Abstract
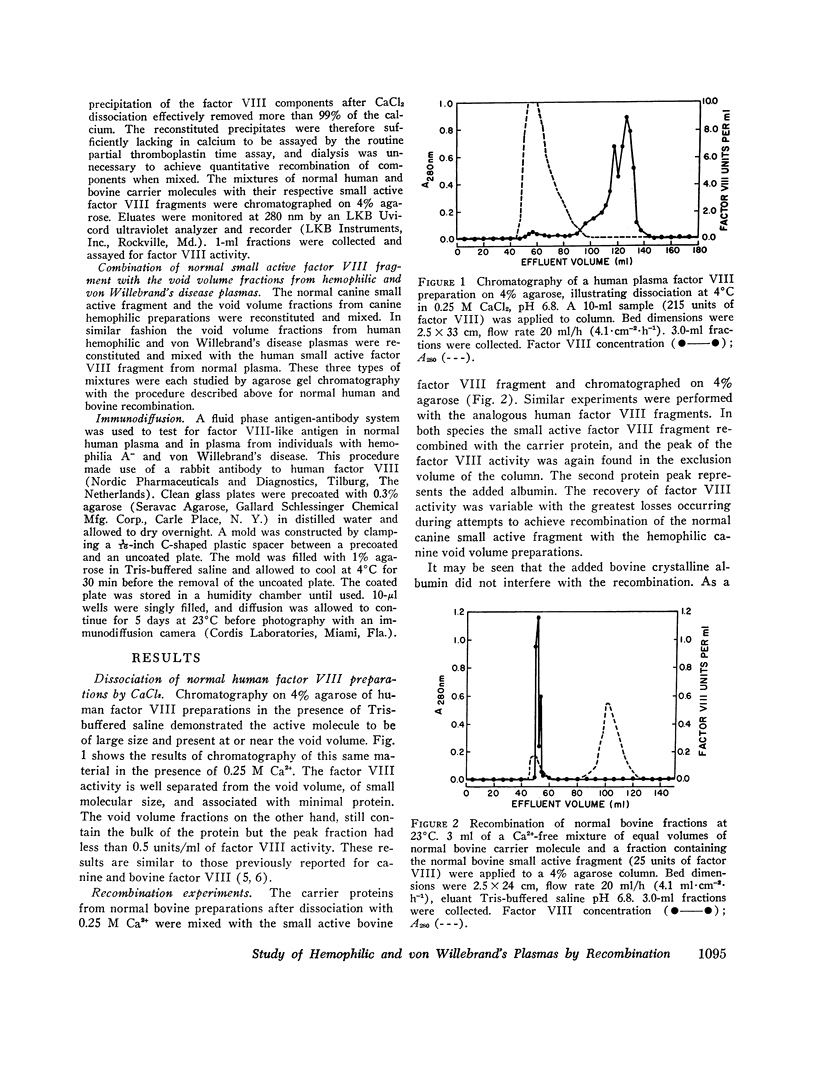
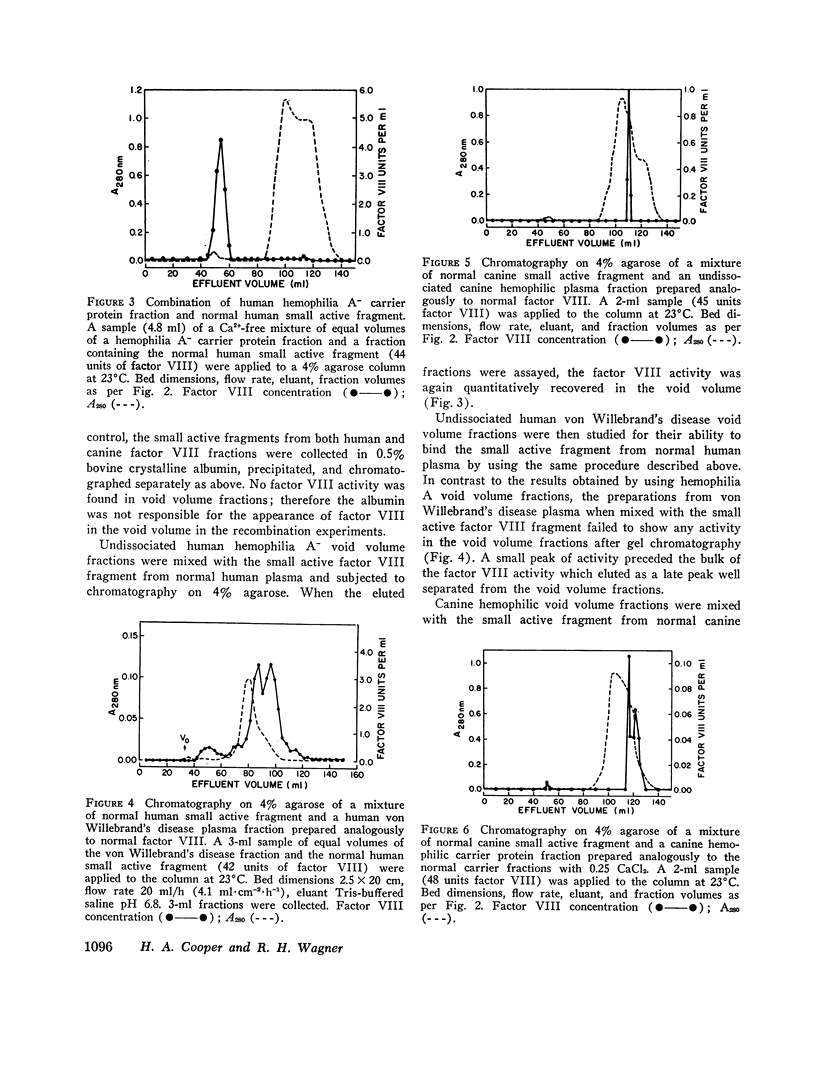
Factor VIII in preparations from normal plasma is a large glycoprotein of greater than 2 million molecular weight which elutes in the exclusion volume of 4% agarose gels at an ionic strength of 0.15. Recent studies have demonstrated that the factor VIII in canine and bovine plasma is a macromolecular complex composed of a large inert carrier protein and a noncovalently bound small fragment which contains the procoagulant active site. This complex is dissociable in 0.25 M CaCl2, and conditions for its recombination have been reported. The present study reports the dissociation characteristics of normal human factor VIII preparations in 0.25 M CaCl2 and the ability to achieve quantitative recombination of the dissociated fragments of normal human and bovine factor VIII after the removal of Ca2+. The recombination technique was used to characterize further the defect in hemophilia and von Willebrand's disease. Void volume preparations from human hemophilia A-, canine hemophilia A, and human von Willebrand's plasma, with no factor VIII procoagulant activity, were mixed with the small active fragment prepared from the normal plasma of their respective species. Chromatography of the three mixtures in agarose gel showed that the fractions from the human hemophilic plasmas contained a molecule that bound the small active normal fragment, but neither the fractions from canine hemophilia A plasmas nor the fractions from the human von Willebrand's plasmas demonstrated evidence of such material. These data suggest that there is present in human hemophilia A plasma a normal functional carrier molecule which is absent or nonfunctional in the plasma of hemophilic dogs and humans with von Willebrand's disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINKHOUS K. M. Plasma antihemophilic factor biological and clinical aspects. Sang. 1954;25(7):738–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow E. M., Graham J. B. Blood coagulation factor VIII (antihemophilic factor): with comments on von Willebrand's disease and Christmas disease. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jan;54(1):23–74. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B., Forman W. B., Ratnoff O. D. Studies on the nature of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). Further evidence relating the AHF-like antigens in normal and hemophilic plasmas. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2191–2197. doi: 10.1172/JCI107404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett E. Abnormality of separate subunits of factor VIII? Lancet. 1973 Apr 21;1(7808):885–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91455-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Griggs T. R., Wagner R. H. Factor VIII recombination after dissociation by CaCl12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2326–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denson K. W., Biggs R., Haddon M. E., Borrett R., Cobb K. Two types of haemophilia (A+ and A-): a study of 48 cases. Br J Haematol. 1969 Aug;17(2):163–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM J. B., BARROW E. M. The pathogenesis of hemophilia; an experimental analysis of the anticephalin hypothesis in hemophilic dogs. J Exp Med. 1957 Aug 1;106(2):273–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Coller B. S., Marchesi S. L. Immunological studies of factor VIII in haemophilia and von Willebrand's disease. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 29;244(139):281–282. doi: 10.1038/newbio244281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Cooper H. A., Webster W. P., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Plasma aggregating factor (bovine) for human platelets: a marker for study of antihemophilic and von Willebrand Factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M. Genetic variants of von Willebrand's disease. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 5;3(5822):317–320. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5822.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M. Two genetic variants of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 22;288(12):595–598. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303222881202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Breckenridge R. T. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII): cross-reacting material in a genetic variant of hemophilia A. Blood. 1968 Dec;32(6):962–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). 3. Comparative binding properties of human and rabbit anti-AHF. Blood. 1972 Apr;39(4):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Specificity of precipitating antibodies in immunological identification of antihaemophilic factor. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):49–51. doi: 10.1038/newbio245049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass L., Ratnoff O. D., Leon M. A. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor 8. I. Precipitation of antihemophilic factor by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI105991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernoff P. B., Rizza C. R. The specificity of antibodies to factor VIII produced in the rabbit after immunization with human cryoprecipitate. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Jun 28;29(3):652–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner K. Inactive factor VIII in hemophilia A and Willebrand's disease. A study of 117 cases. Acta Haematol. 1972;48(5):257–268. doi: 10.1159/000208468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaz M. E., Schmer G., Counts R. B., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of human Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3946–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. The kaolin clotting time; a rapid one-stage method for diagnosis of coagulation defects. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;11(5):406–409. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.5.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLESTER W. D., WAGNER R. H. ANTIBODY TO ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR AND ITS LACK OF REACTION WITH HEMOPHILIC PLASMA. Am J Physiol. 1965 Mar;208:499–507. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Shulman N. R., Gralnick H. R. Studies on the purification and characterization of human factor 8. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2151–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI107022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Kass L., Lang P. D. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). II. Separation of partially purified antihemophilic factor by gel filtration of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):957–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI106055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). V. Immunologic properties of AHF subunits produced by salt dissociation. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):737–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmer G., Kirby E. P., Teller D. C., Davie E. W. The isolation nd characterization of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2512–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. A., Andersen J. C., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. The subunit structure of normal and hemophilic factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2198–2210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Phillips L. L., Rosner W. Separation of sub-units of antihemophilic factor (AHF) by agarose gel chromatography. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Edgington T. S. Factor VIII coagulant activity and factor VIII-like antigen: independent molecular entities. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1015–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


