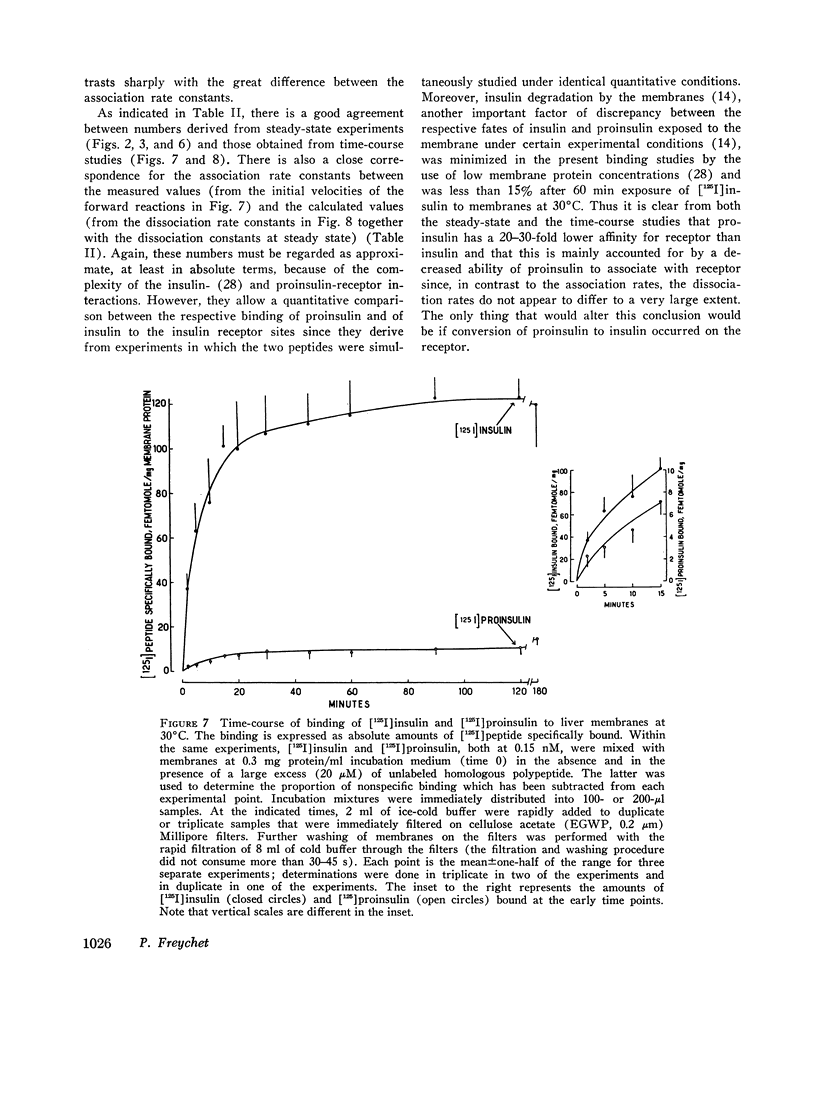
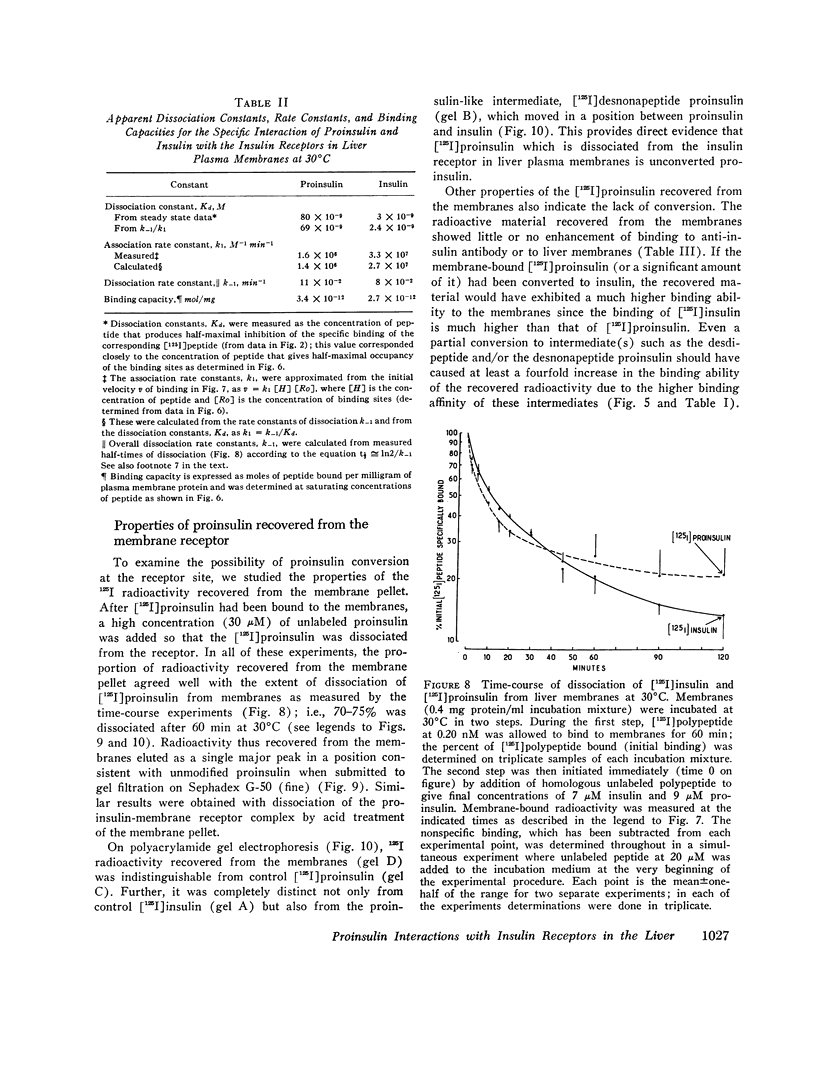
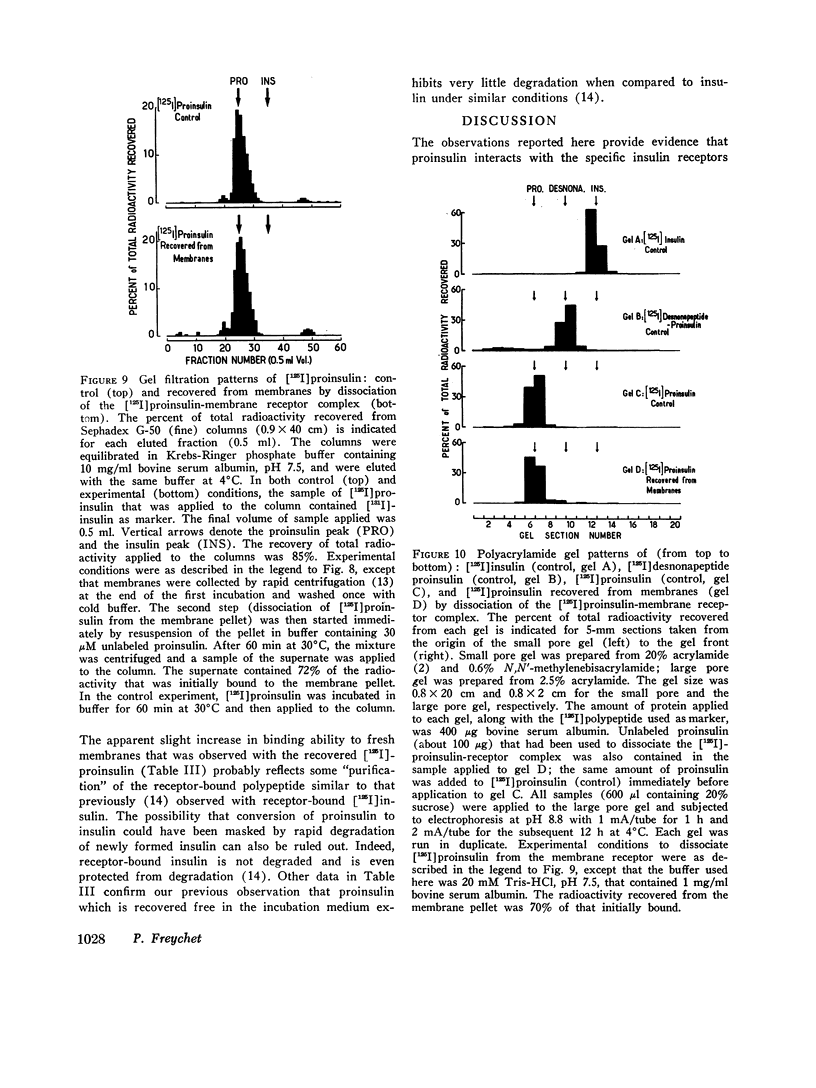
Quantitative data derived from steady-state and transient-state comparative binding studies of both [125I]proinsulin and [125I]insulin indicated that a 20-fold lower association rate constant essentially accounts for the reduced affinity of proinsulin for the insulin receptors. The possibility of proinsulin conversion at the insulin receptor sites was investigated. Material recovered from the membranes upon dissociation of the proinsulin-receptor complex was intact proinsulin and did not exhibit any conversion by a variety of analytical methods.
These results indicate that the lower affinity of proinsulin for the insulin receptor in the liver is an intrinsic property of the proinsulin molecule. The lower uptake of proinsulin by the insulin receptor represents, in addition to a slower degradation of the prohormone, a further mechanism by which proinsulin exerts prolonged, albeit reduced, action in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Quantitative aspects of the reaction between insulin and insulin-binding antibody. J Clin Invest. 1959 Nov;38:1996–2016. doi: 10.1172/JCI103979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bataille D. P., Freychet P., Kitabgi P. E., Rosselin G. E. Gut glucagon: A common receptor site with pancreatic glucagon in liver cell plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 1;30(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80654-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandenburg D., Wollmer A. The effect of a non-peptide interchain crosslink on the reoxidation of reduced insulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Jun;354(6):613–627. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance R. E. Amino acid sequences of proinsulins and intermediates. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):461–467. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance R. E., Ellis R. M., Bromer W. W. Porcine proinsulin: characterization and amino acid sequence. Science. 1968 Jul 12;161(3837):165–167. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank B. H., Veros A. J. Interaction of zinc with proinsulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 23;38(2):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90710-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank B. H., Veros A. J. Physical studies on proinsulin-association behavior and conformation in solution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90362-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Brandenburg D., Wollmer A. Receptor-binding assay of chemically modified insulins. Comparison with in vitro and in vivo bioassays. Diabetologia. 1974 Feb;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00421406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
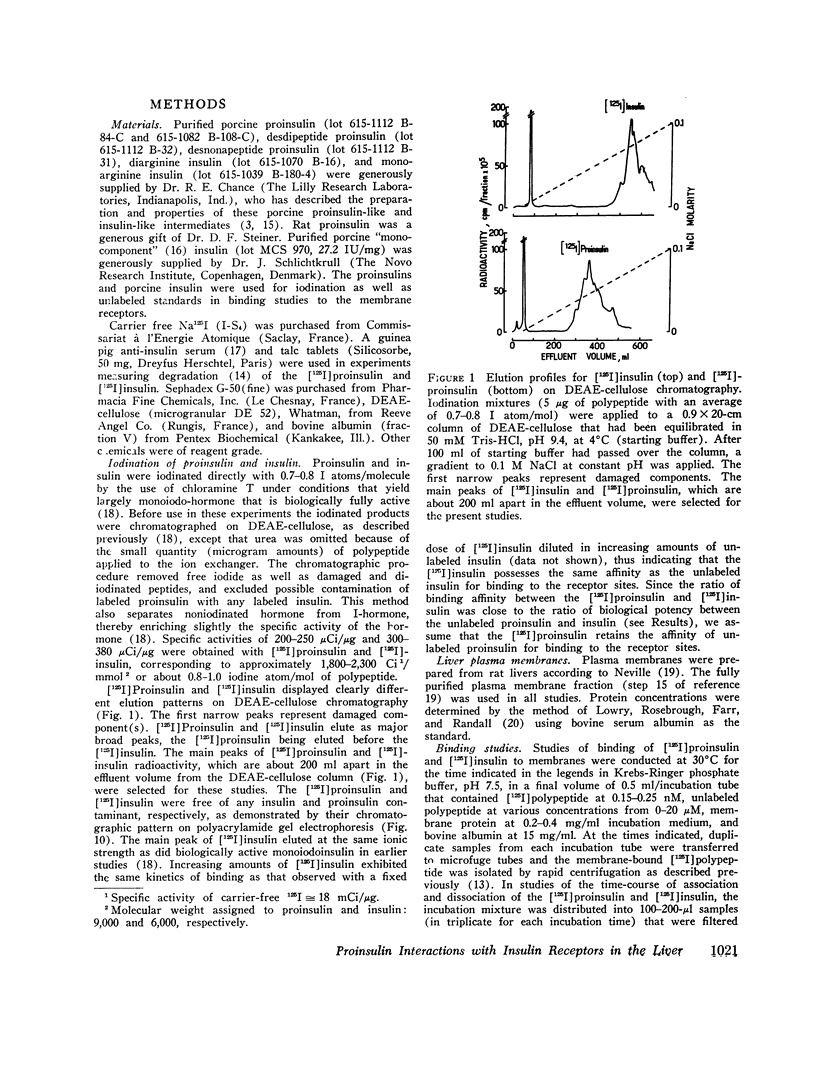
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Roth J., Freychet P., Kahn R. The circulating proinsulin-like components. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):673–677. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman R. A., Lazarus N. R., Recant L. Electrophoretic characterization of circulating human proinsulin and insulin. Diabetologia. 1972 Apr;8(2):136–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01235639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus N. R., Penhos J. C., Tanese T., Michaels L., Gutman R., Recant L. Studies on the biological activity of porcine proinsulin. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):487–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI106258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markussen J., Sundby F. Rat-proinsulin C-peptides. Amino-acid sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):153–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselin G., Dolais J. Application de la méthode radio-immunologique au dosage de l'insuline humaine et au dosage de l'hormone folliculo-stimulante humaine (H. F.S.H.) Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1968 Jul-Sep;26(7):763–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Cho S., Steiner D. F. Evidence for proinsulin in human urine and serum. Lancet. 1968 Jun 22;1(7556):1353–1355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Melani F., Pilkis S., Steiner D. F. Proinsulin. Secretion, metabolism, immunological and biological properties. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Jul;45(Suppl):476–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Pottenger L. A., Mako M., Getz G. S., Steiner D. F. The metabolism of proinsulin and insulin by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):912–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI106886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichtkrull J., Brange J., Christiansen A. H., Hallund O., Heding L. G., Jorgensen K. H. Clinical aspects of insulin--antigenicity. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):649–656. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Cunningham D., Spigelman L., Aten B. Insulin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):697–700. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Hallund O., Rubenstein A., Cho S., Bayliss C. Isolation and properties of proinsulin, intermediate forms, and other minor components from crystalline bovine insulin. Diabetes. 1968 Dec;17(12):725–736. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.12.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F. Proinsulin and the biosynthesis of insulin. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 15;280(20):1106–1113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905152802008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Menahan L. A., Williams R. H. Clearance of porcine insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptide by the isolated rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):894–896. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Winterscheid L. C., Ensinck J. W., Williams R. H. Hypoglycemic activity and immunological half-life of porcine insulin and proinsulin in baboons and swine. Endocrinology. 1971 Mar;88(3):714–717. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-3-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Steiner D. F. Primary structures of the proinsulin connecting peptides of the rat and the horse. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7936–7940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. S., Kitbachi A. E. Biological activity of proinsulin and related polypeptides in the fat tissue. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3753–3761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


