Abstract
High levels of a novel vitamin B12-binding protein (hepatoma B12 BP) have been observed recently in plasma obtained from three adolescent patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. This protein has now been isolated in homogeneous form from the plasma and pleural fluid of two of these patients by the use of affinity chromatography with vitamin B12-Sepharose. The hepatoma B12 BP belongs to the R-type group of B12-binding proteins and is essentially indistinguishable from the recently isolated human milk and saliva R-type proteins in terms of: (a) immunologic properties based on immunodiffusion and immunoprecipitation assays; (b) amino acid composition; (c) molecular weight based on amino acid and carbohydrate content; and (d) absorption spectra. Both hepatoma B12 BPs contain more sialic acid and less fucose than the milk and saliva B12 BPs. All four proteins contain similar amounts of galactose, mannose, galactosamine, and glucosamine. Differences in sialic acid content appear to account for the differences in electrophoretic mobility that were observed among the four proteins. Differences in total carbohydrate content appear to account for the differences in apparent molecular weight that were observed with both gel filtration and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Tumor tissue from one of the patients contained 10 times as much R-type protein as did normal liver tissue from the same patient. This suggests, although it does not prove, that synthesis by the tumor is the cause of the high levels of R-type protein found in the plasma of certain patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Plasma survival studies performed with rabbits indicate that the hepatoma B12 BP has a prolonged plasma survival and suggests that his parameter is also of importance.
Full text
PDF

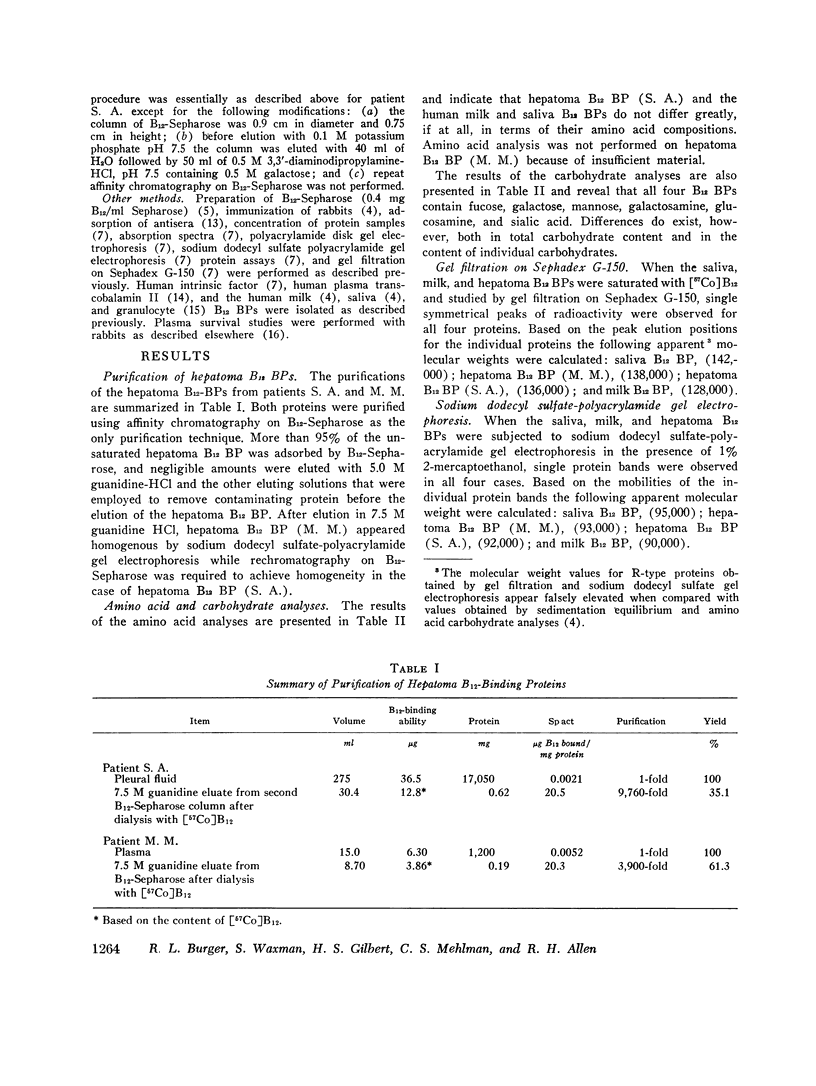



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. 3. Purification and properties of human plasma transcobalamin II. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7709–7717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Preparation and properties of vitamin B12-sepharose. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7695–7701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. II. Purification and properties of a human granulocyte vitamine B12-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7702–7708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Mehlman C. S. Isolation of gastric vitamin B 12 -binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Purification and properties of human intrinsic factor. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3660–3669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield F. J., Scott J. M. Identification of a new vitamin B 12 binder (transcobalamin 3) in normal human serum. Br J Haematol. 1972 Jan;22(1):33–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. L., Allen R. H. Characterization of vitamin B12-binding proteins isolated from human milk and saliva by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7220–7227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R., Herbert V. Deficiency of vitamin B12-binding alpha globulin in two brothers. Blood. 1969 Jan;33(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R. Vitamin B 12 -binding protein abnormality in subjects without myeloproliferative disease. II. The presence of a third vitamin B 12 -binding protein in serum. Br J Haematol. 1972 Jan;22(1):53–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTLIEBLAU K. S., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. RAPID CHARCOAL ASSAY FOR INTRINSIC FACTOR (IF), GASTRIC JUICE UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY, ANTIBODY TO IF, AND SERUM UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräsbeck R. Intrinsic factor and the other vitamin B12 transport proteins. Prog Hematol. 1969;6:233–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M., Mehlman C. S., Allen R. H. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal human intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1274–1283. doi: 10.1172/JCI107674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAU K. S., GOTTLIEB C., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. MEASUREMENT OF SERUM VITAMIN B12 LEVEL USING RADIOISOTOPE DILUTION AND COATED CHARCOAL. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:202–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. M., Bloomfield F. J., Stebbins R., Herbert V. Studies on derivation of transcobalamin 3 from granulocytes. Enhancement by lithium and elimination by fluoride of in vitro increments in vitamin B12-binding capacity. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):228–239. doi: 10.1172/JCI107543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasman S., Gilbert H. S. Characteristics of a novel serum vitamin-B12-binding protein associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Haematol. 1974 Jun;27(2):229–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S., Gilbert H. S. A tumor-related vitamin B12 binding protein in adolescent hepatoma. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 15;289(20):1053–1056. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311152892002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]