Abstract
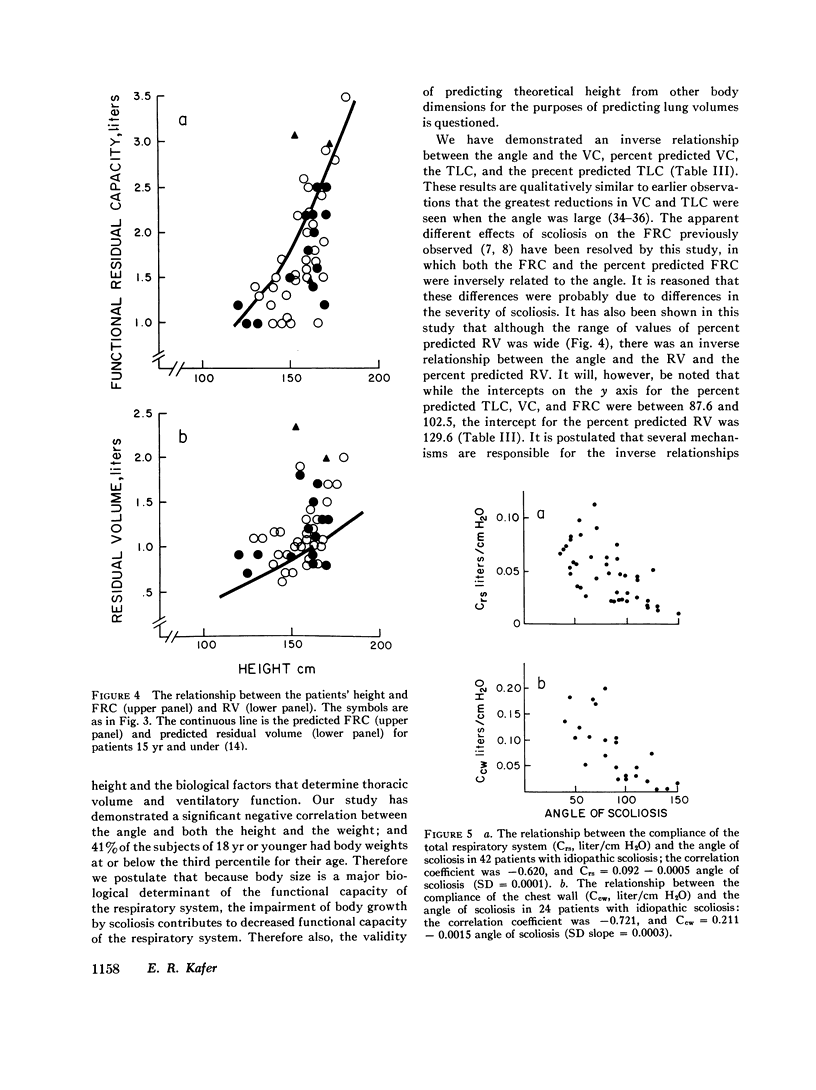
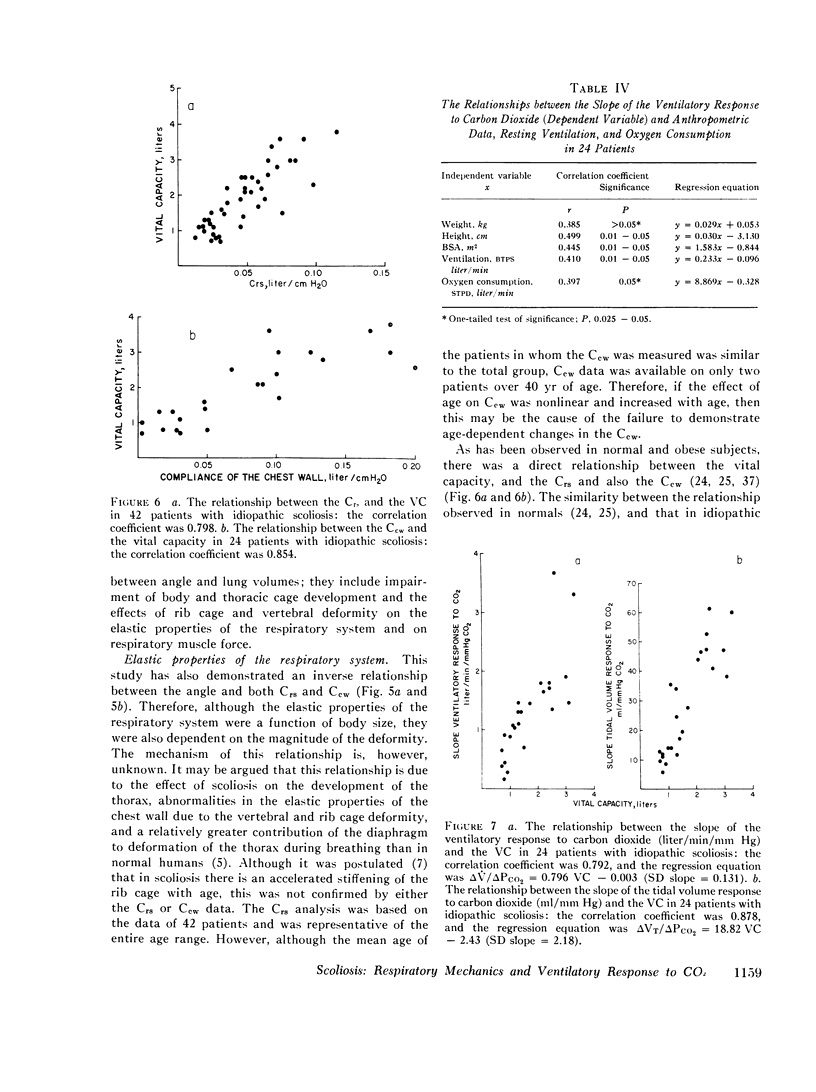
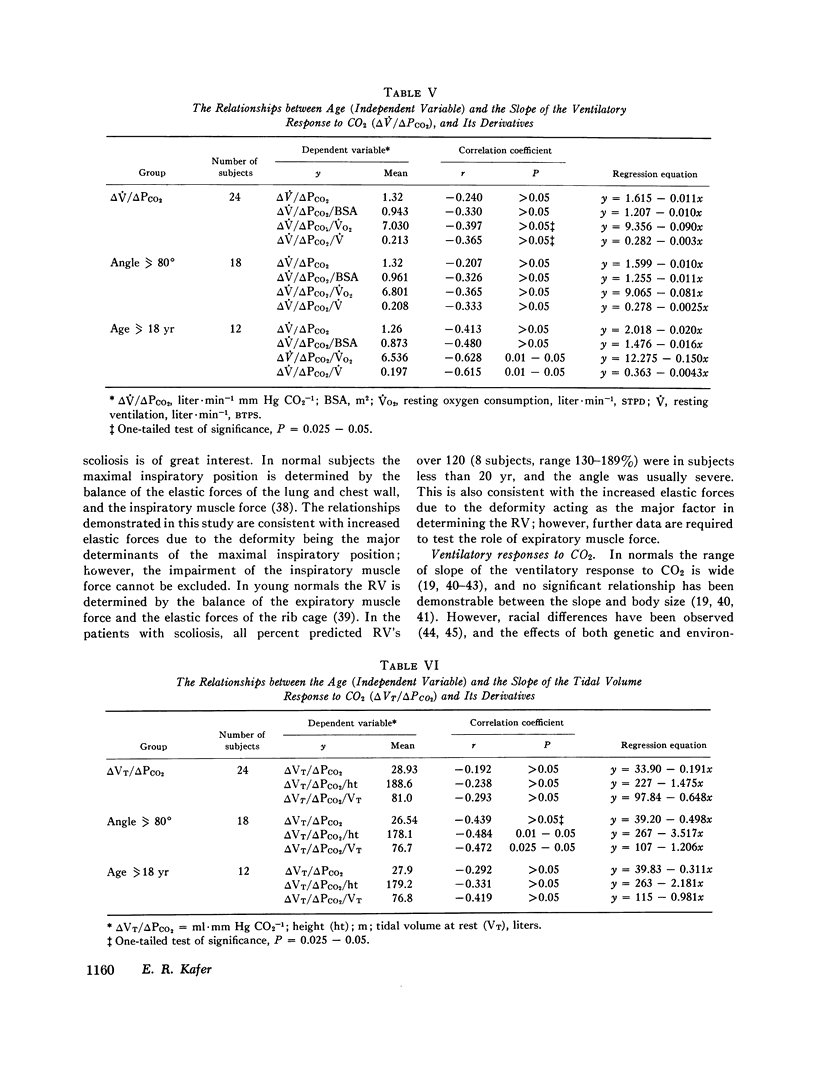
The aims were to examine the effects of scoliosis (angle), and age on lung volumes, elastic properties of the respiratory system, and the ventilatory response to CO2. The mean age of the 55 patients was 25.4 plus or minus SEM 2.5 yr, and the mean angle was 80 plus or minus SEM 4.2. The mean plus or minus SEM percent predicted lung volumes were vital capacity (VC), 60.5 plus or minus 2.7; total lung capacity (TLC), 70,2 plus or minus 2.6; functional residual capacity (frc), 79.3 plus or minus 3.2; and residual volume (RV), 99.7 plus or minus 5.2. The correlation coefficients between the angle of scoliosis and each of the following were significant: TLC (-0.548), percent predicted TLC (-0.547), VC (-0.485), percent predicted VC (-0.523), FRC (-0.533), percent predicted FRC (-0.338), RV (-0.438), and percent predicted RV (-0.318). The mean compliance of the total respiratory system (Crs) was 0.049 litter/cm H2O plus or minus SEM 0.004, and the mean compliance of the chest wall (Ccw) was 0.080 liter/cm H2O plus or minus SEM 0.012. The Crs and Ccw were inversely proportional to the angle (r-0.620 and -0.721) and directly proportional to the height and the weight. The mean deltaV/deltaPco2 was 1.32 liter/min per mm Hg (SEM 0.171), and the mean deltaVt/deltaPco2 was 28.9 ml/mm Hg (SEM 3.64). The correlation coefficients between deltaV/deltaPco2 and the following were height, 0.499; VC, 0.792; TLC, 0.632; AND Crs, 0.520; and between the deltaTt/deltaPco2 and the following were height, 0.500; VC, 0.878; TLC, 0.802; and Crs, 0.590. We conclude that body size and the deformity were the determinants of the lung volumes and the mechanical properties of the respiratory system, and that these variables were the major factors in both the magnitude and pattern of the ventilatory response to CO2. The correlations between age and the mechanical properties of the respiratory sytem, deltaV/deltaPco2, and deltaVt/deltaPco2, were not significant, but the correlation coefficients between age and several of the derivatives of deltaV/deltaPco2 and deltaVt/deltaPco2 were significant.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER J. K., SPALTER H. F., WEST J. R. Modification of the respiratory response to carbon dioxide by salicylate. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):533–537. doi: 10.1172/JCI103101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALEXANDER J. K., WEST J. R., WOOD J. A., RICHARDS D. W. Analysis of the respiratory response to carbon dioxide inhalation in varying clinical states of hypercapnia, anoxia, and acid-base derangement. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):511–532. doi: 10.1172/JCI103100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkinstall W. W., Nirmel K., Klissouras V., Milic-Emili J. Genetic differences in the ventilatory response to inhaled CO2. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jan;36(1):6–11. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGOFSKY E. H., TURINO G. M., FISHMAN A. P. Cardiorespiratory failure in kyphoscoliosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1959 Sep;38:263–317. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195909000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beral V., Read D. J. Insensitivity of respiratory centre to carbon dioxide in the Enga people of New Guinea. Lancet. 1971 Dec 11;2(7737):1290–1294. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90606-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjure J., Grimby G., Kasalický J., Lindh M., Nachemson A. Respiratory impairment and airway closure in patients with untreated idiopathic scoliosis. Thorax. 1970 Jul;25(4):451–456. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjure J., Grimby G., Nachemson A. Correction of body height in predicting spirometric values in scoliotic patients. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(2):191–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO C. G., DUBOIS A. B. Pulmonary function in kyphoscoliosis. Thorax. 1961 Sep;16:282–290. doi: 10.1136/thx.16.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNIACK R. M., BROWN E. A SIMPLE METHOD FOR MEASURING TOTAL RESPIRATORY COMPLIANCE: NORMAL VALUES FOR MALES. J Appl Physiol. 1965 Jan;20:87–91. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1965.20.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis D. K., Ponseti I. V. Long-term follow-up of patients with idiopathic scoliosis not treated surgically. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969 Apr;51(3):425–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRIDGE F., DAVIS J. M. Effect of mechanical factors on respiratory work and ventilatory responses to carbon dioxide. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Sep;14:721–726. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLENLEY D. C. THE CHANGES IN THE RATE OF HUMAN INSPIRATORY WORK PRODUCED BY ALTERATIONS IN THE ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS TENSIONS AND PH. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1964 Oct;49:466–484. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1964.sp001752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Turino G. M. General alveolar hypoventilation: a syndrome of respiratory and cardiac failure in patients with normal lungs. Q J Med. 1966 Apr;35(138):261–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S., Dalton K. J., Holland D., Patton J. M. The effects of added elastic loads on the respiratory response to CO 2 in man. Respir Physiol. 1972 Apr;14(3):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyschuss U., Nilsonne U., Lundgren K. D. Idiopathic scoliosis in old age. I. Respiratory function. Acta Med Scand. 1968 Nov;184(5):365–372. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb02472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLIESEN P. J., COOK C. D., FRIEDLANDER L., AGATHON S. Studies of respiratory physiology in children. I. Mechanics of respiration and lung volumes in 85 normal children 5 to 17 years of age. Pediatrics. 1958 Jul;22(1 Pt 1):80–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPER N. G., BLACK L. F., FOWLER W. S. RELATIONSHIPS OF LUNG VOLUME TO HEIGHT AND ARM SPAN IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH SPINAL DEFORMITY. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Mar;91:356–362. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordanoglou J. Rib movement in health, kyphoscoliosis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Thorax. 1969 Jul;24(4):407–414. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.4.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafer E. R. Respiratory function in paralytic scoliosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Oct;110(4):450–457. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.4.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg R. S., Drage C. W. Attenuation of the ventilatory and heart rate responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia with aging in normal men. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1812–1819. doi: 10.1172/JCI107363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERTSEN C. J. Carbon dioxide and respiration in acid-base homeostasis. Anesthesiology. 1960 Nov-Dec;21:642–651. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196011000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri S., Chaggopadhyay H. P., Sinha A., Karmakar P. C. Respiratory response to carbon dioxide in man. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):393–394. doi: 10.1038/213393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. E., Mead J. Mechanisms determining residual volume of the lungs in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Aug;23(2):221–227. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANKIN H. J., GRAHAM J. J., SCHACK J. CARDIOPULMONARY FUNCTION IN MILD AND MODERATE IDIOPATHIC SCOLIOSIS. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964 Jan;46:53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEAD J., MILIC-EMILI J., TURNER J. M. Factors limiting depth of a maximal inspiration in human subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Mar;18:295–296. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIMARK A., CHERNIACK R. M. Compliance of the respiratory system and its components in health and obesity. J Appl Physiol. 1960 May;15:377–382. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J. M., Howard A. The influence of age, sex, body size and lung size on the control and pattern of breathing during CO 2 inhalation in Caucasians. Respir Physiol. 1972 Dec;16(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROAF R. Rotation movements of the spine with special reference to scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1958 May;40-B(2):312–332. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.40B2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D. J. A clinical method for assessing the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide. Australas Ann Med. 1967 Feb;16(1):20–32. doi: 10.1111/imj.1967.16.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D. J., Leigh J. Blood-brain tissue Pco2 relationships and ventilation during rebreathing. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jul;23(1):53–70. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFER K. E. Respiratory pattern and respiratory response to CO2. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Jul;13(1):1–14. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEAD W. W., FRY D. L., EBERT R. V. The elastic properties of the lung in normal men and in patients with chronic pulmonary emphysema. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Nov;40(5):674–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TING E. Y., LYONS H. A. THE RELATION OF PRESSURE AND VOLUME OF THE TOTAL RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND ITS COMPONENTS IN KYPHOSCOLIOSIS. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Mar;89:379–386. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.89.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROTTER M., GLESER G. C. A re-evaluation of estimation of stature based on measurements of stature taken during life and of long bones after death. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1958 Mar;16(1):79–123. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330160106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROTTER M., GLESER G. C. Estimation of stature from long bones of American Whites and Negroes. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1952 Dec;10(4):463–514. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330100407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURINO G. M., GOLDRING R. M., FISHMAN A. P. COR PULMONALE IN MUSCULOSKELETAL ABNORMALITIES OF THE THORAX. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1965 Sep;41:959–980. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZORAB P. A., HARRISON A., HARRISON W. J. ESTIMATION OF HEIGHT FROM TIBIAL LENGTH. Lancet. 1964 Nov 14;2(7368):1063–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZORAB P. A., PRIME F. J., HARRISON A. Estimation of height from tibial length. Lancet. 1963 Jan 26;1(7274):195–196. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


